Customer adds products to the shopping cart in this sample application of the online store.
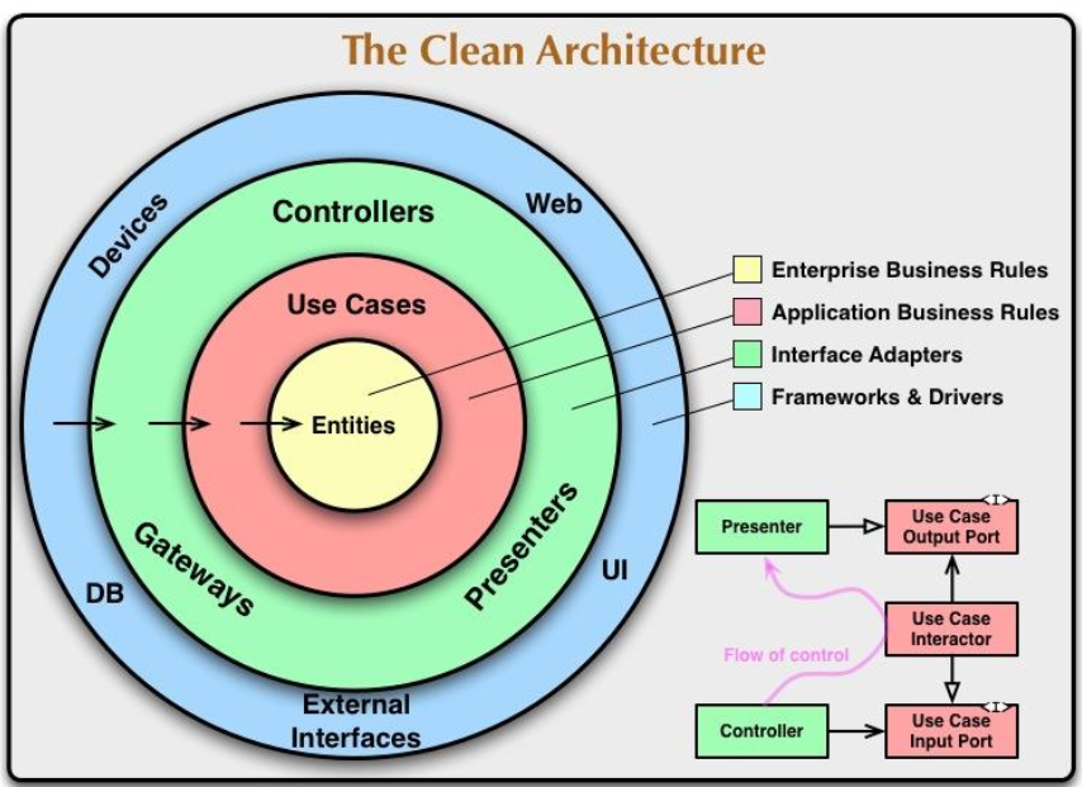
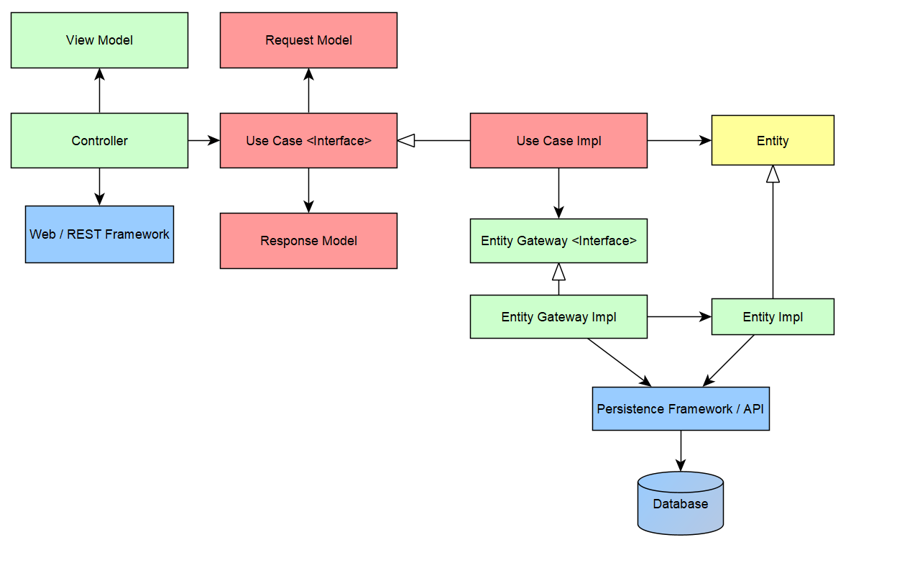
The architecture of the web service Java application follows a Clean Architecture. As such, the core of the application itself is devoid of any delivery framework mechanisms and technology specific details. I.e. Things like SQL and Spring MVC are kept outside of the boundary of the application. It is developed in a use case centric approach, JUnit ensure the behaviour works in class isolation.
- Independent of Frameworks. The architecture does not depend on the existence of some library of feature laden software. This allows you to use such frameworks as tools, rather than having to cram your system into their limited constraints.
- Testable. The business rules can be tested without the UI, Database, Web Server, or any other external element.
- Independent of UI. The UI can change easily, without changing the rest of the system. A Web UI could be replaced with a console UI, for example, without changing the business rules.
- Independent of Database. You can swap out Oracle or SQL Server, for Mongo, BigTable, CouchDB, or something else. Your business rules are not bound to the database.
- Independent of any external agency. In fact your business rules simply don’t know anything at all about the outside world.
- This rule says that source code dependencies can only point inwards
- Nothing in an inner circle can know anything at all about something in an outer circle.
- The name of something declared in an outer circle must not be mentioned by the code in the an inner circle. That includes, functions, classes. variables, or any other named software entity
- Entities encapsulate Enterprise wide business rules
- An entity can be an object with methods, or it can be a set of data structures and functions.
- The software in this layer contains application specific business rules. It encapsulates and implements all of the use cases of the system.
- These use cases orchestrate the flow of data to and from the entities, and direct those entities to use their enterprise wide business rules to achieve the goals of the use case.
- This layer is isolated from the changes in
- Entites
- Databases
- UI
- However, any changes to the operation of the application needs to be made in this layer
The software in this layer is a set of adapters that convert data from the format most convenient for the use cases and entities, to the format most convenient for some external agency such as the Database or the Web