- 探索-如何将单个vue文件转换为小程序所需的四个文件(wxml, wxss, json, js)
探索-如何将单个vue文件转换为小程序所需的四个文件(wxml, wxss, json, js)
最近在做需求的时候,经常是,同一个需求是在h5端实现一次,再在小程序实现一次,公司的h5端是用vue写的,微信小程序则是小程序的原生语言,这就导致了很多很重复的劳动,虽然语言不同,但逻辑和设计都是一模一样的。
而公司也没想过花点时间统一一下,比如考虑使用一下mpvue之类的,所以,在本着偷懒的心态下,开始想着如何能避免重复性的工作,比如只需要写一套代码。但是跟mpvue不一样,不需要一个DSL工程化的东西,只需要转换一下自己想转换的文件。
于是就有了这个想法,把所需要单个vue文件的转换为小程序原生语言所需要的四个文件(wxml, wxss, json, js)
预备知识
AST
在开始之前,需要了解一点AST(抽象语法树)的相关知识。
比如JavaScript在执行之前,会经过词法分析和语法分析两个步骤之后,得到一个抽象语法树。
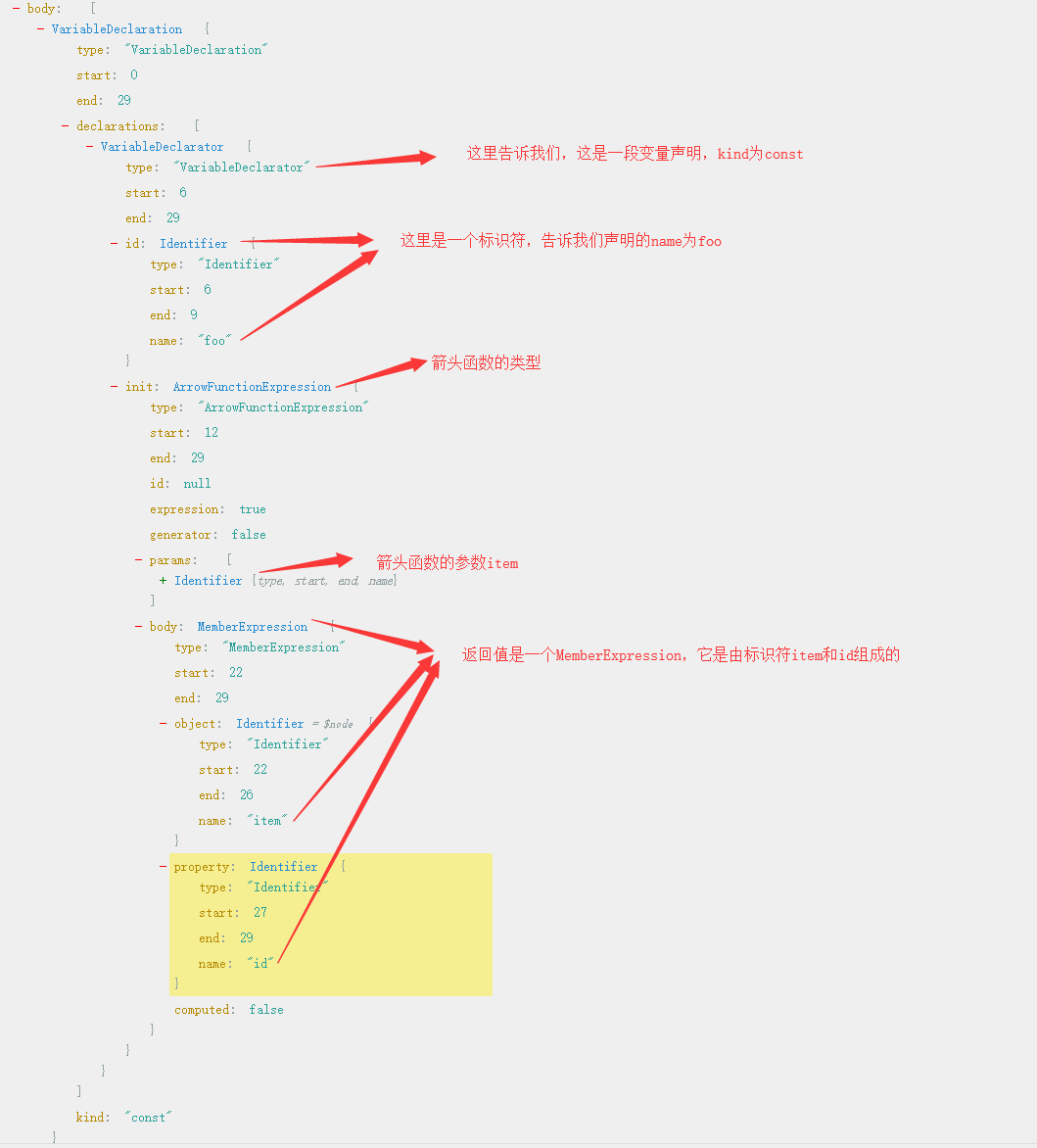
比如下面这段代码
const foo = (item) => item.id得到的抽象语法树如下图。 这是在AST Explorer转换得到的。
可以看到我们的js代码已经被转换成一个json对象,这个json对象的描述了这段代码。 我们可以通过拿到这个json对象去进行树形遍历,从而把这一段js代码进行加工成一段我们想要的代码。比如可以把它转换成一段ES5的代码。
这里就不描述具体步骤了,在后面的将script -> js中有具体描述。
这是js的部分。而在vue中,也是将template中的代码转换成了AST结构的json文件。后面我们需要使用到的postcss也是把less或者css文件转换成一个AST结构的json文件,然后再加工,输出成所需要的文件。
vue-template-compiler
另外还有一个需要了解的是vue-template-compiler。 我们写的单个vue文件叫做SFC(Single File Components)。 vue-template-compiler 就是解析SFC文件,提取每个语言块,将单个VUE文件的template、script、styles分别解析,得到一个json文件。
具体步骤如下。
const fs = require('fs');
const compiler = require('vue-template-compiler')
// 读取vue文件
const vueFileContent = fs.readFileSync('./target/target.vue', 'utf8');
const sfc = compiler.parseComponent(vueFileContent)得到的sfc的json文件的结构如下:
可以看到单个的vue文件已经被解析成了三个部分,styles是一个数组,因为在vue文件中可以写多个style标签。 我们拿到解析后的json文件之后,就可以正式开始了。
style -> wxss文件
首先从最简单的开始。将styles部分转换成wxss文件。
因为在vue中我们使用的是less的语法,所以解析出来的styles中content的代码是less语法。但是小程序需要的是css的语法。所以我们需要将less转换成css。另外在h5端我们less的单位是rem,所以还需要将rem转换成rpx。
将less换成css,将rem转换成rpx的方案有很多,这里采用的是postcss。另外还有gulp的方案也可以试试。
postcss已经有插件可以将less转换成css,rem转换成rpx。所以我们直接用postcss以及postcss的插件(postcss-less-engine, postcss-clean, postcss-rem2rpx)。
具体步骤如下:
const compiler = require('vue-template-compiler')
const postcss = require('postcss');
const less = require('postcss-less-engine');
const clean = require('postcss-clean');
const rem2rpx = require('postcss-rem2rpx');
// 读取vue文件
const vueFileContent = fs.readFileSync('./target/target.vue', 'utf8');
const sfc = compiler.parseComponent(vueFileContent)
// 将styles数组中的content合并成一个字符串
const stylesSting = sfc.styles.reduce((pre, cur) => {
return pre + cur.content.trim() + '\n'
}, '')
postcss([
less({ strictMath: true }),
rem2rpx({ rootFontSize: 50 }),
clean()
])
.process(stylesSting, { parser: less.parser, from: 'res-styles-ast.less' })
.then((result) =>{
fs.writeFileSync('./dist/res-style.wxss', result.css);
