If a repository contains a meta.yaml file to build conda packages, the process of building and uploading packages to an Anaconda user or organization is automatized by this GitHub Action. The user has only to be sure that the repository have access to the corresponding Anaconda token.
In summary, this GitHub Action does the following:
- It is suggested that the action is triggered by a release or a prerelease publication.
- The action checks if the meta.yaml file exists in the directory specified by the user.
- It compiles then the list of packages to the platform and Python version specified by the user.
- Finally, the action uploads all packages built to the Anaconda user or organization specified by the user, with the label
specified by the user (the option
autosets the value of the label as 'main' for releases and 'dev' to prereleases).
This GitHub Action was developed by the Computational Biology and Drug Design Research Unit -UIBCDF- at the Mexico City Children's Hospital Federico Gómez. Other GitHub Actions can be found at the UIBCDF GitHub site.
In addition to define the workflow to use this action in the '.github/workflow' directory of your repository. There are three things you have to solve: having an Anaconda token to authorize the access to your conda repository or organization, using Git tags as package version numbers in the metadata file with the conda build instructions, and a Yaml file to create a conda environment to work with conda-build.
In order to upload a package to your anaconda user or organization, you have to define an Anaconda API token. There are two ways you can easily do it. From the command line you can execute:
# In case of uploading to a user profile
# Replace 'MyToken' with the name you want for your token
TOKEN=$(anaconda auth --create --name MyToken)or
# Replace 'MyToken' with the name you want for your token
# Replace 'MyOrg' with the name of your organization
TOKEN=$(anaconda auth --create --name MyToken --org MyOrg)After that, You can access to the value of your token:
echo $TOKENThere is another way to create and manage your tokens. You can do it with the web page of your Anaconda user or organization. In that page, the menu entrie 'Settings--> Access' shows the following form:
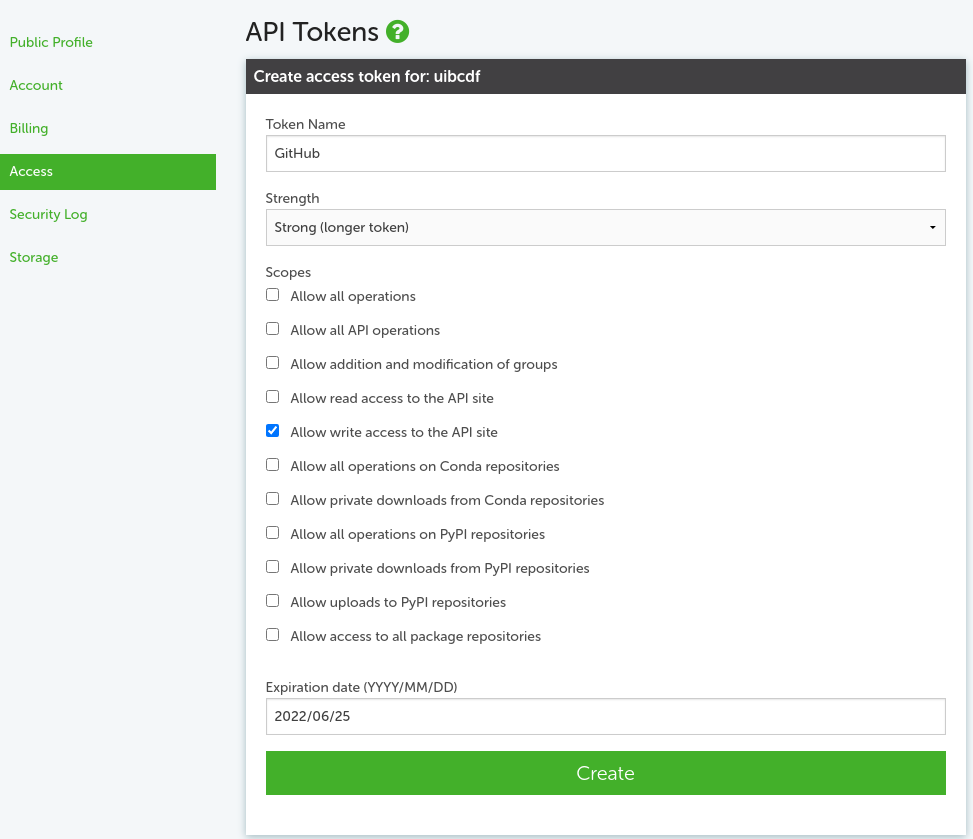
In this form mark the option 'Allow write access to the API site', choose a name and an expiration date for your new token, and click 'Create'. Below this form, you will find the list of your tokens to view their value or remove them.
