It's a pretty bad solution for Queen's Attack II Problem by bishop15.
Click here to get problem page.
You will be given a square chess board with one queen and a number of obstacles placed on it. Determine how many squares the queen can attack.
A queen is standing on an n x n chessboard. The chess board's rows are numbered from 1 to n, going from bottom to top. Its columns are numbered from 1 to n, going from left to right. Each square is referenced by a tuple, (r, c), describing the row, r , and column, c , where the square is located.
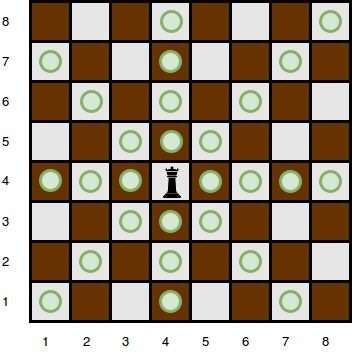
The queen is standing at position (rq, cq) . In a single move, she can attack any square in any of the eight directions (left, right, up, down, and the four diagonals). In the diagram below, the green circles denote all the cells the queen can attack from (4, 4):
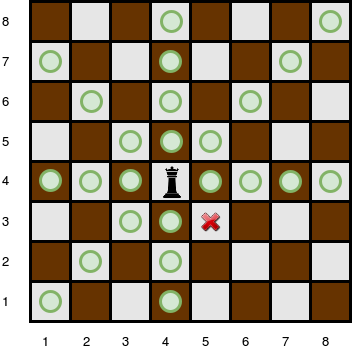
There are obstacles on the chessboard, each preventing the queen from attacking any square beyond it on that path. For example, an obstacle at location (3, 5) in the diagram above prevents the queen from attacking cells (3, 5), (2, 6), and (1, 7):
Given the queen's position and the locations of all the obstacles, find and print the number of squares the queen can attack from her position at (rq, rc) . In the board above, there are 24 such squares.
Complete the queensAttack function in the editor below. It should return an integer that describes the number of squares the queen can attack.
queensAttack has the following parameters:
- n: an integer, the number of rows and columns in the board
- k: an integer, the number of obstacles on the board
- r_q: integer, the row number of the queen's position
- c_q: integer, the column number of the queen's position
- obstacles: a two dimensional array of integers where each element is an array of 2 integers, the row and column of an obstacle
The first line contains two space-separated integers n and k, the length of the board's sides and the number of obstacles. The next line contains two space-separated integers rq and cq, the queen's row and column position. Each of the next k lines contains two space-separated integers r[i] and c[i], the row and column position of obstacle[i].
- 0 < n <= 10^5
- 0 <= k <= 10^5
- A single cell may contain more than one obstacle.
- There will never be an obstacle at the position where the queen is located.
For 30% of the maximum score:
- 0 < n <= 100
- 0 <= k <= 100
For 55% of the maximum score:
- 0 < n <= 1000
- 0 <= k <= 10^5
Print the number of squares that the queen can attack from position (rq, cq).
4 0
4 4
9
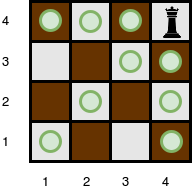
The queen is standing at position (4, 4) on a 4 x 4 chessboard with no obstacles:
5 3
4 3
5 5
4 2
2 3
10
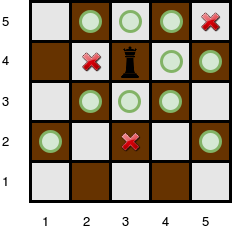
The queen is standing at position (4, 3) on a 5 x 5 chessboard with k = 3 obstacles:
The number of squares she can attack from that position is 10.
1 0
1 1
0
Since there is only one square, and the queen is on it, the queen can move 0 squares.
- x | X axis of Queen's location.
- y | Y axis of Queen's location.
- del | Total deleted cells number which is blocked by obstacles.
- mid | Middle value of n x n matrix.
- rank | Rank describes the obstacles' distance to mid.
- xEyB contains the obstacle's y-axis. Obstacle's y-axis is greater than Queen's one when both x-axises are same.
- xEyK contains the obstacle's y-axis. Obstacle's y-axis is less than Queen's one when both x-axises are same.
