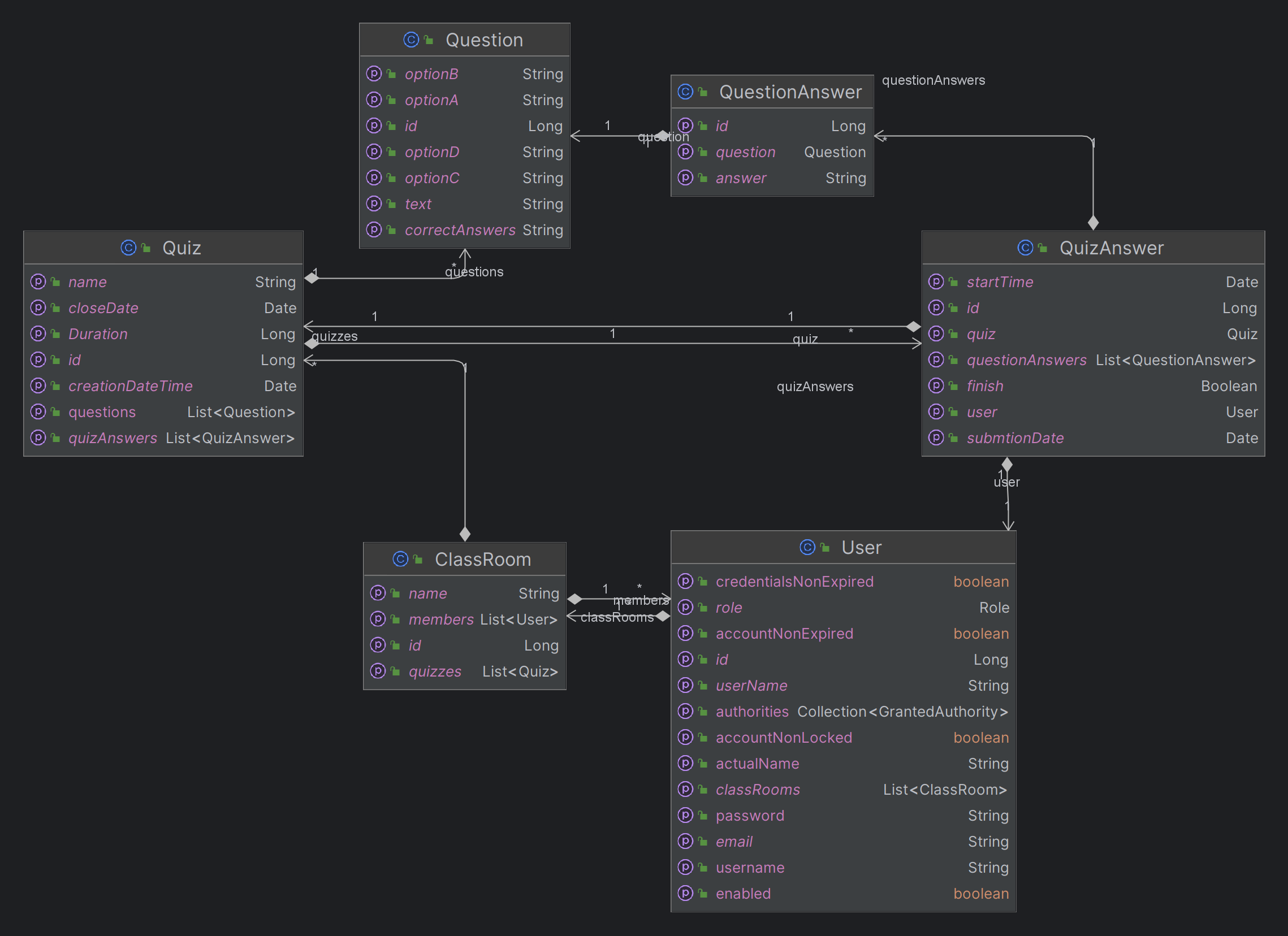
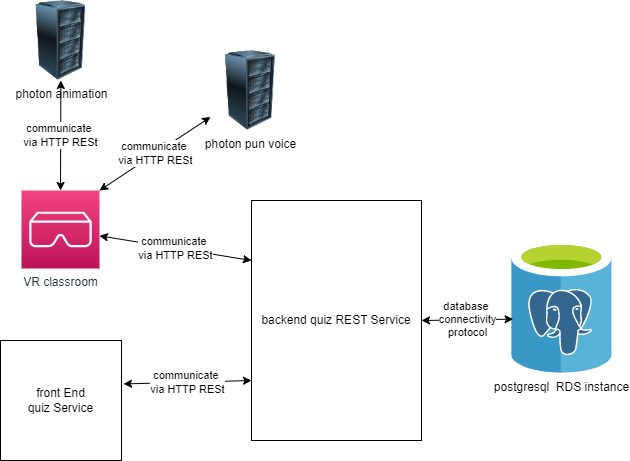
api to manage classrooms and quiz's for graduation project vr and front end parts project is under development
https://classroom-api.onrender.com
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 17 or above
- PostgreSQL Database (You can either use a local PostgreSQL instance or connect to a remote one)
- Clone the project repository from Git (if it's not already cloned).
