N.B.: The project has evolved since I first wrote the Readme. The original idea is described below.
This project demonstrates how one might build an application, comprised out of several modules. The modules are expanding in a tree like structure, from the main module (Composition), which is the only module that the Example app depends on.
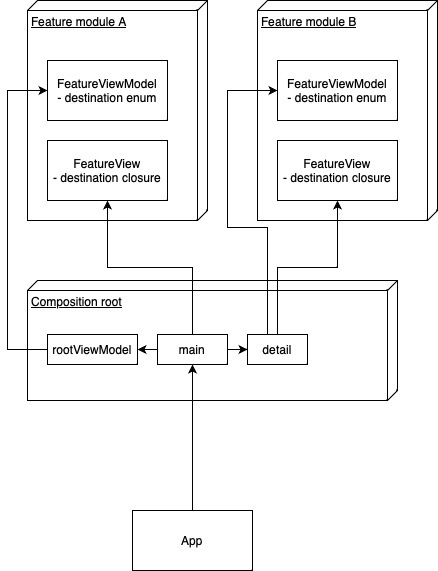
If we peak into the implementation of the Composition module, we can see how it depends on its leaf modules, FeatureA and FeatureB. These modules further depend on other modules, or their child features (in case of FeatureB).
Additionally, resources such as images and fonts are modelled in form of libraries as well, thereby available to any module that requires them.
Following the pattern of tree based structure, navigating between screens is modelled similarly. A feature's ViewModel can hold a destination property of enum type, explicitly defining the possible navigation destinations that particular View(Model) can reach.
If a featue requires to build a specific view hierarchy, it can construct ViewModels with populated destination properties and the Views will react accordingly, displaying the desired view to the user.
The goal of this case study is to model an application with many dependencies and modules, bringing them all together in the pattern known as Composition root.
This sample comprises of the main App project, bundled together with 3 submodules - Models, a shared package declaring the data types; FeatureA, one sample of a module and FeatureB, another module similar to FeatureA.
According to the dependency inversion principle, Features A and B delegate their dependencies upward to the implementor. In order to simplify this case study, the only dependencies exposed are the destination views from either feature.
The navigation is modelled in a tree-based fashion. Each feature has a ViewModel which holds the destination property, an enum type, thereby allowing only one destination being active at one time. This allows for a more natural modelling than having a boolean for each destination (which allows for non-sensical combinations).