C# server streaming features of the Kinect 2 such as speech & gesture recognition, skeleton tracking and original images
The server written in C# uses the Kinect SDK v2 to get the RGBD raw image, skeleton tracking information, recognized speech. It also uses the text-to-speech from Microsoft. Then it streams JSON data over the network using the Publisher/Subscriber pattern from the ZeroMQ network library. A Linux client has been written in Python but it can be written in any other language that is compatible with ZeroMQ. Features are controllable through a Graphical User Interface on Windows, or through the code from any Linux/Windows client. The clients can for instance enable features (speech recognition on, skeleton tracking off, …) and parameters (set new speech to recognize, change language, …) from remote.
Be sure that you have Windows 8 or later versions otherwise you won't be able to install the SDK of Kinect2.
You have to download and install these following features and SDKs :
Kinect 2 SDK : https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=44561
Microsoft Speech platform - SDK (Version 11) : https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=27226
Microsoft Speech Platform - Runtime (Version 11) : Note : Get both x86 and x64 versions if you're running 64bits processor https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=27225
Language Pack : Chose languages that you want to set for the Speech Recognition https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=43662
Media feature pack for N and KN version of Windows 8 : https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=30685
Media feature pack for N and KN version of Windows 10 : https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=48231
The speech recognition allows to recognize words, tree of words that is defined in an XML grammar file that is passed as a parameter. When a speech is recognized, the application displays the sentence and/or the semantics depending of the requested output. A semantic value contains information that matches a path through the grammar file and that is more easily usable than the text itself. The application allows to enable or disable the display of those values. Example of grammar rules:
<rule id="playAction">
<one-of>
<item> play </item>
<item> start </item>
<item> begin </item>
</one-of>
</rule>
<rule id="fileWords">
<one-of>
<item> song </item>
<item> tune </item>
<item> track </item>
<item> item </item>
</one-of>
</rule>Here there is two rules, one that defines the play action and the other that defines the word following this action. If we say “play the song” or “start the tune” or “begin the item” the recognized text will be different but the semantic will be the same “play/song”.
How to use client for speech recognition:
- With a copied/pasted grammar file :
from kinect2.client import Kinect2Client
kinect = Kinect2Client("yourIP")
def callback_speech(msg):
print msg
kinect.speech.set_callback(callback_speech)
grammar = '''<grammar version="1.0" xml:lang="en-US" root="rootRule"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/06/grammar">
<rule id="rootRule">
<one-of>
<item> Hello </item>
<item> Bye </item>
</one-of>
</rule>
</grammar>'''
kinect.speech.params.set_grammar(grammar, "hello_grammar")
kinect.speech.start()- With a list or a dictionary:
Use a list to use only words without semantics and use a dictionary if you want to associate a semantic to words.
def callback_speech(msg):
print msg
kinect.speech.set_callback(callback_speech)
dictionary = {"hello everyone" : "hello", "good bye" : "bye"}
kinect.speech.params.set_vocabulary(dictionary, "en-US")
kinect.speech.start()Note : Don't use both set_vocabulary and set_grammar for the grammar, just use one.
The confidence threshold can be changed (from 0.1 to 1.0).