Now, the last step. The repository where you want to include this GitHub Action has to have access, quietly, to the value of this token. But you have to protect it, including the token string explictly in the workflow is far from being a good idea. To solve this problem, GitHub includes for your GitHub repositories or organizations, the possibility to store 'encrypted secrets'. You can find documentation about it in the GitHub docs site. Let's see here how to store the Anaconda token accesible for any public repository of an organization. Look for the section 'Settings -> Secrets' in the organization main web page in GitHub and click on the button 'New organization scret'. Briefly, choose a new name -this way for the variable storing the token value in GitHub- and copy the value of your token (a long string of "random" characters). As you can see in the secret creation form, you can give access to all public repositories in the organization or just a selected set of them (also to your private ones depending on your plan).
After all this process, what matters to use this GitHub Action is the name of the secret with the Anaconda token value.
The instructions to build the new conda packages are defined by means of a YAML file usually named 'meta.yaml'. It is your work having this file well implemented. Here you can find a guide to decide the building parameters in this file.
In this metadata file, the conda-build recipe includes setting the version number of the new
package. To avoid adding it manually and to use the release or prerelease GitHub tags as version label, use {{ environ['GIT_DESCRIBE_TAG'] }} in the package: version: field of the 'meta.yaml' file. Then, the first lines or your 'meta.yaml' file should look like this:
package:
name: package_name # write your library name
version: "{{ environ['GIT_DESCRIBE_TAG'] }}"
source:
path: ../../
build:
number: 1Remember that version numbers including the dash character "-" are not supported by conda-build as package versions. If you want to release a version like "1.0.0-beta.1", replace it with something like "1.0.0b1". Check PEPE-86 verlib conventions for further details.
Building your conda packages requires dependencies that can be solved with a temporary conda environment. You already know that the list of dependencies of your library are specified in your 'meta.yaml' file with the compilation instructions, but the required channels needed to find them need to be provided. In the case of this GitHub Action, these channels are taken from the Yaml file with the details to execute the packages compilation (see the section "Documentation conda environment"). This Yaml file will look like:
channels: # write here the list of channels to look for your library dependencies
- uibcdf
- conda-forge
- default
dependencies: # Keep this block with only these two packages
- anaconda-client
- conda-buildTo include this GitHub Action, put a Yaml file (named 'build_and_upload_conda_packages.yaml', for instance) with the following content in the directory '.github/workflows' of your repository:
name: Build and upload conda packages
on:
release:
types: ['released', 'prereleased']
# workflow_dispatch: # Un comment line if you also want to trigger action manually
jobs:
conda_deployment_with_new_tag:
name: Conda deployment of package with Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
strategy:
matrix:
python-version: ["3.8", "3.9", "3.10"]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Conda environment creation and activation
uses: conda-incubator/setup-miniconda@v2
with:
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
environment-file: devtools/conda-envs/build_env.yaml # Path to the build conda environment
auto-update-conda: false
auto-activate-base: false
show-channel-urls: true
- name: Build and upload the conda packages
uses: uibcdf/action-build-and-upload-conda-packages@v1.3.0
with:
meta_yaml_dir: devtools/conda-build
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }} # Values previously defined in `matrix`
platform_linux-64: true
platform_osx-64: true
platform_win-64: true
user: uibcdf
label: auto
token: ${{ secrets.ANACONDA_TOKEN }} # Replace with the right name of your secretWhen the package is built from a pure python library, conda convert can produce packages for a
long list of platforms. Instead, if you have to build a package that contains compiled code, conda convert does not work and just the platform of the host machine will be built. In this former
case, if you want to produce packages for instance for 'linux-64', 'osx-64' and 'win-64, use
something like the following:
name: Build and upload conda packages
on:
release:
types: ['released', 'prereleased']
# workflow_dispatch: # Un comment line if you also want to trigger action manually
jobs:
conda_deployment_with_new_tag:
name: Conda deployment of package for platform ${{ matrix.os }} with Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
matrix:
os: [macOS-latest, ubuntu-latest, windows-latest]
python-version: ["3.8", "3.9", "3.10"]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Conda environment creation and activation
uses: conda-incubator/setup-miniconda@v2
with:
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
environment-file: devtools/conda-envs/build_env.yaml # Path to the build conda environment
auto-update-conda: false
auto-activate-base: false
show-channel-urls: true
- name: Build and upload the conda packages
uses: uibcdf/action-build-and-upload-conda-packages@v1.3.0
with:
meta_yaml_dir: devtools/conda-build
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }} # Values previously defined in `matrix`
user: uibcdf
label: auto
token: ${{ secrets.ANACONDA_TOKEN }} # Replace with the right name of your secretThese are the input parameters of the action:
