Optimizing an ML Pipeline in Azure
Overview
This project is part of the Udacity Azure ML Nanodegree. In this project, we build and optimize an Azure ML pipeline using the Python SDK and a provided Scikit-learn model. This model is then compared to an Azure AutoML run.
Summary
In 1-2 sentences, explain the problem statement: e.g "This dataset contains data about... we seek to predict..." We used data from UCI's mahine learning (ML) repository. This data is from a Portuguese banking institiution and the ML goal is to predict if a client will subscribe to a term deposit following a marketing campaign. This, therefore, is a classification problem.
In 1-2 sentences, explain the solution: e.g. "The best performing model was a ..." We undertook two approaches or experiments. One using Logistic Regression (LR) with Azure's HyperDrive for hyperparameter tuning. The other was leveraging Azure's AutoML to find the best ML classifier with the corresponding best hyperparameters. The best model was found by AutoML and is a VotingEnsemble.
Scikit-learn Pipeline
Explain the pipeline architecture, including data, hyperparameter tuning, and classification algorithm.
The Scikit-Learn (SL) pipeline includes a flow of retrieving data from a URI and a function to clean the data and convert it into a pandas dataframe.
Default LR hyperparameters were stated using SL documentation. And a scoring measure was declared (Accuracy and AUC-weighted).
We declare a base conda environment, using a YAML file, to keep future experiments stable.
We used HyperDrive for hyperparameter tuning with RandomParameterSampling as our parameter sampler.
We declare a search space for four (4) hyperparemeters such as solver and regularization penalty. Our primary metric was AUC_weighted.
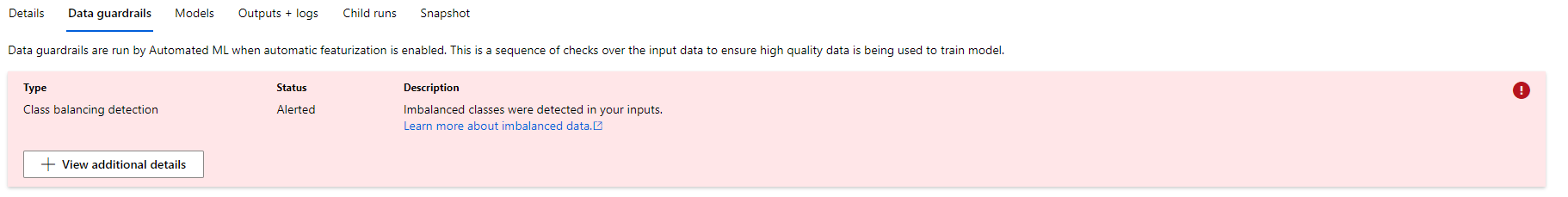
Using area-under-the-curve (AUC) vs. accuracy is a more balanced approach for datasets with imbalanced classes for prediction.
This is evident in the other experiment we ran with AutoML (see image below on 'Data guardrails'). A classification algorithm might have a high accuracy but it may be due to bias towards the majority class while the minority class considered as noise.
The entire experiment pipeline in Azure was executed in a jupyter notebook though the functions were declared in a python script and passed as modules in the .ipynb file.
What are the benefits of the parameter sampler you chose? The benefits of using a randomized search approach for hyperparemeter tuning is that it is computationally not as intensive as searching the entire grid of our parameter space. This might also carry cost implications.
What are the benefits of the early stopping policy you chose? In truth, a boilerplate code was used to declare an early termination (Bandit) policy. However, we do declare a slack factor of 0.2 - so any run with less that 1/(1+0.2) of the best run will be terminated. This decision can have time and cost implications as benefits.
AutoML
In 1-2 sentences, describe the model and hyperparameters generated by AutoML. AutoML chose a VotingEnsemble with a weighted AUC of 0.95 as the classifier. This is most likely a tree-based ensemble due to its hyperparemeters such as L1 regularization term set at ~1.67 and the tree construction algorithm being histogram-based.
Pipeline comparison
Compare the two models and their performance. What are the differences in accuracy? In architecture? If there was a difference, why do you think there was one? We used AUC_weighted however with the flexibility to evaluate accuracy on both experiments. Accuracy for AutoML was 0.92 and for the tuned logistic regression (LR) was 0.91. AUC_weighted for AutoML was 0.95 versus 0.81 for LR. Logistic regression is different from AutoML's best model which is a tree-based algorithim. The difference is most likely due to AutoML's VotingEnsemble 'ensembling' the decisions of many boosted and bagged trees to classify. This is unlike logistic regression which classifies using a sigmoid function.
Future work
What are some areas of improvement for future experiments? Why might these improvements help the model? For future experiments, we will consider performing our own data augmentation on a training set. Augmentation is the approach whereby we oversample the minority class while we downsample the majority using a Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique, or SMOTE, approach for instance. Data augmentation has shown better results using AutoML and this improvement might help our models in the future.
Proof of cluster clean up
If you did not delete your compute cluster in the code, please complete this section. Otherwise, delete this section. Image of cluster marked for deletion