}, (err) =>{
console.log(err);
});这里有几个需要注意的点。
1.由于styles是一个数组,postcss需要处理的是一个字符串,所以我们需要事先使用reduce把styles数组中的content合并成一个字符串。
2.在rem2rpx中,需要设置一个rootFontSize,这就需要根据自己的项目情况来。
3.如果style中有@import "./assets/styles/mixin.less";这样的import代码,则需要把这个文件copy到本地来。
4.这里安装的less包版本为"less": "2.7.1",版本3以上好像postcss-less-engine好像会失效。
script -> js文件
babel
在进行这个步骤之前,先得讲一个很重要的工具,就是 Babel
在将vue中的script部分转换成小程序需要的js文件过程中,最重要的就是Babel。
比如需要把created方法转换为小程序的 onLoad 或者 组件中的 attached方法, 我们需要使用Babel把script部分的代码解析成一个AST抽象语法树,再用Babel的api去转换和修改这颗抽象语法树,最后再生成所需要的代码。
bable在这里就像一把带有魔法的手术刀, 可以把现有代码转换成任意代码。这一点有点lisp的感觉。
总结一下 Babel 的三个主要步骤是:
1.解析(parse)
利用 babylon 对源代码字符串进行解析并生成初始 AST 抽象语法树
2.转换(transform)
遍历初始的 AST 抽象语法树,babel 中有个babel-core ,它向外暴露出 babel.transform 接口。
3.生成(generate)
生成部分 babel 会利用 babel-generator 将转换后的 AST 树转换为新的代码字符串。
以上是理论,下面我们来实践一下。还是那上面AST的箭头函数来练手,将它变成一个ES5语法的函数。
const babel = require('babel-core')
const types = require('babel-types'); // types就是用来构造一个新的node节点的
const visitor = {
ArrowFunctionExpression(path) { // 在visitor中拦截箭头函数
let params = path.node.params // 获取函数参数
const returnStatement = types.returnStatement(path.node.body) //构建一个return表达式
const blockStatement = types.blockStatement([returnStatement]) // 构建一个blockStatement
// babel-types的functionExpression构造成一个新的ES function语法的函数
let func = types.functionExpression(null, params, blockStatement, false, false)
//替换当前箭头函数节点
path.replaceWith(func)
},
VariableDeclaration(path) { // 在visitor中变量声明
path.node.kind = 'var'
}
}
const scriptContent = 'const foo = (item) => item.id' // 源代码
const result = babel.transform(scriptContent, {
plugins: [
{ visitor }
]
})
console.log(result.code.trim())
// 结果为:
// var foo = function (item) {
// return item.id;
// };以上只是简单地讲解了下babel运行原理,然后举了一个简单的例子,整个过程基本是这样的,复杂的部分主要是对每一个需要拦截的节点进行处理。
如果想多了解一点可以参考一下这里
处理import导入文件
现在可以正式开始了。
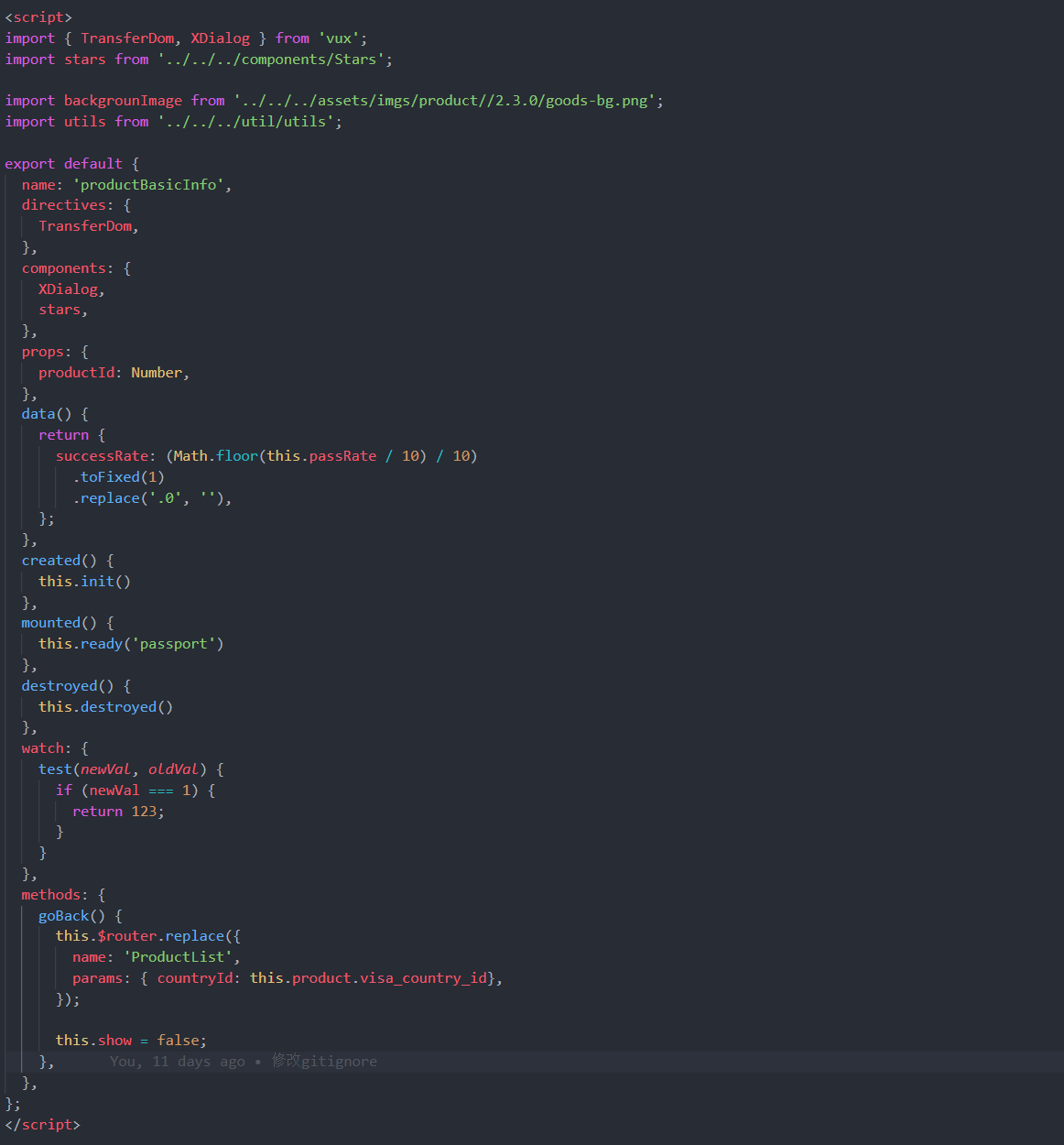
可以看到在 export default 中有 directives 和 components 两个属性与import导入的文件有关
小程序中,directives不需要,需要删除这个节点,同时也要删除import进来的这个文件;components也不需要,但是components 中的文件需要放到小程序的json文件中的usingComponents中。
所以下面先处理import部分:
// ......
const compiler = require('vue-template-compiler')
const babelrc = path.resolve('./.babelrc') //拿到本地的 babelrc 的配置
const vueFileContent = fs.readFileSync('./target/target.vue', 'utf8');
const sfc = compiler.parseComponent(vueFileContent)
const scriptContent = sfc.script.content // 拿到解析后的sfc中的script部分的源代码