| Input parameters | Description | Required | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| meta_yaml_dir | Path to the directory where the meta.yaml file with building instructions is located | Yes | |
| python-version | Python version of the built packages | Yes | |
| platform_host | Build packages for the host platform | No | True |
| platform_all | Build packages for all supported platforms | No | False |
| platform_linux-64 | Build a package for the platform: linux-64 | No | False |
| platform_linux-32 | Build a package for the platform: linux-32 | No | False |
| platform_osx-64 | Build a package for the platform: osx-64 | No | False |
| platform_osx-arm64 | Build a package for the platform: osx-arm64 | No | False |
| platform_linux-ppc64 | Build a package for the platform: linux-ppc64 | No | False |
| platform_linux-ppc64le | Build a package for the platform: linux-ppc64le | No | False |
| platform_linux-s390x | Build a package for the platform: linux-s390x | No | False |
| platform_linux-armv6l | Build a package for the platform: linux-armv6l | No | False |
| platform_linux-armv7l | Build a package for the platform: linux-armv7l | No | False |
| platform_linux-aarch64 | Build a package for the platform: linux-aarch64 | No | False |
| platform_win-32 | Build a package for the platform: linux-win-32 | No | False |
| platform_win-64 | Build a package for the platform: linux-win-64 | No | False |
| upload | Upload the built package to Anaconda. Setting to False is useful to test build correctness in CI | No | True |
| overwrite | Do not cancel the uploading if a package with the same name is found already in Anaconda | No | False |
| user | User or organization name to upload packages to on anaconda.org | True | |
| label | Name of the label to upload the package ('main', 'dev', ...). If the value is equal to 'auto', the action will automatically label releases as 'main' and prereleases as 'dev' | True | auto |
| token | Anaconda token to authorize the uploading (more info here) | Yes |
They are placed in the with: subsection of the step named Build and upload the conda packages of the above workflow example file:
- name: Build and upload the conda packages
uses: uibcdf/action-build-and-upload-conda-packages@v1.3.0
with:
meta_yaml_dir: devtools/conda-build
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }} # Values previously defined in `matrix`
platform_linux-64: true
platform_osx-64: true
platform_win-64: true
channel: uibcdf
label: dev
token: ${{ secrets.ANACONDA_TOKEN }}At this point, you can probably wonder: but the python version of the package is specified in the 'meta.yaml' file, isn't it?
To define the python versions of the packages created by the GitHub Action you should use the input
parameter of the workflow named strategy: matrix: python-version.
strategy:
matrix:
python-version: ["3.8", "3.9", "3.10"]No matter the python version found in the 'meta.yaml' file, this action will make all the work to convert the building instructions to the python versions you specify in your GitHub workflow.
Typically this workflow is called in a deployment step, e.g. after a pull-request has succeeded and a new tag is added to the repository, or when a release is created. This means deployment generally occurs without checking if any errors to the build process were introduced in a pull request or code change.
To address this the upload option is provided. Setting upload: false will run all the steps in the workflow except uploading to Anaconda, and this can be done in a CI workflow to test build correctness, and catch errors during the pull-request process.
For example, this is an equivalent CI workflow for the deployment workflow above:
name: Test Build of conda packages
# Controls when the action will run.
on:
# Triggers the workflow on push or pull request events but only for the main branch
push:
branches: [ main ]
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]
# Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
conda_deployment_with_new_tag:
name: Test conda deployment of package with Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
strategy:
matrix:
python-version: ["3.8", "3.9", "3.10"]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Conda environment creation and activation
uses: conda-incubator/setup-miniconda@v2
with:
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
environment-file: devtools/conda-envs/build_env.yaml # Path to the build conda environment
auto-update-conda: false
auto-activate-base: false
show-channel-urls: true
- name: Build but do not upload the conda packages
uses: uibcdf/action-build-and-upload-conda-packages@v1.3.0
with:
meta_yaml_dir: devtools/conda-build
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }} # Values previously defined in `matrix`
platform_linux-64: true
platform_osx-64: true
platform_win-64: true
user: uibcdf
label: auto
upload: false
token: ${{ secrets.ANACONDA_TOKEN }} # Replace with the right name of your secretThis GitHub Action was developed to solve a need of the UIBCDF. And to be used, additionally, as example of house-made GitHub Action for researchers and students in this lab.
Other tools you can find in the market doing these same tasks are mentioned below. We recognize and thank the work of their developers. Many of those GitHub Actions were used by us to learn how to set up our own one.
If you think that your GitHub Action should be mentioned here, fell free to PR with a new line.
https://github.com/fdiblen/anaconda-action
https://github.com/MichaelsJP/conda-package-publish-action
https://github.com/Jegp/conda-package-publish-action
https://github.com/amauryval/publish\_conda\_package\_action
https://github.com/elbeejay/conda-publish-action
https://github.com/maxibor/conda-package-publish-action
https://github.com/m0nhawk/conda-package-publish-action
https://github.com/fcakyon/conda-publish-action