Development Projects
Note: The Python/R codes in these repository are for development purpose they should not be used in production stage.
Production stage machine learning models are built using pipelines and classes. They need to be robust, maintainable and scalable.
Data Science Projects
The respository contains jupyter notebook codes of data science/machine learning course work and competitions.
The content lays down a general approach that is used for solving Data Science problem.
Achievements
- 3rd Rank out of 1702 participants in a competition organized by Analytics India Magazine for predicting the price of used cars. The winning code is here.
-
15/1187 participats in a competition hosted by Analyticss India Magazine for predicting price of flight tickets.
-
220/10516 - Overall Analytics Vidhya Rak.
1) Problem Defiation
To make a remarkable contribution, we need to start by asking the right question. The problem statement identifies the current state, the desired future state and any gaps between the two.
Image source: Research planning - Business Aalytics in Real World @ IIM Ahmedabad.A problem statement is an important communication tool that can help ensure everyone working on a project knows what the problem they need to address is and why the project is important.
2) Data Science Methodology
2.1) Data Collection
In the research planning image, towards the end we have Sources of info, a well designed problem statement delivers the
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
2.2) Exploratory Data Analysis
Exploratory Data Analysis is an approach to summarize and identify important characterstics of the data using visualization and statistical plots. It encourages to test hypothesis, detect relationship, analyze missing values and/or detect outliers.
Image source: Capstone project @ IIM Ahmedabad. — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —2.3) PreProcessing
Pre-processing refers to the transformations applied to our data before feeding it to the algorithm. Specifically, Feature Engineering refers to extraction of new features/columns using domain knowledge and Feature Extraction refers dimensionality reduction using technique such as PCA, LDA etc.
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
2.4) Split Dataset
Models are build to work on new data - future data. As such, data is split into three sets train data test data & validation data. In a time series model, the order of data split is preserved.
An appropriate data split assist the modeler to avoid overfitting. Overfitting occurs when the trained model is not generalized on unseen data, similarly Underfitting occurs when model is not able to learn enough from the training data.
Image source: Machine Learning Project @ IIM Ahmedabad.The benefit of data split can be seen in the above (learning curves) plots. Both plots indicates overfitting. Had data not been split, it would have been difficult to notice this while modeling.
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
2.5) Model Training
Regression and Classification are two of the primary models in data science. Other fews are forecasting (time series), survival (both regression and classification) & panel data (time series for each panel).
Commonly used models
- Linear model (Linear & Logistic Regression, Linear SVM)
- Decision Tree-based model (XGboost, LightGBM, Random Forest)
- Survival (Kaplan Meier, Cox Proportioal Hazard, Random Forest Survival)
- Neural Networks (CNN, RNN, LSTM)
A list of over 200 data science can be found here.
Image source: Model Complexity, Accuracy and Interpretability - Medium
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
2.6) Hyperparameter tuning
Methods such as Grid search, Randomized search, and Bayesian hyperparameter tuning are used to identify optimal hyperparameters of a model.
