Linear submodule count increase is generally accompanied by an exponential growth of headache: Keeping Git submodules up to date is monotonous and — more importantly — interruptive work. Managing your dependencies shouldn't keep you from being productive! Matryoshka can automate your submodule updates and enable you to run them without losing focus of your real task:
Disclaimer: Use at your own risk. I cannot be held responsible for data loss.
If you encounter any trouble though, please let me know
- Clone the repository
- Enter
matryoshkaand grant scripts permissions to be executed:
$ chmod +x *.sh- Assure your Git submodules are setup properly and these commands have been run at least once since adding your latest modules:
$ git submodule init
$ git submodule update- Optional: I prefer to have this script ready at all times without manually typing out its path. I suggest creating an
aliaswithin your.bashrc:
# Add this inside your shell's rc file:
alias MATRYOSHKA="path/to/matryoshka/matryoshka.sh"Depending on your setup you may have to restart / reload your shell afterwards.
To enable your colleagues to access the script right within your repository, add it as a submodule:
# Optional — Containing Subdirectory
$ mkdir tools
$ cd tools
# Check your staging area for uncommit changes, the following changes
# will be staged automatically:
$ git submodule add https://github.com/t89/matryoshka.git matryoshka
$ git submodule update --init
$ git commit -m "Add Matryoshka submodule"
-
Enter your repo directory and call the script
bash path/to/matryoshka.sh(or use the more convenientalias) -
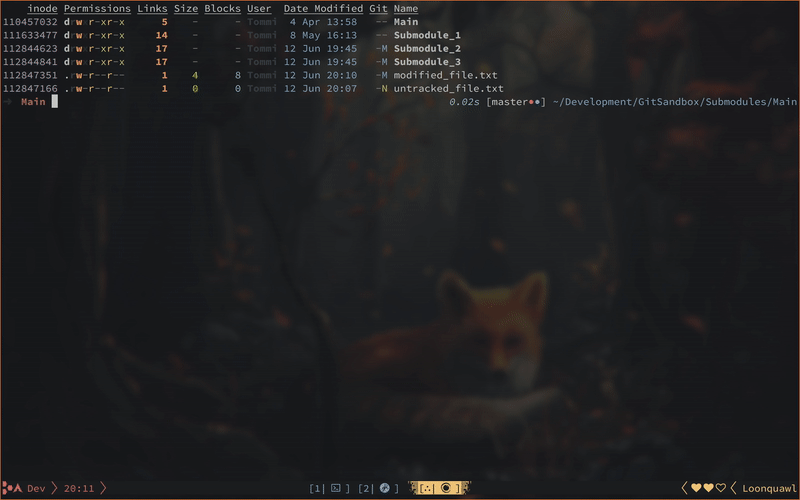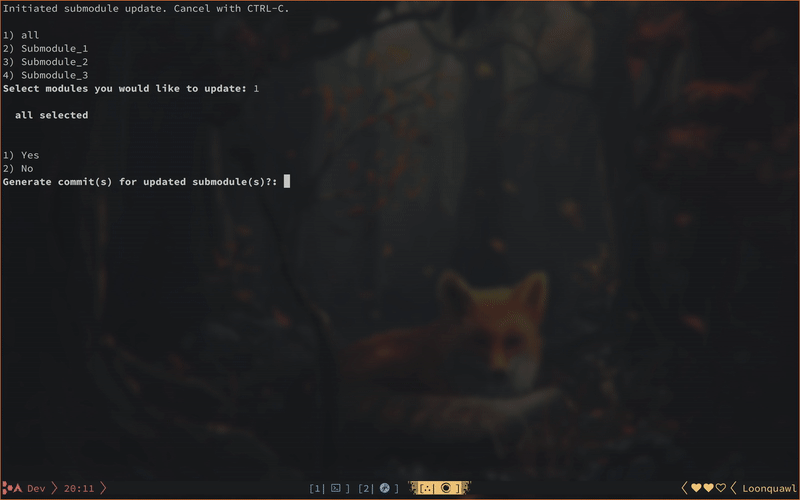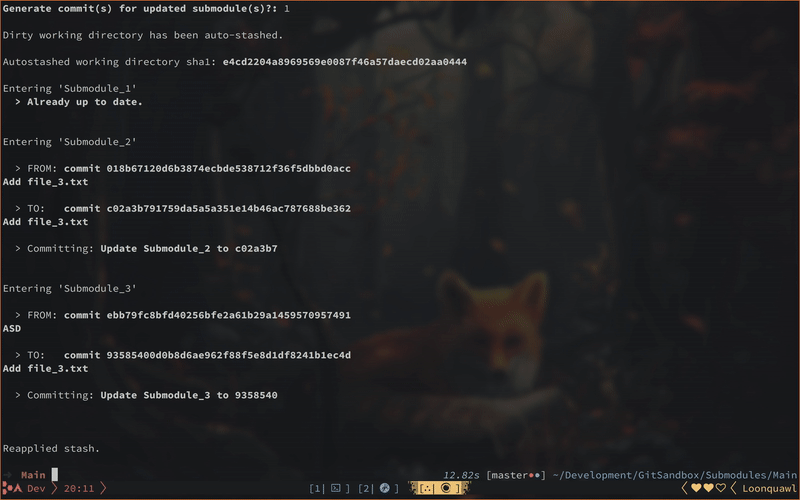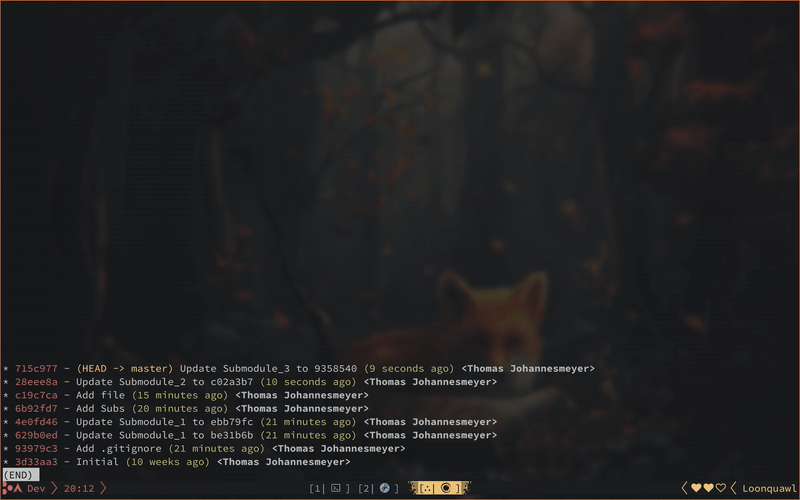
You are presented with a list of available submodules. Select all or a specific one.
-
Decide if you would just like to update and leave the changes unstaged and uncommitted or generate a commit for each updated submodule individually.
- Matryoshka checks if the working directory is dirty
- If it is dirty a stash will be created with an attached message:
"Submodule update <date>" - The hash of this stash will be printed for you. If anything goes wrong, you can always grab your changes using this hash.
- Iterate through submodules, creating a dedicated commit for each (updated) module. The commit-msg follows the following style:
"Update <submodule_name> to <shortened_hash>". - Popping the stash
- Thomas Johannesmeyer - www.geeky.gent
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details
The framework and code are provided as-is, but if you need help or have suggestions, you can contact me anytime at opensource@geeky.gent.
If you have got any suggestions, please feel free to share them with me. :)