const babelOptions = { extends: babelrc, plugins: [{visitor: parseImportVisitor}] } // 配置一个 parseImportVisitor
const result = babel.transform(scriptContent, babelOptions)
fs.writeFileSync('./dist/res-js.js', result.code.trim());下面是在parseImportVisitor中拦截ImportSpecifier,ImportDefaultSpecifier具体处理,ImportDefaultSpecifier是从node_modules中导入的文件,ImportSpecifier是从自己写的文件。 要对两个type进行相同的处理可以用一个管道符号 | ,像这样ImportSpecifier|ImportDefaultSpecifier
const parseImportVisitor = {
"ImportSpecifier|ImportDefaultSpecifier"(path) {
const currentName = path.node.local.name // 获取import进来的名称,比如上图中script的基本结构的 TransferDom, XDialog, stars
const parentPath = path.findParent((path) => path.isImportDeclaration()); //找到当前节点的 ImportDeclaration 类型父节点
const [ ExportDefaultDeclaration ] = parentPath.container.filter(item => item.type === 'ExportDefaultDeclaration') //通过父节点去找到 ExportDefaultDeclaration 类型的节点,就是export default中代码
const { properties } = ExportDefaultDeclaration.declaration // 获取 export default 中所有属性
const [ directivesProperty ] = properties.filter(item => item.key.name === 'directives')
if (directivesProperty) {
const { properties } = directivesProperty.value // directives中的属性值
// 遍历 directives 中的属性值
properties.forEach(p => {
const value = p.value.name || p.value.value
if (value === currentName) {
// 如果在 directives中找到了和当前import进来的名字一样的,就需要把当前的节点删除
// 比如 import { TransferDom, XDialog } from 'vux'; 删除后会变成 import { XDialog } from 'vux';
path.remove()
if (!parentPath.node.specifiers.length) { //如果父节点为空,需要把父节点也完全删除
path.parentPath.remove()
}
}
})
}
// 上面对 directives 的处理是直接删除
// 下面对 components 的处理则需要保存起来,主要是保存在 path.hub.file 中的 metadata 中
const { metadata } = path.hub.file
const [ componentsProperty ] = properties.filter(item => item.key.name === 'components')
const usingComponents = {...metadata.usingComponents} //创建一个 usingComponents 对象
if (componentsProperty) {
const { properties } = componentsProperty.value // 获取 components 中的属性值
// 遍历 components 中的属性值
properties.forEach(p => {
const value = p.value.name || p.value.value
if (value === currentName) {
// 如果在 components 中找到了和当前import进来的名字一样的,就需要把当前的节点放入 usingComponents 中,然后删除
usingComponents[value] = parentPath.node.source.value
path.remove()
if (!parentPath.node.specifiers.length) { //如果父节点为空,需要把父节点也完全删除
path.parentPath.remove()
}
}
})
}
metadata.usingComponents = usingComponents
},
}上面的代码将 components 中的组件放到了 path.hub.file.metadata中,这样可便于在最后拿到结果的时候把 usingComponents 直接写到 json 文件中。
// 生成json文件
// ......
