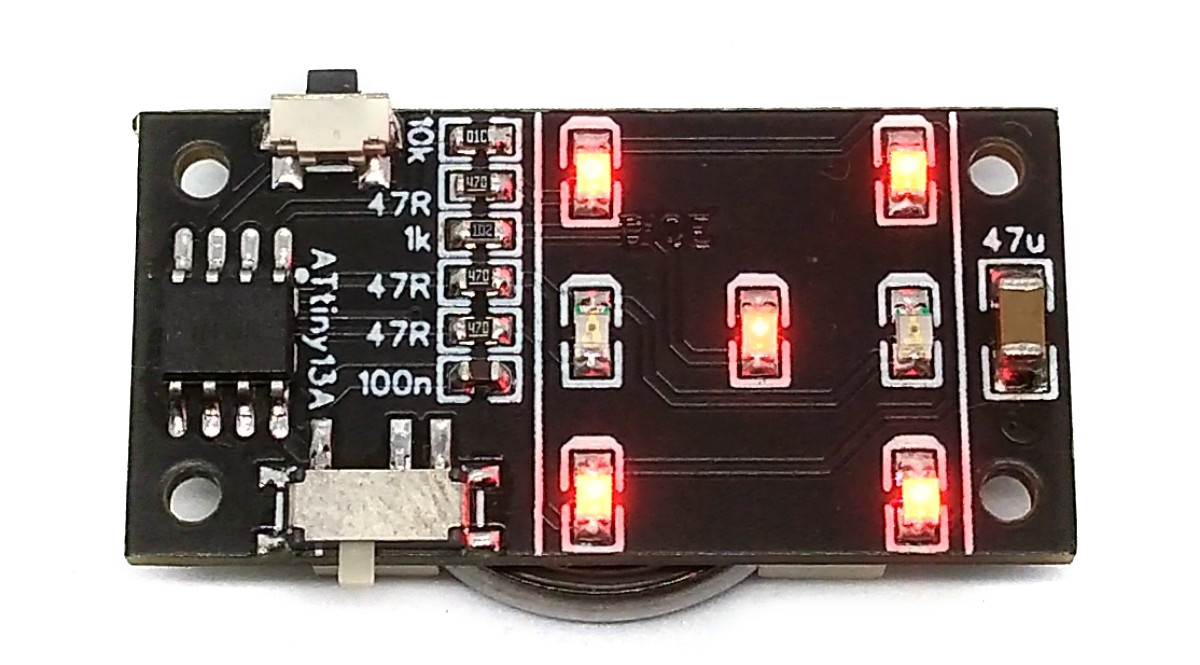
TinyDice is a tiny (35mm * 17mm) electronic dice powered by ATtiny13A.
- Project Video (YouTube): https://youtu.be/Zr3TuCeP4eM
- Design Files (EasyEDA): https://easyeda.com/wagiminator/attiny10-tinydice-smd
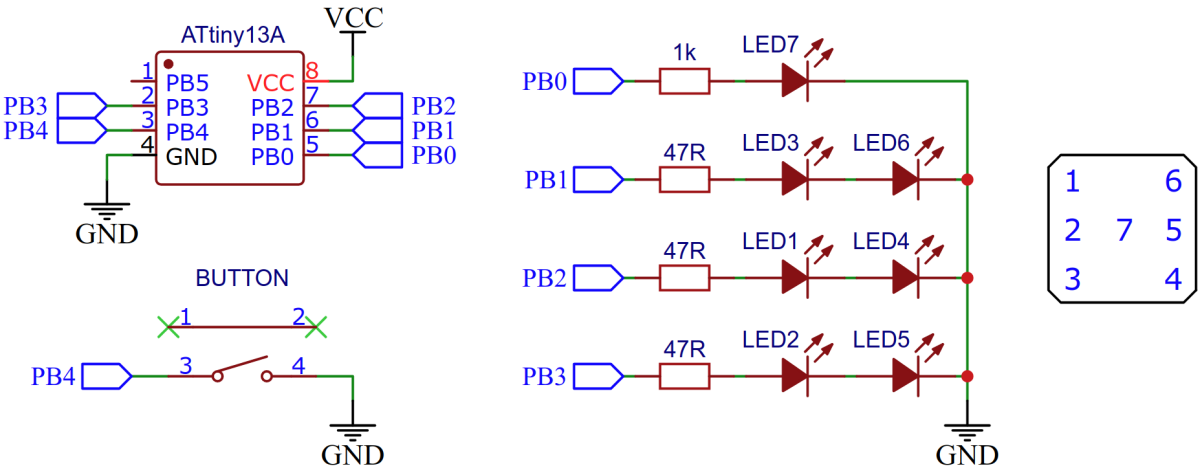
The wiring is pretty simple:
The fact that the opposite pairs of dots on a dice always appear together was used for the circuit diagram. This means that there is no need for Multi or Charlieplexing. However, the supply voltage must be at least twice as high as the forward voltage of the LEDs. Therefore only red LEDs and the rechargeable LIR2032 li-ion batteries should be used.
