Time series discretization with SAX
Implements Symbolic Aggregate Approximation of time series in Java; implements a multi-threaded SAX discretization. This code is released under GPL v.2.0.
The library is available through Maven Central and is built by TravisCI: .
0.0 SAX transform in a nutshell
An illustration of a time series of 128 points converted into the word of 8 letters:
Find more information about SAX at its authors pages: SAX overview by Jessica Lin, Eamonn Keogh's SAX page, or at sax-vsm wiki page.
The key publications introducing SAX:
[1] Lin, J., Keogh, E., Patel, P., and Lonardi, S., Finding Motifs in Time Series, The 2nd Workshop onTemporal Data Mining, the 8th ACM Int'l Conference on KDD (2002)
[2] Patel, P., Keogh, E., Lin, J., Lonardi, S., Mining Motifs in Massive Time Series Databases, In Proc. ICDM (2002)
Citing this work:
If you are using this implementation for you academic work, please cite our Grammarviz 2.0 paper:
[Citation] Senin, P., Lin, J., Wang, X., Oates, T., Gandhi, S., Boedihardjo, A.P., Chen, C., Frankenstein, S., Lerner, M., GrammarViz 2.0: a tool for grammar-based pattern discovery in time series, ECML/PKDD Conference, 2014.
Variable-length time series recurrent and anomalous patterns detection
If you are interested in the time series motif and discord discovery, please check out our new tool called GrammarViz 2.0 -- based on SAX, Grammatical Inference, and algorithmic (Kolmogorv complexity) it enables variable-length time series recurrent and anomalous patterns detection.
1.0 Building
The code is written in Java and I use maven to build it:
$ mvn package -P single
[INFO] Scanning for projects...
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Building jmotif-sax
[INFO] task-segment: [package]
...
[INFO] Building jar: /media/Stock/git/jmotif-sax/target/jmotif-sax-0.1.1-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESSFUL
2.0 Time series to SAX conversion using CLI
The jar file can be used to convert a time series (represented as a single-column text file) to SAX via sliding window in command line:
$ java -jar target/jmotif-sax-0.1.1-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar
Usage: <main class> [options]
Options:
--alphabet_size, -a
SAX alphabet size, Default: 3
--data, -d
The input file name
--out, -o
The output file name
--strategy
SAX numerosity reduction strategy
Default: EXACT, Possible Values: [NONE, EXACT, MINDIST]
--threads, -t
number of threads to use, Default: 1
--threshold
SAX normalization threshold, Default: 0.01
--window_size, -w
SAX sliding window size, Default: 30
--word_size, -p
SAX PAA word size, Default: 4
When run, it prints the time series point index and a corresponding word:
$ java -jar "target/jmotif-sax-0.1.1-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar" \
-d src/resources/test-data/ecg0606_1.csv -o test.txt
$ head test.txt
0, aabc
8, aacc
13, abcc
20, abcb
...
3.0 API usage
There two classes which implement sequential end-to-end workflow for SAX and a parallel implementation of the discretization. These are TSProcessor and SAXProcessor.