- Import the project into your favorite Java IDE (e.g., IntelliJ, Eclipse, etc.).
- Build the project to resolve dependencies.
JWT (JSON Web Token) is used for authentication purposes, and here's how you can configure its value:
jwt_secret: oIhbd+QIyZnylJiHfnjjXcnHGXMicUqu9+no8qHAyXw=
Replace the value after jwt_secret: with your desired JWT secret key.
This section includes the database configuration using PostgreSQL. You'll need to specify the database URL, username, and password.
#postgres config
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:postgresql://dpg-ci4ln3dph6eva34s0md0-a.oregon-postgres.render.com:5432/class_room
username: class_room_user
password: gwjeYYLoCFCKI6wcwHgk2MYDuo5SmrX0
# url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/classroom_api?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true
# username: postgres
# password: admin
driver-class-name: org.postgresql.DriverIf you are running a local PostgreSQL instance, you can comment out the first set of URL, username, and password lines and uncomment the second set, and update them with your local database credentials.
This section includes Hibernate configuration properties for JPA.
spring:
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true
properties:
hibernate:
format_sql: false
These properties control how Hibernate manages the database schema and SQL logs. The above configuration specifies that Hibernate should update the schema automatically (ddl-auto: update) and show SQL queries in the console (show-sql: true). You can adjust these settings according to your requirements.
This section configures logging levels for the application. In this example, the logging level for the package com.tawfeek.quizApi is set to DEBUG.
logging:
level:
com.tawfeek.quizApi: DEBUG
You can customize logging levels for different packages or classes based on your debugging needs.
Once you have configured the properties and set up the database, you can run the Spring Boot application from your IDE. The application will start, and you can access it through the specified endpoints and interact with it based on your project's functionality.
To run the Spring Boot application using Maven, follow these steps:
-
Open a terminal (command prompt) window or a terminal within your IDE.
-
Navigate to the root directory of the Spring Boot project, where the
pom.xmlfile is located. -
Build the project using Maven by executing the following command:
mvn clean package
This command will compile the Java code, run tests, and package the application into a JAR file.
-
Once the build is successful, you can run the Spring Boot application using the following command:
mvn spring-boot:run
Maven will start the embedded Tomcat server and deploy your application. You should see logs indicating that the application is running.
-
By default, the application will be accessible at
http://localhost:8080. Open your web browser and navigate to this URL to access the application. -
If you need to stop the running application, you can press
Ctrl + Cin the terminal where the application is running. This will terminate the Spring Boot application.
Note: Ensure that you have properly configured the properties, such as the database URL, username, and password, in the application.yml file before running the application. Also, make sure that your PostgreSQL database is running and accessible before starting the Spring Boot application.
Now, you can interact with your Spring Boot application through the specified endpoints and test its functionality.
To dockerize the Spring Boot project using the provided Dockerfile, follow these steps:
-
Make sure you have Docker installed on your machine.
