The aim of this project is to understand Mathematics by realizing abstract concepts as codes. Mathematical axioms correspond to protocols, and objects satisfying some axioms correspond to structs.
With Xcode installed, you can run SwiftyMath on the Swift-REPL by:
$ swift build
$ swift -I .build/debug/ -L .build/debug/ -ldSwiftyMath
Try something like:
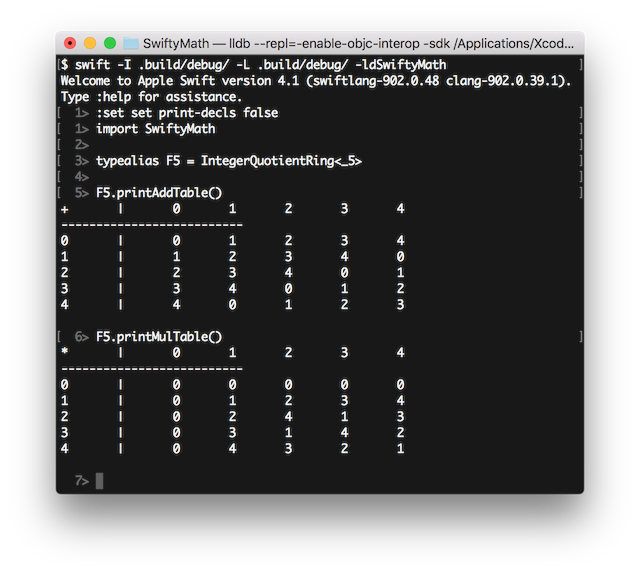
:set set print-decls false // suppress print-decl
import SwiftyMath
typealias F5 = IntegerQuotientRing<_5>
F5.printAddTable()
F5.printMulTable()$ mkdir YourProject
$ cd YourProject
$ swift package init --type executable
// swift-tools-version:4.0
// The swift-tools-version declares the minimum version of Swift required to build this package.
import PackageDescription
let package = Package(
name: "YourProject",
dependencies: [
// Dependencies declare other packages that this package depends on.
- // .package(url: /* package url */, from: "1.0.0"),
+ .package(url: "https://github.com/taketo1024/SwiftyMath.git", from: "0.1.0"),
],
targets: [
// Targets are the basic building blocks of a package. A target can define a module or a test suite.
// Targets can depend on other targets in this package, and on products in packages which this package depends on.
.target(
name: "YourProject",
- dependencies: []),
+ dependencies: ["SwiftyMath", "SwiftyTopology"]),
]
)import SwiftyMath
let a = 𝐐(4, 5) // 4/5
let b = 𝐐(3, 2) // 3/2
print(a + b) // 23/10$ swift run
23/10
We make use of mathematical symbols such as sets 𝐙, 𝐐, 𝐑, 𝐂 and operators ⊕, ⊗ etc. Copy the folder CodeSnippets to ~/Library/Developer/Xcode/UserData/ then you can quickly input these symbols by the completion of Xcode.
let a = 𝐐(4, 5) // 4/5
let b = 𝐐(3, 2) // 3/2
a + b // 23/10
a * b // 6/5
b / a // 15/8typealias M = Matrix<_2, _2, 𝐙> // Matrix of integers with fixed size 2×2.
let a = M(1, 2, 3, 4) // [1, 2; 3, 4]
let b = M(2, 1, 1, 2) // [2, 1; 1, 2]
a + b // [3, 3; 4, 6]
a * b // [4, 5; 10, 11]
a + b == b + a // true: addition is commutative
a * b == b * a // false: multiplication is noncommutativetypealias S_5 = Permutation<_5>
let s = S_5(cyclic: 0, 1, 2) // cyclic notation
let t = S_5([0: 2, 1: 3, 2: 4, 3: 0, 4: 1]) // two-line notation
s[1] // 2
t[2] // 4
(s * t)[3] // 3 -> 0 -> 1
(t * s)[3] // 3 -> 3 -> 0typealias P = Polynomial<𝐐>
let f = P(0, 2, -3, 1) // x^3 − 3x^2 + 2x
let g = P(6, -5, 1) // x^2 − 5x + 6
f + g // x^3 - 2x^2 - 3x + 6
f * g // x^5 - 8x^4 + 23x^3 - 28x^2 + 12x
f % g // 6x - 12
gcd(f, g) // 6x - 12typealias Z_4 = IntegerQuotientRing<_4>
Z_4.printAddTable()+ | 0 1 2 3
----------------------
0 | 0 1 2 3
1 | 1 2 3 0
2 | 2 3 0 1
3 | 3 0 1 2
typealias F_5 = IntegerQuotientField<_5>
F_5.printMulTable()* | 0 1 2 3 4
--------------------------
0 | 0 0 0 0 0
1 | 0 1 2 3 4
2 | 0 2 4 1 3
3 | 0 3 1 4 2
4 | 0 4 3 2 1
// Construct an algebraic extension over 𝐐:
// K = 𝐐(√2) = 𝐐[x]/(x^2 - 2).
struct p: _Polynomial { // p = x^2 - 2, as a struct
typealias K = 𝐐
static let value = Polynomial<𝐐>(-2, 0, 1)
}
typealias I = PolynomialIdeal<p> // I = (x^2 - 2)
typealias K = QuotientField<Polynomial<𝐐>, I> // K = 𝐐[x]/I
let a = Polynomial<𝐐>(0, 1).asQuotient(in: K.self) // a = x mod I
a * a == 2 // true!import SwiftyMath
import SwiftyTopology
let S2 = SimplicialComplex.sphere(dim: 2)
let H = Homology(S2, 𝐙.self)
print("H(S^2; 𝐙) =", H.detailDescription, "\n")H(S^2; 𝐙) = {
0 : 𝐙, [(v1)],
1 : 0, [],
2 : 𝐙, [-1(v0, v2, v3) + -1(v0, v1, v2) + (v1, v2, v3) + (v0, v1, v3)]
}
let RP2 = SimplicialComplex.realProjectiveSpace(dim: 2)
let H = Homology(RP2, 𝐙₂.self)
print("H(RP^2; 𝐙₂) =", H.detailDescription, "\n")H(RP^2; 𝐙₂) = {
0 : 𝐙₂, [(v1)],
1 : 𝐙₂, [(v0, v1) + (v1, v2) + (v0, v3) + (v2, v3)],
2 : 𝐙₂, [(v0, v2, v3) + (v3, v4, v5) + (v2, v3, v5) + (v1, v2, v5) + (v0, v4, v5) + (v1, v3, v4) + (v0, v1, v5) + (v1, v2, v4) + (v0, v2, v4) + (v0, v1, v3)]
}
Swifty Math is licensed under CC0 1.0 Universal.