Timer0 is used to constantly change the number of pips in the background. Chance is created by the uncertainty of the moment the button is pressed by the user, which brings the current number of pips to display. As long as nothing else needs to be done, the ATtiny remains in IDLE and only wakes up when you press a button (pin change interrupt). Then it rolls the dice, in which a series of numbers are shown on the dice with increasing time interval. Finally, the last number shown remains and the ATtiny changes back to IDLE. The number of pips shown on the dice corresponds to the respective variable pips, which is constantly changed by the timer overflow interrupt. A simple matrix is used to control the LEDs, with which the respective number is converted into the values for the PORTB register.
// Libraries
#include <avr/io.h> // for GPIO
#include <avr/sleep.h> // for sleep mode
#include <avr/interrupt.h> // for interrupts
#include <util/delay.h> // for delays
// Global variables
volatile uint8_t pips = 0; // current number of pips
// Main function
int main(void) {
// Local variables
uint8_t matrix[] = {0b00110001, // 1
0b00110100, // 2
0b00110011, // 3
0b00110110, // 4
0b00110111, // 5
0b00111110};// 6 - for converting pips to pins
// Setup pins
DDRB = 0b00001111; // PB0 - PB3 as output, PB4 input
PORTB = 0b00110001; // pull-up for PB4/5; LED7 on
// Setup timer/counter
TCCR0A = 0b00000000; // no output
TCCR0B = 0b00000011; // set prescaler to 64
TIMSK0 = 0b00000010; // enable timer overflow interrupt
// Setup pin change interrupt
GIMSK = 0b00100000; // turn on pin change interrupts
PCMSK = 0b00010000; // pin change interrupt on button pin
SREG |= 0b10000000; // enable global interrupts
// Disable unused peripherals and set sleep mode to save power
ACSR = 0b10000000; // disable analog comperator
PRR = 0b00000001; // shut down ADC
set_sleep_mode(SLEEP_MODE_IDLE);// set sleep mode to IDLE
// Loop
while(1) {
sleep_mode(); // go to sleep
if(~PINB & 0b00010000) { // if button pressed:
for(uint8_t i = 0; i < 16; i++) { // roll the dice
uint8_t del = (i << 4); // increasing delay between pip-shows
while(del--) _delay_ms(1); // set the delay
PORTB = matrix[pips]; // show current number of pips
}
while(~PINB & 0b00010000); // wait for button released
_delay_ms(10); // debounce
}
}
}
// Timer0 overflow interrupt service routine
ISR(TIM0_OVF_vect) {
if(++pips > 5) pips = 0; // cycle number of pips on every timer overflow
}
// Pin change interrupt service routine
EMPTY_INTERRUPT(PCINT0_vect); // nothing to be done here, just wake up from sleepSince there is no ICSP header on the board, you have to program the ATtiny either before soldering using an SOP adapter, or after soldering using an EEPROM clip. The AVR Programmer Adapter can help with this.
- Make sure you have installed MicroCore.
- Go to Tools -> Board -> MicroCore and select ATtiny13.
- Go to Tools and choose the following board options:
- Clock: 1.2 MHz internal osc.
- BOD: BOD disabled
- Timing: Micros disabled
- Connect your programmer to your PC and to the ATtiny.
- Go to Tools -> Programmer and select your ISP programmer (e.g. USBasp).
- Go to Tools -> Burn Bootloader to burn the fuses.
- Open TinyDice.ino and click Upload.
- Make sure you have installed avrdude.
- Connect your programmer to your PC and to the ATtiny.
- Open a terminal.
- Navigate to the folder with the hex-file.
- Execute the following command (if necessary replace "usbasp" with the programmer you use):
avrdude -c usbasp -p t13 -U lfuse:w:0x2a:m -U hfuse:w:0xff:m -U flash:w:tinydice.hex
- Make sure you have installed avr-gcc toolchain and avrdude.
- Connect your programmer to your PC and to the ATtiny.
- Open a terminal.
- Navigate to the folder with the makefile and sketch.
- Run
PROGRMR=usbasp make installto compile, burn the fuses and upload the firmware (change PROGRMR accordingly).
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)