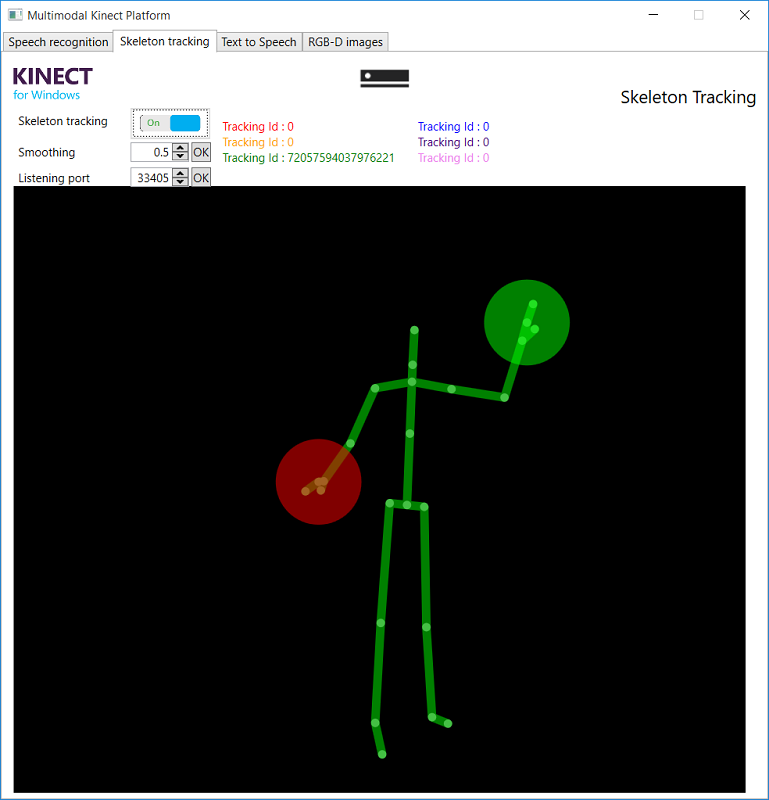
This feature can track 6 bodies at the same time. Each body is composed of 25 joints and has a unique ID. However, if a person leaves the area and then comes back in, his/her ID won't be the same. The state of the hand is also recognized. There is 5 different cases for the hand state:
- Open (Green)
- Close (Red)
- Lasso: pointing with 2 fingers (Blue)
- Unknown
- Not tracked It is also possible to apply smoothing (from 0.0 to 0.9).
The face tracking allows to get emotions and status of a given face such as:
- Happy
- Looking away
- Mouth opened
- Wearing glasses
The faces are not linked to a particular body.
How to use client for skeleton tracking + gesture recognition :
def callback_skeleton(msg):
print msg
kinect.skeleton.set_callback(callback_skeleton)
kinect.skeleton.start()The callback message is a dictionary that contains position and orientation of each joints of bodies. Each body is represented by his unique ID.
Here is a part of the message:
{"72057594037936411":
{"SpineBase":
{"Position":
{"X":0.127514437,"Y":-0.424461663,"Z":1.16753507},
"Orientation":
{"X":0.0213763285,"Y":0.9140423,"Z":0.0726106241,"W":0.398494}},
"SpineMid":
{"Position":
{"X":0.119915694,"Y":-0.139736772,"Z":1.21115172},
"Orientation":
{"X":0.009492177,"Y":0.5913789,"Z":0.0322428234,"W":-0.8056931}}}}The text-to-speech uses the speech synthesizer from Microsoft to asynchronously speak some sentences. Those sentences are sent by the client. It possible to change the gender and the language of the synthesizer. The application allows to queue messages, if this option is enabled then the synthesizer waits that the current speech is completed before starting another one, if this is disabled then the synthesizer cancels all queue and speech operations.
From the client, we can send text-to-speech request such as:
kinect.tts.params.set_language('english')
kinect.tts.params.queue_off()
kinect.tts.start()
kinect.tts.say("Hello everyone")Note : The speech recognition is disabled when a text is synthesized to avoid the speech engine to recognize some words said by the text-to-speech.
This feature allows to get:
- RGB image of size 1920 * 1080 using the HD camera of the sensor
- IR image of size 424 * 515 with the infrared camera of the sensor that is used to create a mapping
- a mapping between both RGB and IR images that gives every pixel's coordinates of the IR image in the RGB frame
- a mask that represent every missing pixels (-infinity, -infinity) of the mapping used for the inpaint function of OpenCV to smooth the mapping
The server sends uncompressed data (byte arrays) so it might overload the network. It's possible to grab frame by frame instead of using a continuous stream.
From the client, we can get a set of image (frame grabbing) and then show it such as :
kinect.rgbd.start()
kinect.rgbd.enable_frame_grabbing()
rgb, mapping, mask = kinect.rgbd.grab_frame()
cv2.imshow("rgb", rgb)
cv2.imshow("mapping", mapping)
cv2.imshow("mask", mask)
cv2.waitKey(100)The client uses data sent by the server to reconstruct images using openCV.
For example, let's get a set of image :
Color image (1920 * 1080)
Raw depth image (512 * 424)
Mapped image (489 * 275)
Mask (489 * 275)
Smoothing (489 * 275)
This feature also permits to send the audio beam of the Kinect sensor as byte array. So the client receives chunks of sound and treat them as wished.
If you can't load the xml file, try to remove comments and the first line that defines the xml file