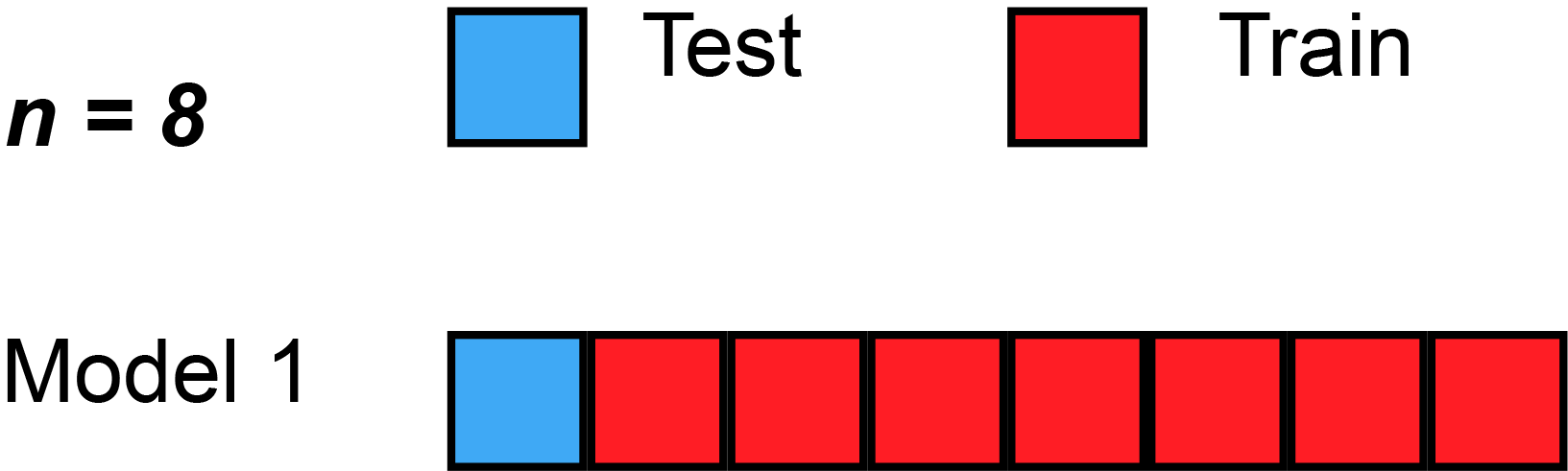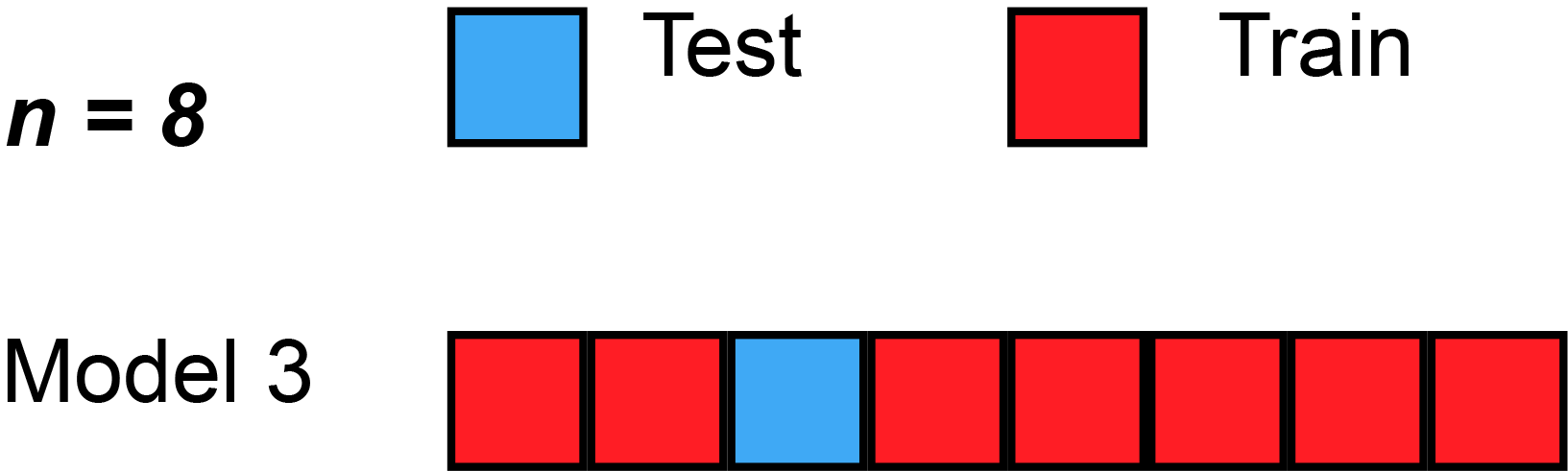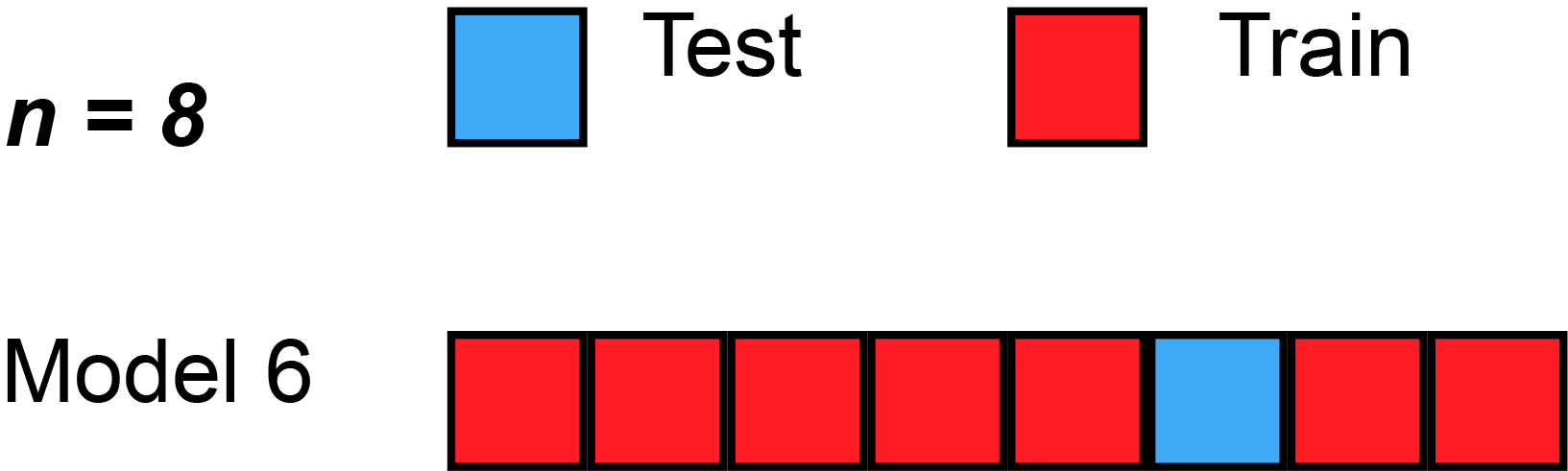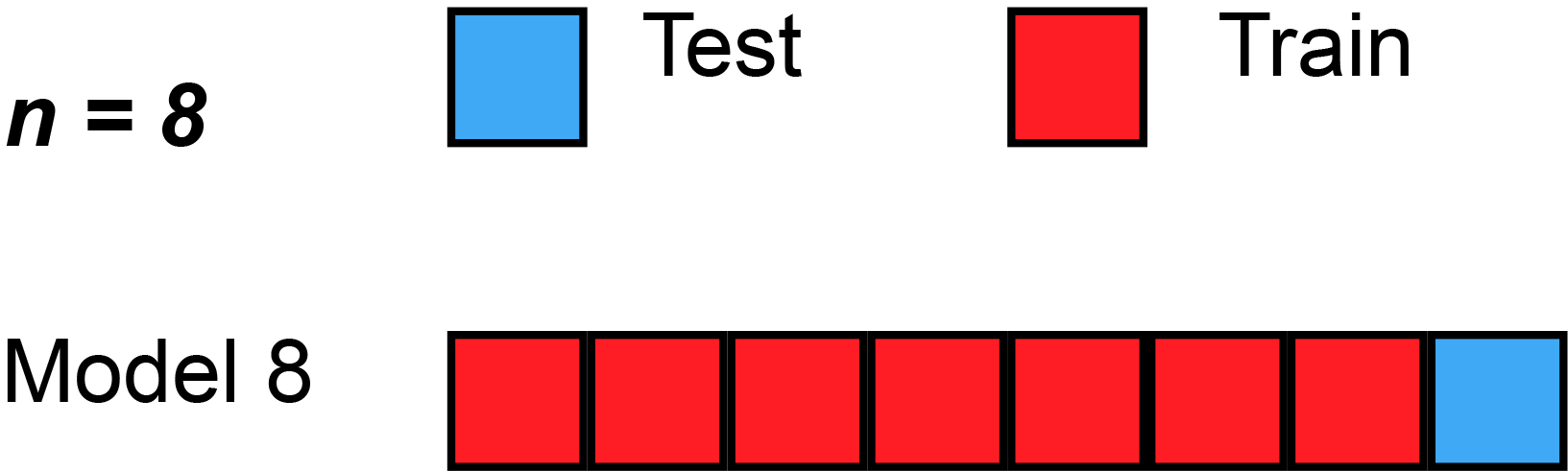
A formal approach to identify optimal hyperparameter is to use the cross-validation technique. There are various type of cross-validation techniques such as k-fold cv, Leave one out cv, k-fold stratified cross-validation, etc.
source: https://en.wikipedia.org
In the above animation, the dataset is split into eight section. In each round, seven section are used for training and the holdout section is used for testing the models.
