This project is about multi-threading: the program simulates a dinner between a group of nbr_of_philo philosophers. They share a bowl of spahghetti in the middle of the table and one fork per person.
A fork is placed between each philosopher; a philosopher can only eat with the help of the two forks on its left and on its right.
Mutex should be used to lock the forks for each philosopher to prevent them from stealing each other forks.
Once a philosopher has eaten for time_to_eat milliseconds, he starts to sleep for time_to_sleep milliseconds and then starts to think. He thinks for as long as he canm but at least 2 milliseconds.
If a philsopher has not started eating since time_to_die milliseconds after the beginning of the simulation or the beginning of his last meal, he dies.
The program displays the logs of the simulation according to the following format:
timestamp_in_msXhas taken a forktimestamp_in_msXis eatingtimestamp_in_msXis sleepingtimestamp_in_msXis thinkingtimestamp_in_msXdied
The full subject can be found here.
Clone the library and use make to compile
git clone https://github.com/theozanchi/42_Berlin_Philosophers/tree/main
cd 42_Berlin_Philosophers
make
The program expects 4 or 5 arguments:
nbr_of_philo: the number of philosophers and also the number of forkstime_to_die: if a philosopher didn’t start eatingtime_to_diemilliseconds since the beginning of their last meal or the beginning of the simulation, they dietime_to_eat: the time it takes for a philosopher to eat. During that time, they will need to hold two forkstime_to_sleep: The time a philosopher will spend sleeping- [optional]
nbr_of_meals: If all philosophers have eaten at leastnbr_of_mealstimes, the simulation stops. If not specified, the simulation stops when a philosopher dies
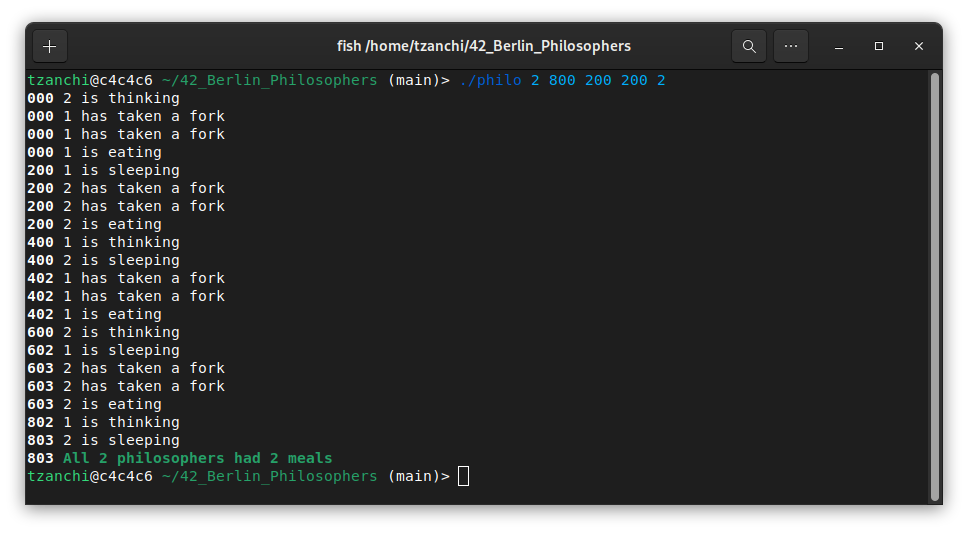
Example of a valid simulation, where all philosophers survive:
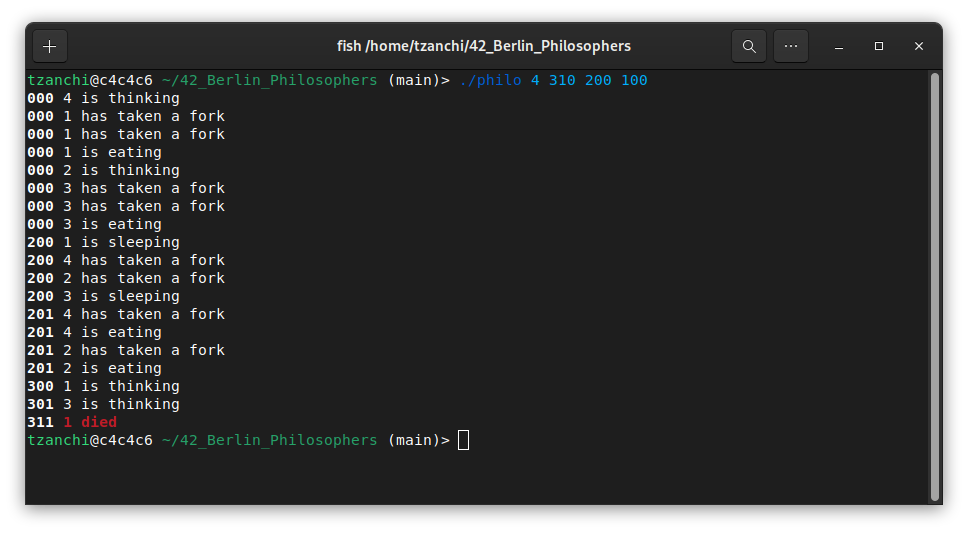
Example of a simulation that does not allow all philosophers to survive:
The program is safe to use for simulations up to 200 philosophers