const result = babel.transform(scriptContent, babelOptions)
const jsonFile = {
component: result.metadata.isComponent ? true : undefined,
usingComponents: result.metadata.usingComponents // 取出 metadata中的usingComponents
}
fs.writeFileSync('./dist/res-json.json', circularJSON.stringify(jsonFile, null, 2)); // 写到 json 文件中处理ExportDefaultDeclaration
接下来处理 export default 中的代码。所以需要加一个 visitor
const scriptContent = sfc.script.content
const babelOptions = { extends: babelrc, plugins: [{visitor: parseImportVisitor}, { visitor: parseExportDefaultVisitor }] } // 这里添加了 一个 parseExportDefaultVisitor的方法
const result = babel.transform(scriptContent, babelOptions)
fs.writeFileSync('./dist/res-js.js', result.code.trim());下面是 parseExportDefaultVisitor
const parseExportDefaultVisitor = {
ExportDefaultDeclaration: function (path) { // 这里拦截 ExportDefaultDeclaration
// 这里只处理 ExportDefaultDeclaration, 就是把export default 替换成 Page 或者 Component
// 其它都交给 traverseJsVisitor 处理
path.traverse(traverseJsVisitor)
// 把export default 替换成 Page 或者 Component
const { metadata } = path.hub.file
const { declaration } = path.node
const newArguments = [declaration]
const name = metadata.isComponent ? 'Component' : 'Page'
const newCallee = types.identifier(name)
const newCallExpression = types.CallExpression(newCallee, newArguments)
path.replaceWith(newCallExpression)
}
}这里需要注意的点是, export default 如何替换成 Page 或者 Component ,在 traverseJsVisitor 会判断当前文件是否是一个组件, 然后把isComponent保存到metadata中,在ExportDefaultDeclaration就可以取到 isComponent 的值,从而决定是生成 Page还是Component。
而在小程序 Page({}) 或者Component({}) 是一个CallExpression, 所以需要构造一个CallExpression 来替换掉ExportDefaultDeclaration
处理props, created, mounted, destroyed
在traverseJsVisitor来处理props, created, mounted, destroyed
props => properties
created => attached || onLoad
mounted => ready || onReady
destroyed => detached || onUnload
这里只是做了一下简单映射,如果onShow或者active等其它生命周期或者其它属性需要映射的话,以后慢慢改进。
// ......
const traverseJsVisitor = {
Identifier(path) {
const { metadata } = path.hub.file
// 替换 props
if (path.node.name === 'props') {
metadata.isComponent = true //在这里判断当前文件是否是一个组件
const name = types.identifier('properties') //创建一个标识符
path.replaceWith(name) // 替换掉当前节点
}
if (path && path.node.name === 'created'){
let name
if (metadata.isComponent) { //判断是否是组件
name = types.identifier('attached') //创建一个标识符
} else {
name = types.identifier('onLoad') //创建一个标识符
}
path.replaceWith(name) // 替换掉当前节点
}
if (path && path.node.name === 'mounted'){
let name
if (metadata.isComponent) { //判断是否是组件
name = types.identifier('ready') //创建一个标识符
} else {
name = types.identifier('onReady') //创建一个标识符
}
path.replaceWith(name) // 替换掉当前节点
}
if (path && path.node.name === 'destroyed'){
let name
if (metadata.isComponent) { //判断是否是组件
name = types.identifier('detached') //创建一个标识符
} else {
name = types.identifier('onUnload') //创建一个标识符
}
path.replaceWith(name) // 替换掉当前节点
}
},
}处理 methods
往 traverseJsVisitor 中 再加入一个 ObjectProperty的拦截器,因为小程序中,组件文件的方法都是写在 methods 属性中, 而在非组件文件中 方法是直接和生命周期一个层级的,所以需要对 methods 进行处理
// ......
const traverseJsVisitor = {
ObjectProperty: function (path) {
const { metadata } = path.hub.file
//是否是组件,如果是则不动, 如果不是,则用 methods 中的多个方法一起来替换掉当前的 methods节点
if (path && path.node && path.node.key.name === 'methods' && !metadata.isComponent) {
path.replaceWithMultiple(path.node.value.properties );
return;
}
// 删除 name directives components
if (path.node.key.name === 'name' || path.node.key.name === 'directives' || path.node.key.name === 'components') {
path.remove();
return;
}
},
}将this.xxx 转换成 this.data.xxx, 将 this.xx = xx 转换成 this.setData
这里其实是留了坑的,因为如果有多个this.xx = xx ,我这里并没有将他们合并到一个this.setData中,留点坑,以后填...
// ......
const traverseJsVisitor = {
// 将this.xxx 转换成 this.data.xxx
MemberExpression(path) { // 拦截 MemberExpression
const { object, property} = path.node
if (object.type === 'ThisExpression' && property.name !== 'data') {
const container = path.container
if (container.type === 'CallExpression') {
return;
}
if (property.name === '$router') {
return;
}
// 将 this.xx 转换成 this.data.xx
const dataProperty = types.identifier('data')
const newObject = types.memberExpression(object, dataProperty, false)
const newMember = types.memberExpression(newObject, property, false)
path.replaceWith(newMember)
}
},
// 将 this.xx == xx 转换成 this.setData
AssignmentExpression(path) { // 拦截 AssignmentExpression
const leftNode = path.node.left
const { object, property } = leftNode
if (leftNode.type === 'MemberExpression' && leftNode.object.type === 'ThisExpression') {
const properties = [types.objectProperty(property, path.node.right, false, false, null)]
const arguments = [types.objectExpression(properties)]
const object = types.thisExpression()
const setDataProperty = types.identifier('setData')
const callee = types.memberExpression(object, setDataProperty, false)
const newCallExpression = types.CallExpression(callee, arguments)
path.replaceWith(newCallExpression)
}
},
}处理 props中的default;把 data 函数转换为 data 属性;处理watch
// ......