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
2.7) MLOps using ML Flow
A predictive model is an iterative process, involving different features, various models and tuning the best hyperparameters. Due to it's iterative nature, outputs of the model needs to be stored and compared for performance.
ML Flow platform from databricks stores models, parameters, metrics, and artifacts. A simple UI makes it easy to compare different models.
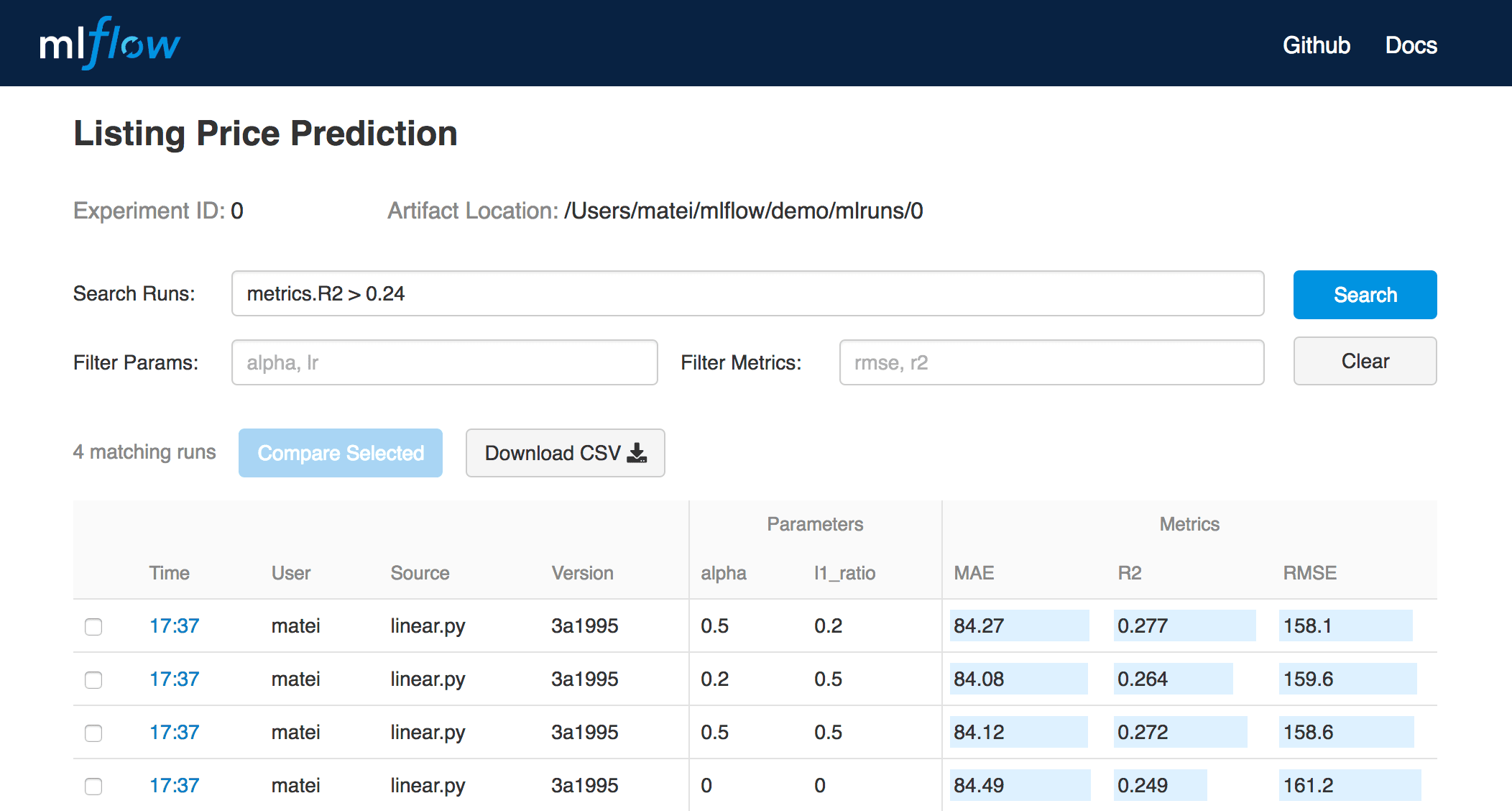
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
2.8) eXplainable AI
XAI is a subset of data science/machine learning that helps humans understand the solution provided by the algorithams.