Each philosopher is represented by a structure that contains the reference to a thread that will be use to simulate the life of a philosopher (eat, sleep, think).
typedef struct s_philo
{
size_t id;
int left_fork_id;
int right_fork_id;
clock_t last_meal;
pthread_mutex_t last_meal_mutex;
size_t nbr_of_meals;
int philo_is_full;
pthread_t routine;
struct s_data *data;
struct s_philo *next;
} t_philo;
All the data is nested into a macro t_data structure that contains a reference to the philosopher with ID 1.
typedef struct s_data
{
size_t nbr_of_philo;
clock_t time_to_die;
clock_t time_to_eat;
clock_t time_to_sleep;
size_t nbr_of_meals;
int end_of_simulation;
pthread_mutex_t end_of_simulation_mutex;
size_t nbr_of_full_philo;
pthread_mutex_t nbr_of_full_philo_mutex;
t_philo *philo;
pthread_mutex_t *forks;
pthread_mutex_t display_mutex;
clock_t start_time;
int start_of_simulation;
pthread_mutex_t start_of_simulation_mutex;
} t_data;
The following functions are part of the project:
/*_utils_1.c*/
int ft_atoi(const char *nptr);
int ft_isspace(int c);
int ft_isdigit(int c);
int ft_isnumeric(char *str);
int ft_strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2);
/*_utils_2.c*/
int ft_min(int a, int b);
int ft_max(int a, int b);
clock_t get_time(void);
int display_log(char *log, t_philo *philo);
void wait_for_start(t_data *data);
/*end.c*/
void destroy_forks(t_data *data);
void free_philosopher(t_philo *philosopher);
int free_data(t_data *data, int exit_code);
int join_philo_threads(t_data *data);
/*init.c*/
t_philo *new_philosopher(size_t philo_id, t_data *data);
int init_philosophers(t_data *data);
int init_forks(t_data *data);
int init_data(t_data *data, char **argv);
int launch_threads(t_data *data);
/*main.c*/
int check_arguments(int argc, char **argv);
int main(int argc, char **argv);
/*monitor_routine.c*/
int philo_is_dead(t_philo *philo);
int all_full_philo(t_data *data);
void monitor_routine(t_data *data);
/*philo_routine.c*/
void takes_forks(t_philo *philo);
void is_eating(t_philo *philo);
void is_sleeping(t_philo *philo);
void is_thinking(t_philo *philo);
void *routine(void *void_philo);