Discretizing time-series by chunking:
// instantiate needed classes
NormalAlphabet na = new NormalAlphabet();
SAXProcessor sp = new SAXProcessor();
// read the input file
double[] ts = TSProcessor.readFileColumn(dataFName, 0, 0);
// perform the discretization
String str = sp.ts2saxByChunking(ts, paaSize, na.getCuts(alphabetSize), nThreshold);
// print the output
System.out.println(str);
Discretizing time-series via sliding window:
// instantiate needed classes
NormalAlphabet na = new NormalAlphabet();
SAXProcessor sp = new SAXProcessor();
// read the input file
double[] ts = TSProcessor.readFileColumn(dataFName, 0, 0);
// perform the discretization
SAXRecords res = sp.ts2saxViaWindow(ts, slidingWindowSize, paaSize,
na.getCuts(alphabetSize), nrStrategy, nThreshold);
// print the output
Set<Integer> index = res.getIndexes();
for (Integer idx : index) {
System.out.println(idx + ", " + String.valueOf(res.getByIndex(idx).getPayload()));
}
Multi-threaded discretization via sliding window:
// instantiate needed classes
NormalAlphabet na = new NormalAlphabet();
SAXProcessor sp = new SAXProcessor();
// read the input file
double[] ts = TSProcessor.readFileColumn(dataFName, 0, 0);
// perform the discretization using 8 threads
ParallelSAXImplementation ps = new ParallelSAXImplementation();
SAXRecords res = ps.process(ts, 8, slidingWindowSize, paaSize, alphabetSize,
nrStrategy, nThreshold);
// print the output
Set<Integer> index = res.getIndexes();
for (Integer idx : index) {
System.out.println(idx + ", " + String.valueOf(res.getByIndex(idx).getPayload()));
}
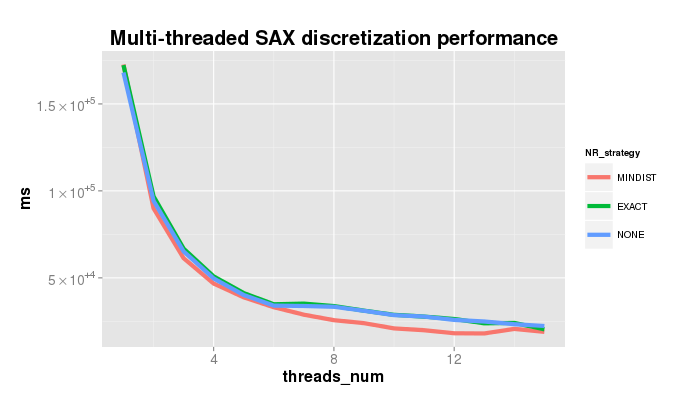
The plot below shows the speedup achieved when using the parallelized SAX version on the dataset 300_signal1.txt of length 536,976 points. Parameters used in the experiment: sliding window size 200, PAA size 11, alphabet size 7, and three different NR strategies.
4.0 Threaded performance
5.0 Use cases
5.1 Time series recurrent pattern (motif) discovery
Class SAXRecords implements a method for getting the most frequent SAX words:
Alphabet na = new NormalAlphabet();
double[] series = TSProcessor.readFileColumn(DATA_FNAME, 0, 0);
SAXProcessor sp = new SAXProcessor();
saxData = sp.ts2saxViaWindow(series, WIN_SIZE, PAA_SIZE, na.getCuts(ALPHABET_SIZE),
NR_STRATEGY, NORM_THRESHOLD);
ArrayList<SAXRecord> motifs = saxData.getMotifs(10);
SAXRecord topMotif = motifs.get(0);
System.out.println("top motif " + String.valueOf(topMotif.getPayload()) + " seen " +
topMotif.getIndexes().size() + " times.");
5.2 Time series rare pattern (discord, anomaly) detection using HOT-SAX
Class HOTSAXImplementation implements two methods for rare patterns discovery:
5.2.1 Trie-based time series discord discovery
Alphabet na = new NormalAlphabet();
double[] series = TSProcessor.readFileColumn(DATA_FNAME, 0, 0);
discordsTrie = HOTSAXImplementation.series2Discords(series, WIN_SIZE, ALPHABET_SIZE,
DISCORDS_TO_REPORT, new LargeWindowAlgorithm(), NORM_THRESHOLD);
System.out.println("The best discord: " + discordsTrie.get(0));
5.2.2 Hash-table-based time series discord discovery (allows PAA and alphabet sizes to differ)
discordsHash = HOTSAXImplementation.series2DiscordsWithHash(series, WIN_SIZE, PAA_SIZE,
ALPHABET_SIZE, DISCORDS_TO_REPORT, new LargeWindowAlgorithm(), NORM_THRESHOLD);
System.out.println("The best discord: " + discordsHash.get(0));