const traverseJsVisitor = {
ObjectMethod: function(path) {
// 替换 props 中 的defalut
if (path && path.node && path.node.key.name === 'default') {
const parentPath = path.findParent((path) => path.isObjectProperty());
const propsNode = parentPath.findParent((findParent) => findParent.isObjectExpression()).container
if (propsNode.key.name === 'properties') {
const key = types.identifier('value')
const value = path.node.body.body[0].argument
const newNode = types.objectProperty(key, value, false, false, null)
path.replaceWith(newNode)
}
}
if (path && path.node.key.name === 'data') {
const key = types.identifier('data')
const value = path.node.body.body[0].argument
const newNode = types.objectProperty(key, value, false, false, null)
path.replaceWith(newNode)
}
if (path && path.node && path.node.key.name === 'created') {
const watchIndex = path.container.findIndex(item => item.key.name === 'watch')
const watchItemPath = path.getSibling(watchIndex)
if (watchItemPath) {
const { value } = watchItemPath.node
const arguments = [types.thisExpression(), value]
const callee = types.identifier('Watch')
const newCallExpression = types.CallExpression(callee, arguments)
path.get('body').pushContainer('body', newCallExpression);
watchItemPath.remove()
}
return;
}
},
}这里有一点需要注意的是watch的处理,因为小程序没有watch,所以我在小程序手写了一个简单watch
而且小程序中的watch需要放在onLoad 或者attached 生命周期中。
// 以下两个函数实现watch 未实现deep功能
const Watch = (ctx, obj) => {
Object.keys(obj).forEach((key) => {
defineProperty(ctx.data, key, ctx.data[key], (value) => {
obj[key].call(ctx, value);
});
});
};
const defineProperty = (data, key, val, fn) => {
Object.defineProperty(data, key, {
configurable: true,
enumerable: true,
get() {
return val;
},
set(newVal) {
if (newVal === val) return;
if (fn) fn(newVal);
val = newVal;
},
});
};所以只需要将vue中的watch转换为这样子的形式的写法就行了。比如:
watch: {
test(newVal, oldVal) {
if (newVal === 1) {
return 123;
}
}
},需要转换成
Watch(this, {
test(newVal, oldVal) {
if (newVal === 1) {
return 123;
}
}
})处理路由跳转
处理路由跳转有点复杂,需要将this.$router.push 或者 this.$router.replace 转换为 wx.navigateTo 或者 wx.redirectTo
把 this.$router 的 params 参数和 query 参数合并到一起
并合成一个字符串url,比如:
this.$router.push({
name: 'ProductList',
params: { countryId: this.product.visa_country_id},
});需要转换成
wx.navigateTo({
url: `ProductList?countryId=${this.data.product.visa_country_id}`
});下面是具体转换过程:
const traverseJsVisitor = {
CallExpression(path) {
// 处理 router 路由跳转
const { arguments, callee } = path.node
const { object, property } = callee
if (object && object.type === 'MemberExpression' && object.property.name === '$router') { //拦截到$router