- xKyE contains the obstacle's x-axis. Obstacle's x-axis is less than Queen's one when both y-axises are same.
- xByE contains the obstacle's x-axis. Obstacle's x-axis is greater than Queen's one when both y-axises are same.
- xKyKx contains the bottom-left obstacle's x-axis.
- xKyKy contains the bottom-left obstacle's y-axis.
- xKyBx contains the top-left obstacle's x-axis.
- xKyBy contains the top-left obstacle's y-axis.
- xByKx contains the bottom-right obstacle's x-axis.
- xByKy contains the bottom-right obstacle's y-axis.
- xByBx contains the top-right obstacle's x-axis.
- xByBy contains the top-right obstacle's y-axis.
This code finds the maximum available cells using matrix dimension and Queen's location. Doesn't count any of obstacles.
if (n % 2 === 0) {
mid = (n + 1) / 2;
rank = Math.max(
Math.floor(Math.abs(x - mid)),
Math.floor(Math.abs(y - mid))
);
total = (n / 2 - 1) * 4 + 1 - rank * 2 + (n - 1) * 2;
} else {
mid = (n + 1) / 2;
rank = Math.max(Math.abs(x - mid), Math.abs(y - mid));
total = (n - 1) * 2 - rank * 2 + (n - 1) * 2;
}This code filters the obstacles array to find the closest obstacles to Queen.
obstacles.forEach(obs => {
// obs[1]=x, obs[0]=y;
if (obs[1] === x && obs[0] > y) xEyB = obs[0] < xEyB ? obs[0] : xEyB;
else if (obs[1] === x && obs[0] < y) xEyK = obs[0] > xEyK ? obs[0] : xEyK;
else if (obs[0] === y && obs[1] < x) xKyE = obs[1] > xKyE ? obs[1] : xKyE;
else if (obs[0] === y && obs[1] > x) xByE = obs[1] < xByE ? obs[1] : xByE;
else if (Math.abs(obs[0] - y) === Math.abs(obs[1] - x)) {
if (obs[1] < x && obs[0] < y) {
if (obs[1] > xKyKx && obs[0] > xKyKy) {
xKyKx = obs[1];
xKyKy = obs[0];
}
} else if (obs[1] < x && obs[0] > y) {
if (obs[1] > xKyBx && obs[0] < xKyBy) {
xKyBx = obs[1];
xKyBy = obs[0];
}
} else if (obs[1] > x && obs[0] < y) {
if (obs[1] < xByKx && obs[0] > xByKy) {
xByKx = obs[1];
xByKy = obs[0];
}
} else if (obs[1] > x && obs[0] > y) {
if (obs[1] < xByBx && obs[0] < xByBy) {
xByBx = obs[1];
xByBy = obs[0];
}
}
}
});This code calculates total number of deleted cells.
obstacles.forEach(obs => {
// obs[1]=x, obs[0]=y;
if (obs[1] === x && obs[0] > y) xEyB = obs[0] < xEyB ? obs[0] : xEyB;
else if (obs[1] === x && obs[0] < y) xEyK = obs[0] > xEyK ? obs[0] : xEyK;
else if (obs[0] === y && obs[1] < x) xKyE = obs[1] > xKyE ? obs[1] : xKyE;
else if (obs[0] === y && obs[1] > x) xByE = obs[1] < xByE ? obs[1] : xByE;
else if (Math.abs(obs[0] - y) === Math.abs(obs[1] - x)) {
if (obs[1] < x && obs[0] < y) {
if (obs[1] > xKyKx && obs[0] > xKyKy) {
xKyKx = obs[1];
xKyKy = obs[0];
}
} else if (obs[1] < x && obs[0] > y) {
if (obs[1] > xKyBx && obs[0] < xKyBy) {
xKyBx = obs[1];
xKyBy = obs[0];
}
} else if (obs[1] > x && obs[0] < y) {
if (obs[1] < xByKx && obs[0] > xByKy) {
xByKx = obs[1];
xByKy = obs[0];
}
} else if (obs[1] > x && obs[0] > y) {
if (obs[1] < xByBx && obs[0] < xByBy) {
xByBx = obs[1];
xByBy = obs[0];
}
}
}
});