-
Save the provided Dockerfile in the root directory of your Spring Boot project, alongside the
pom.xmlfile. -
Open a terminal (command prompt) window or a terminal within your IDE.
-
Navigate to the root directory of your Spring Boot project, where the Dockerfile is located.
-
Build the Docker image using the following command:
docker build -t quiz-api:latest .This command tells Docker to build an image with the tag
quiz-api:latestusing the current directory (.) as the build context. -
Once the Docker build is successful, you can run the Docker container based on the built image using the following command:
docker run -p 8080:8080 quiz-api:latest
This command runs a Docker container based on the
quiz-api:latestimage and maps port 8080 from the container to port 8080 on the host machine, allowing you to access the Spring Boot application athttp://localhost:8080. -
The Spring Boot application is now running inside the Docker container.
Explanation of Dockerfile:
- The Dockerfile uses multi-stage builds to keep the final image lightweight and efficient.
- The first stage (
build) uses a Maven-based image to build the Java application. It copies the source code andpom.xml, then runs Maven to package the application as a JAR file. - The second stage (
package) uses the OpenJDK image to create a runtime image for the application. It copies the JAR file built in the first stage and sets it as the entry point to run the Spring Boot application. - The
EXPOSE 8080instruction exposes port 8080 inside the container. - The
ENTRYPOINTinstruction sets the command that will be executed when the container starts. In this case, it runs the Spring Boot application using thejava -jarcommand with the specified JAR file.
After following these steps, your Spring Boot application should be successfully dockerized and running inside a Docker container.
Watch the Demo Quiz Classroom app
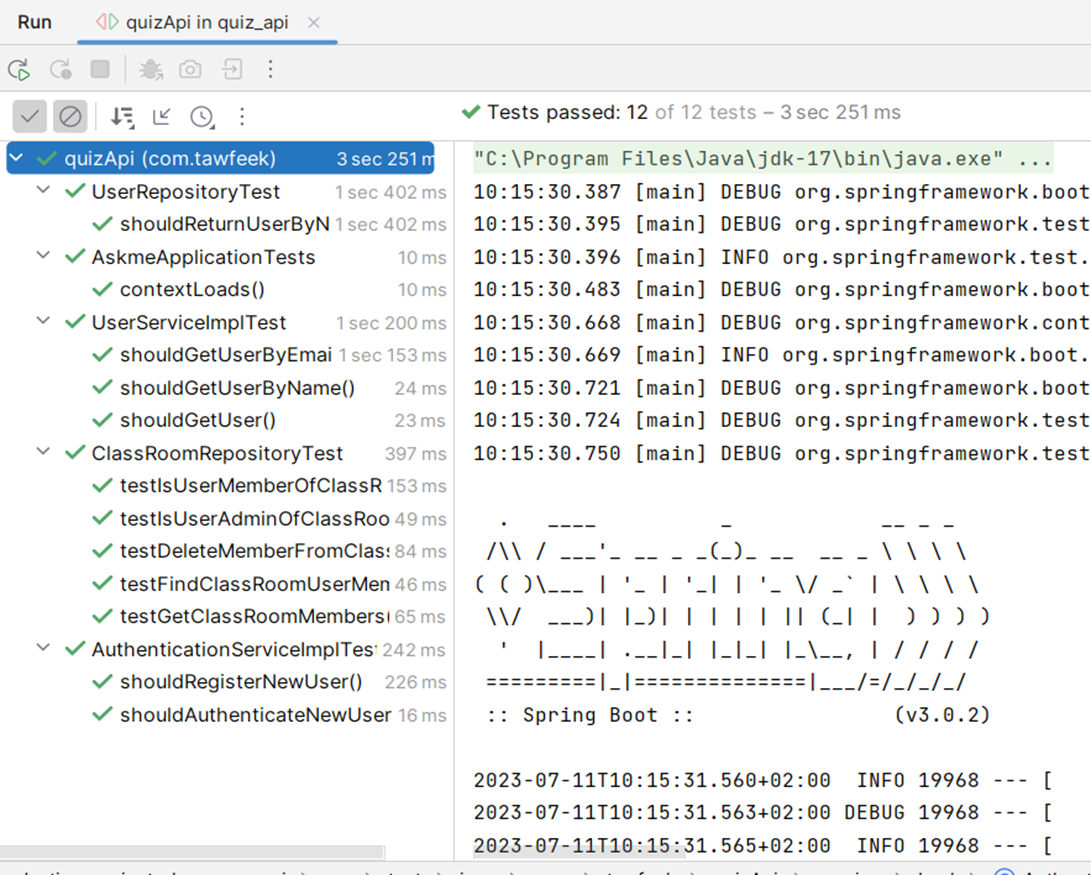
We also use unit tests using Junit5 and AssertJ and mocking using Mockito for Spring API unit testing.