const properties = arguments[0].properties
// vue里面这里只能获取到 路由名称,但是小程序需要的是page页面的路径,这里就没有做转换了,直接拿了路由名称充当小程序跳转的url,到时候手动改
const [ nameInfo ] = properties.filter(item => item.key.name === 'name')
const [ paramsInfo ] = properties.filter(item => item.key.name === 'params') //拿到router的params参数
const [ queryInfo ] = properties.filter(item => item.key.name === 'query') //拿到router的query参数
// 把params和query的参数都合并到一个数组当中去,然后 map 出 key 和 value
const paramsValue = paramsInfo && paramsInfo.value
const queryValue = queryInfo && queryInfo.value
const paramsValueList = paramsValue && paramsValue.properties ? paramsValue.properties : []
const queryValueList = queryValue && queryValue.properties ? queryValue.properties : []
const paramsItems = [].concat(paramsValueList, queryValueList).map(item => ({ key: item.key, value: item.value }))
const url = types.identifier('url') // 创建一个 叫做 url 的标识符
const routeName = nameInfo.value.value // 跳转的路由名称
let expressions, quasis
if (paramsItems.some(item => types.isCallExpression(item.value) || types.isMemberExpression(item.value))) {
const expressionList = paramsItems.filter(item => types.isCallExpression(item.value) || types.isMemberExpression(item.value))
const literalList = paramsItems.filter(item => types.isLiteral(item.value))
// 把参数都合并成一个字符串
const templateElementLastItem = literalList.reduce((finalString, cur) => {
return `${finalString}&${cur.key.name}=${cur.value.value}`
}, '')
const templateElementItemList = expressionList.map((item, index) => {
if (index === 0) {
return `${routeName}?${item.key.name}=`
}
return `&${item.key.name}=`
})
expressions = expressionList.map(item => item.value)
quasis = [ ...templateElementItemList, templateElementLastItem ].map(item => {
return types.templateElement({ raw: item, cooked: item }, false)
})
}
const newTemplateLiteral = types.templateLiteral(quasis, expressions) //创建一个 templateLiteral
const objectProperty = types.objectProperty(url, newTemplateLiteral, false, false, null)
// 构造一个CallExpression
let newPoperty
if (property.name === 'replace') {
newPoperty = types.identifier('redirectTo')
}
if (property.name === 'push') {
newPoperty = types.identifier('navigateTo')
}
const newArguments = [types.objectExpression([objectProperty])]
const newObject = types.identifier('wx')
const newCallee = types.memberExpression(newObject, newPoperty, false)
const newCallExpression = types.CallExpression(newCallee, newArguments)
path.replaceWith(newCallExpression)
}
}
}转换结果