Significant variables / Feature Importance: Significant variables and feature importance plot provide us the important variables used in the model. With domain expertise, we can match these variables to ensure the stability of the model.
Partial Dependence Plot: The partial dependence plot (short PDP or PD plot) shows the marginal effect one or two features have on the predicted outcome of a machine learning model
Individual Conditional Expectation: Individual Conditional Expectation (ICE) plots display one line per instance that shows how the instance's prediction changes when a feature changes.
SHapley Additive exPlanation (SHAP): The goal of SHAP is to explain the prediction of an instance x by computing the contribution of each feature to the prediction. The SHAP explanation method computes Shapley values from coalitional game theory.
source: Python SHAP package
Libraries such as AI Fairness 360 and FAIRLEARN can be used to evaluate the fairness and biasness of the model.
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
2.9) Model Evaluation
Only once we have finalized a model. We evaluate its performance on the test dataset. Our objective is to find out the best model that can be generalized on unseen data. High performance on the test dataset can help us conclude that the model has found the best parameters used for our data.
Even though the modeling building process ends here, however, this does not meet our end objective.
3) Deployment & Monitorig
Batch Prediction
Next, we go into more details about the prediction of models once deployed.
In a situation where we do not need real-time prediction, e.g., predicting employee attrition, we can process our data in batches.
We set up scheduled jobs to generate predictions in specific intervals such as hourly, daily, or weekly. Such batch predictions are usually part of the ETL process whereby the predictions are stored in databases, preferably a relational database management system.
Google Big Query, Amazon's Redshift, and Azure Synapse are all data warehouses that can be used to store and process batch predictions. For on premise, we can use any column-oriented relationship database management system such as SQL Server or Oracle SQL.
Rest API
In cases where we need real-time prediction, e.g., an Application Programming Interface (API) can be set up. In Python, we can use flask, Django, or fast API to generate API.
A few points to consider while using API.
-
Testing: Ensure that API is tested thoroughly in terms of security, performance, reliability, and maintainability.
-
Asynchronization: Our system should handle each request separately; this becomes extremely important when serving a large number of an API request.
-
Task queue: Even with the best infrastructure, systems do go down. Using a task queue, we can be sure that request received during downtime is served once the system is back up and running.
source:- Prateek's Blog
-
CICD: Model deployment is more like software engineering; thus, a DevOps approach such as continuous improvement and continuous deployment ensures that the latest updates are tested and applied as soon as possible.
-
Cloud Infrastructure: We can use cloud platforms such as GCP, Azure, or AWS to build the required infrastructure. Features such as compute engine, lambda functions, virtual machines, etc., are easily set up for prototyping and converting to production. Lastly, automatic scaling through a load balancer is extremely helpful to scale up or scale down our API request as per the demand.
Docker In some organizations, the job of a data scientist ends once we have a finalized the model. However, many organizations expect data scientists to provide a production-ready model to the development team.
We can use docker images to build the model pipeline. A docker image is a document with a set of instructions for creating the container. The steps include all relevant information such as the operating system, packages, files, and folders, etc., required to build the same environment for our model.
With all these steps involved, we can notice that building a robust real-time model is a humongous task and requires special skills and a team to keep it up are running.
References
- Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow
- Python Machine Learning
- Interpretable Machine Learning
- Machine Learning Mastery Blog