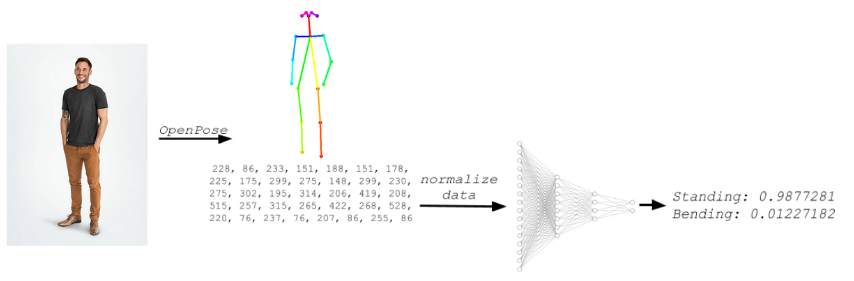
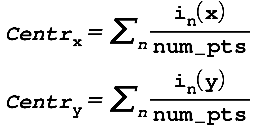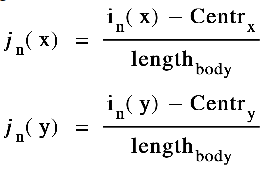This neural network was built to classify human poses (standing, bending and crouching) based on human skeleton information (key-points) produced by OpenPose.
Human keypoints used in this neural network is produced by OpenPose. There are 18 key-points representing for human skeletons as described below:
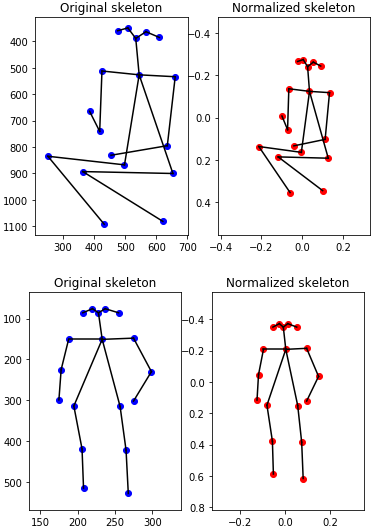
For each person, the coordinates of the singular point in is obtained, where n is the joint number. The size of each human skeleton in a frame is varied due to camera distance and camera angle. To prepare the data for the input of the neural network, the coordinates are normalized relative to the body length and relative to the center of gravity.
The Euclidean distance between two points (A, B) is defined as below:
def euclidean_dist(a, b):
# This function calculates the euclidean distance between 2 point in 2-D coordinates
# if one of two points is (0,0), dist = 0
# a, b: input array with dimension: m, 2
# m: number of samples
# 2: x and y coordinate
try:
if (a.shape[1] == 2 and a.shape == b.shape):
# check if element of a and b is (0,0)
bol_a = (a[:,0] != 0).astype(int)
bol_b = (b[:,0] != 0).astype(int)
dist = np.linalg.norm(a-b, axis=1)
return((dist*bol_a*bol_b).reshape(a.shape[0],1))
except:
print("[Error]: Check dimension of input vector")
return 0Since OpenPose does not always generate 18 key-points for each human in the frame because of occlusion or human skeleton cropping, some key-points representing the body part can be omitted (assigned to origin 0). Length of head will thus be defined as maximum number among distance from neck to ears, from neck to eyes, from nose to ears and from nose to eyes. This definition of length of head would reduce the probability that length of head is zero.
length_head = maximum(E_dist(neck, eye), E_dist(neck, ear), E_dist(nose, eye), E_dist(nose, ear))Length of torso is maximum of distance from neck to left and right hips:
length_torso = maximum(E_dist(neck, right_hip), E_dist(neck, left_hip))Length of right and left legs are calculated as below formula:
length_right/left-leg = E_dist(hip, knee) + E_dist(knee, ankle)Length of leg is defined as the maximum of length of right and left legs:
length_leg = maximum(length_left-leg, length_right-leg)The length of human body is calculated as sum of length of head, length of torso and length of leg.
length_body = length_head + length_torso + length_legThe center of gravity is calculated as:
where num_pts is the number of keypoints generated by Openpose (num_pts <= 18)
Then the coordinate of each keypoint is normalized as:
Applying pre-processing process, the normalized key-points would be in the similar distribution as original key-points but in range of (-1, 1):
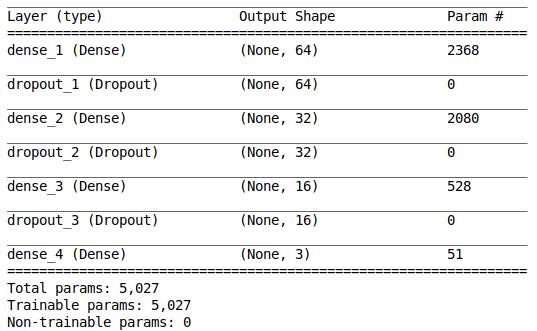
The normalized coordinates (jn(x) and jn(y)) will be fed into a neural network. Since the input size to neural network is small (size = 36 for 18 key-points), it only required a shallow network with 2 hidden layers for classification with high accuracy. Dropout technique also is applied to reduce overfitting. Neural network is built by Keras as summarized below:
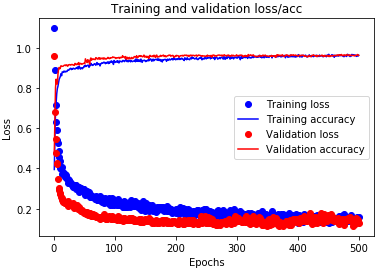
Train on 2676 samples, validate on 701 samples
After 500 epochs:
Epoch 500/500
2676/2676 [==============================] - 0s 38us/step - loss: 0.1567 - acc: 0.9638 - val_loss: 0.1304 - val_acc: 0.9629
The below code convert Keras model to frozen Tensorflow model
python3 keras_to_tensorflow.py -input_model_file pose_classifier.h518 key-points generated from OpenPose will be used as input for this model. See pose_classifier_inference.ipynb for details.
@article{ refId0,
author = {{Pismenskova, Marina} and {Balabaeva, Oxana} and {Voronin, Viacheslav} and {Fedosov, Valentin}},
title = {Classification of a two-dimensional pose using a human skeleton},
DOI= "10.1051/matecconf/201713205016",
url= "https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201713205016",
journal = {MATEC Web Conf.},
year = 2017,
volume = 132,
pages = "05016",
}