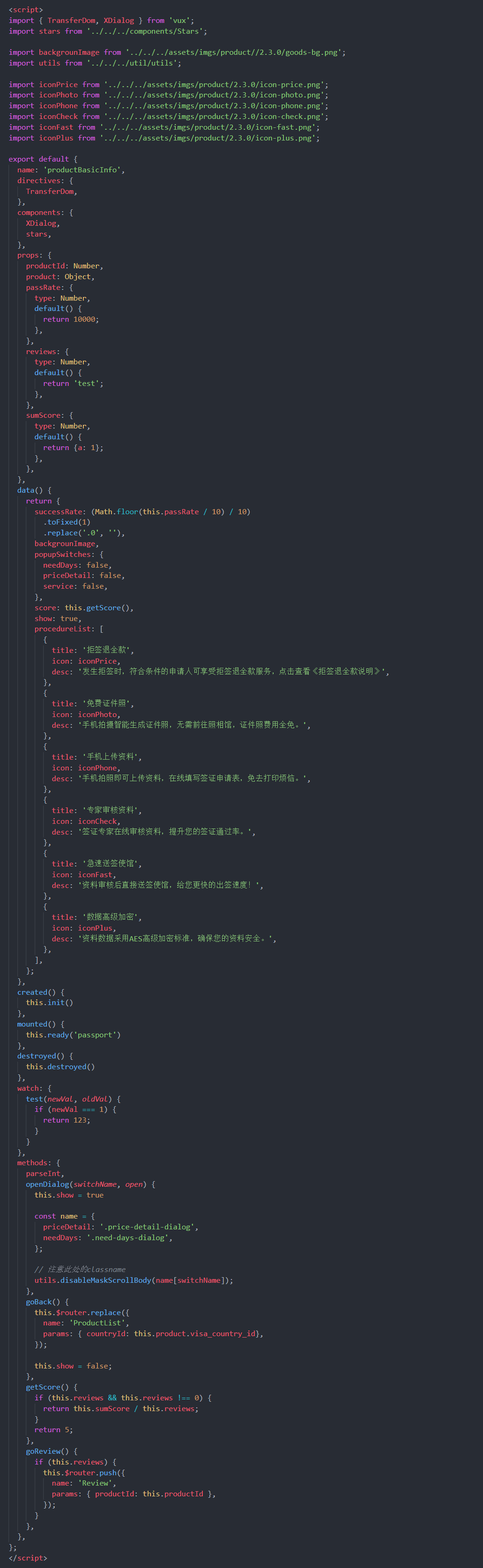
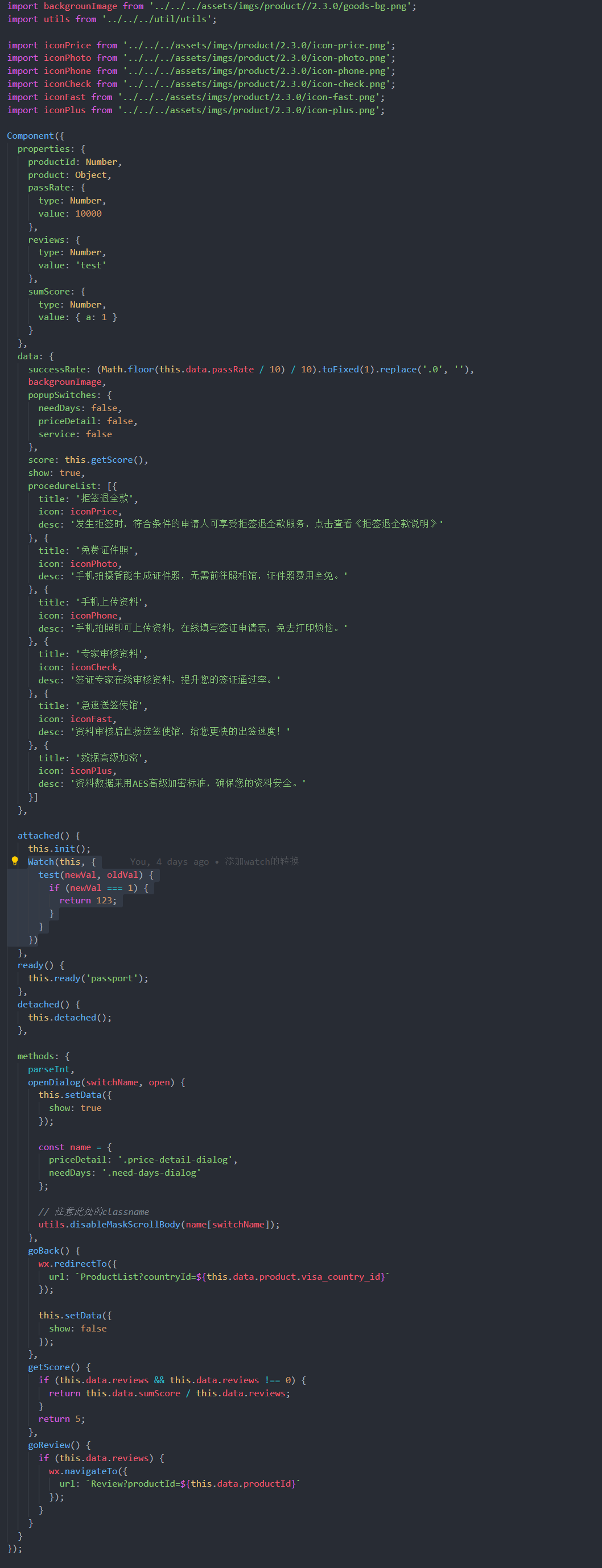
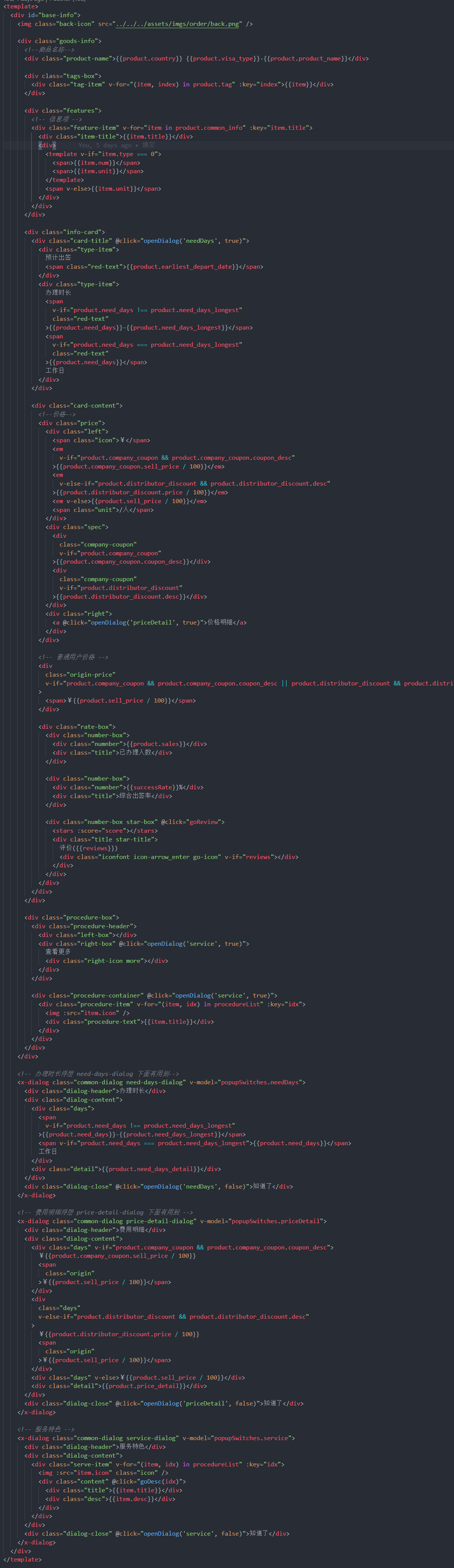
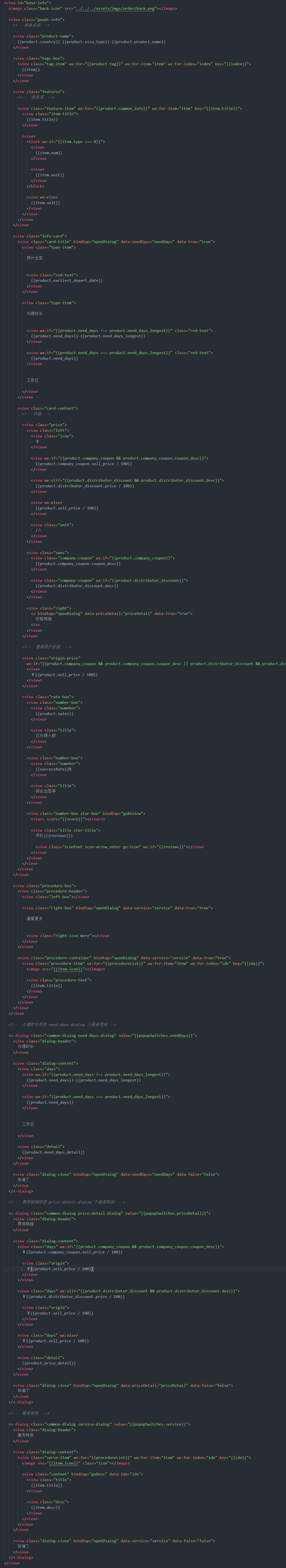
这里有一个例子。
template -> wxml文件
将 template 代码转换为 AST树
接下来是 将 template 部分 转换为 wxml 文件。这里要先用 vue-template-compiler 的 compiler 将 template 代码转换为 AST树。
然后再实现一个解析这个 AST树的函数 parseHtml
const compiler = require('vue-template-compiler')
// 读取vue文件
const vueFileContent = fs.readFileSync('./target/target.vue', 'utf8');
const sfc = compiler.parseComponent(vueFileContent)
const astTplRes = compiler.compile(sfc.template.content, {
comments: true,
preserveWhitespace: false,
shouldDecodeNewlines: true
}).ast
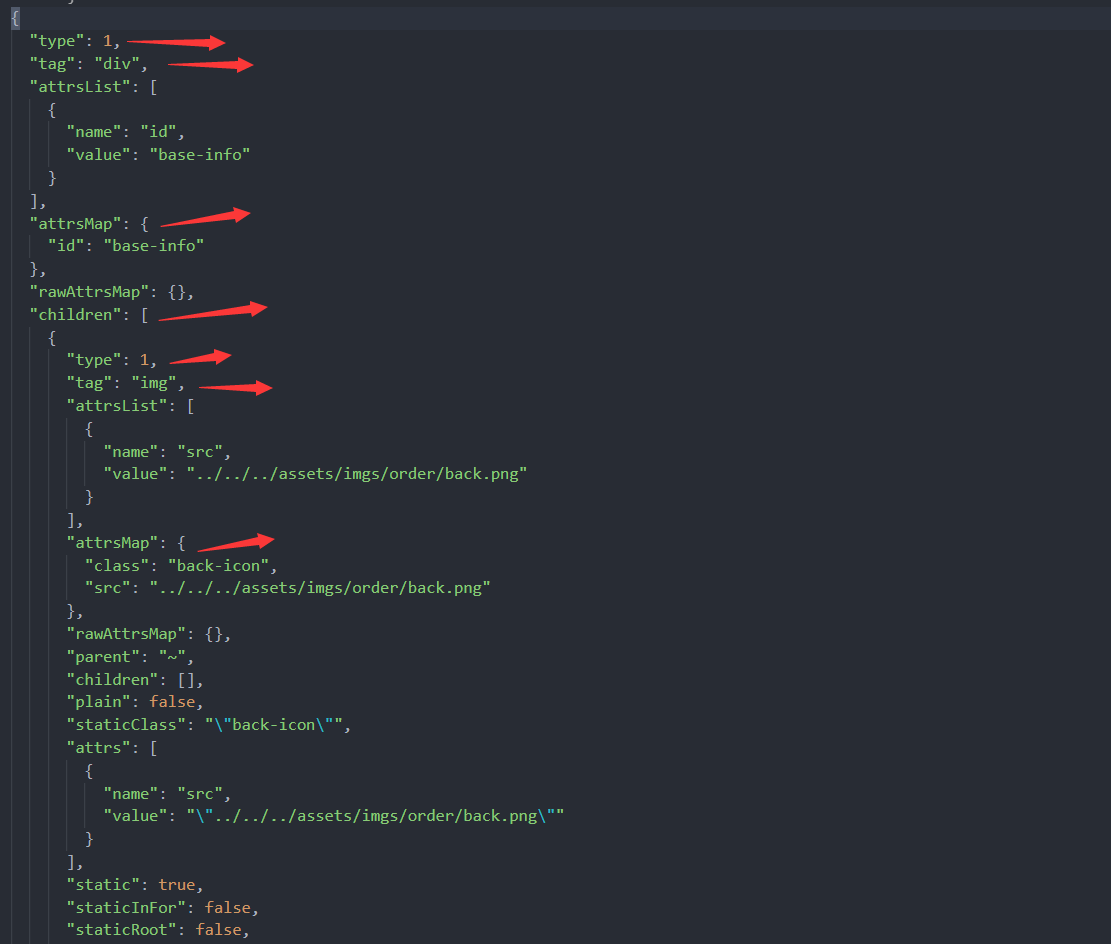
const wxmlResult = parseHtml(astTplRes)可以看出对我们有用的属性就几个
- tag: 标签
- type: 类型,1-标签;2-表达式节点(Mustache);3-纯文本节点和comment节点
- attrsMap: 标签上的属性集合
- children: 元素的子元素,需要递归遍历处理
还有一些特殊的属性
- classBinding、styleBinding: 动态绑定的class、style
- if、elseif、else: 条件语句中的条件
- ifConditions: 条件语句的else、elseif的节点信息都放在ifConditions的block里了
- isComment:是否是注释
给AST树的每个节点加上开始标签和结束标签
拿到这个结构之后要怎么转换呢。
我的思路是,因为这是一个树形结构,所以可以采用深度优先遍历,广度优先遍历或者递归遍历。
通过遍历给每一个节点加上一个开始标签 startTag,和一个 结束标签 endTag。这里采用递归遍历。
代码如下:
const parseHtml = function(tagsTree) {
return handleTagsTree(tagsTree)
}const handleTagsTree = function (topTreeNode) {
// 为每一个节点生成开始标签和结束标签
generateTag(topTreeNode)
};
// 递归生成 首尾标签
const generateTag = function (node) {
let children = node.children
// 如果是if表达式 需要做如下处理
if (children && children.length) {
let ifChildren
const ifChild = children.find(subNode => subNode.ifConditions && subNode.ifConditions.length)
if (ifChild) {
const ifChildIndex = children.findIndex(subNode => subNode.ifConditions && subNode.ifConditions.length)
ifChildren = ifChild.ifConditions.map(item => item.block)
delete ifChild.ifConditions
children.splice(ifChildIndex, 1, ...ifChildren)
}
children.forEach(function (subNode) {
generateTag(subNode)
})
}
node.startTag = generateStartTag(node) // 生成开始标签
node.endTag = generateEndTag(node) //生成结束标签
}下面是生成开始标签的代码:
const generateStartTag = function (node) {
let startTag
const { tag, attrsMap, type, isComment, text } = node
// 如果是注释
if (type === 3) {
startTag = isComment ? `<!-- ${text} -->` : text
return startTag;
}
// 如果是表达式节点
if (type === 2) {
startTag = text.trim()
return startTag;
}
switch (tag) {
case 'div':
case 'p':
case 'span':
case 'em':
startTag = handleTag({ tag: 'view', attrsMap });
break;
case 'img':
startTag = handleTag({ tag: 'image', attrsMap });
break;
case 'template':
startTag = handleTag({ tag: 'block', attrsMap });
break;