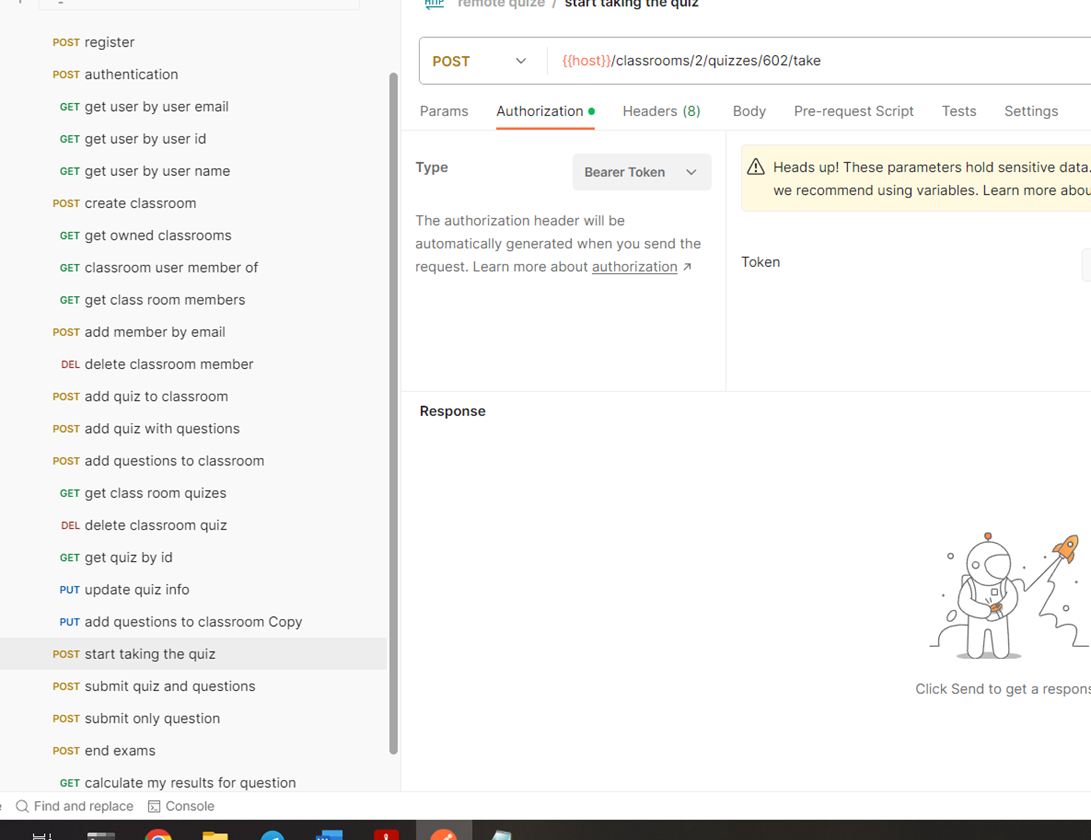
We use postman for testing the REST API endpoints. Postman is an API platform for building and using APIs. Postman simplifies each step of the API lifecycle and streamlines collaboration so you can create better APIs—faster. Collection URL to test: https://www.postman.com/cloudy-equinox-313118/workspace/githubpublic/collection/17623503-78bafc83-7901-4698-bd41-0c3389636035?action=share&creator=17623503