default:
startTag = handleTag({ tag, attrsMap });
}
return startTag
}
const handleTag = function ({
attrsMap,
tag
}) {
let stringExpression = ''
if (attrsMap) {
stringExpression = handleAttrsMap(attrsMap)
}
return `<${tag} ${stringExpression}>`
}
// 这个函数是处理 AttrsMap,把 AttrsMap 的所有值 合并成一个字符串
const handleAttrsMap = function(attrsMap) {
let stringExpression = ''
stringExpression = Object.entries(attrsMap).map(([key, value]) => {
// 替换 bind 的 :
if (key.charAt(0) === ':') {
return `${key.slice(1)}="{{${value}}}"`
}
// 统一做成 bindtap
if (key === '@click') {
const [ name, params ] = value.split('(')
let paramsList
let paramsString = ''
if (params) {
paramsList = params.slice(0, params.length - 1).replace(/\'|\"/g, '').split(',')
paramsString = paramsList.reduce((all, cur) => {
return `${all} data-${cur.trim()}="${cur.trim()}"`
}, '')
}
return `bindtap="${name}"${paramsString}`
}
if (key === 'v-model') {
return `value="{{${value}}}"`
}
if (key === 'v-if') {
return `wx:if="{{${value}}}"`
}
if (key === 'v-else-if') {
return `wx:elif="{{${value}}}"`
}
if (key === 'v-else') {
return `wx:else`
}
if (key === 'v-for') {
const [ params, list ] = value.split('in ')
const paramsList = params.replace(/\(|\)/g, '').split(',')
const [item, index] = paramsList
const indexString = index ? ` wx:for-index="${index.trim()}"` : ''
return `wx:for="{{${list.trim()}}}" wx:for-item="${item.trim()}"${indexString}`
}
return `${key}="${value}"`
}).join(' ')
return stringExpression
}结束标签很简单。 这里是生成结束标签的代码:
const generateEndTag = function (node) {
let endTag
const { tag, attrsMap, type, isComment, text } = node
// 如果是表达式节点或者注释
if (type === 3 || type === 2) {
endTag = ''
return endTag;
}
switch (tag) {
case 'div':
case 'p':
case 'span':
case 'em':
endTag = '</view>'
break;
case 'img':
endTag = '</image>'
break;
case 'template':
endTag = '</block>'
break;
default:
endTag = `</${tag}>`
}
return endTag
}将开始标签和结束标签合并
拿到开始标签和结束标签之后,接下来就是重组代码了。
const handleTagsTree = function (topTreeNode) {
// 为每一个节点生成开始标签和结束标签
generateTag(topTreeNode)
return createWxml(topTreeNode)
}; // 递归生成 所需要的文本
const createWxml = function(node) {
let templateString = '';
const { startTag, endTag, children } = node
let childrenString = ''
if (children && children.length) {
childrenString = children.reduce((allString, curentChild) => {
const curentChildString = createWxml(curentChild)
return `${allString}\n${curentChildString}\n`
}, '')
}
return `${startTag}${childrenString}${endTag}`
}转换结果
转换完的格式还是需要自己调整一下。
总结
留下的坑其实还蛮多,做这个也是想偷点懒,有什么可以一起交流。
完整代码在 ast-h5-wp