This is the project reposetory for Independent Study Fall 2022 at University of Coloradoo Boulder.
- Understand how self driving cars work, read papers, go through courses
- Train a self-driving car using behavioral cloning in a simulated environment
- 08/22/2022 : Data simulation and generation and Data loader
- 09/5/2022 : Start implementing the NVIDIA architecture
- 09/19/2022 : Explore different prediction metrics apart from the ones mentioned in the paper
- 10/3/2022 : Explore on different architectures suitable in comparison to the current architecture
- 10/17/2022 : Run experiments, Evaluate on other simulated environments(if time permits)
- 10/31/2022 : Explore different data augmentation techniques
- 11/14/2022 : Work on optimization, and hyper-parameter tuning, etc.
- 11/28/2022 : Write a report( preferably IEEE format same as last IS report)
- 12/12/2022 : Get a review/feedback
- Udacity's self-driving car simulator - https://github.com/udacity/self-driving-car-sim
- NVIDIA's paper- End to End Learning for Self-Driving Cars
- Reference for data augmentation- Improving Behavioral Cloning with Human-Driven Dynamic Dataset Augmentation
- For data generation I am using Udacity's open source car simulator
- The tool was created by Udacity using Unity for there nanodegree students, later they open sourced it for boarder research community
- To generate the dataset, one needs to play the game in the simulator in driving/training mode. This was particularly challenging for me
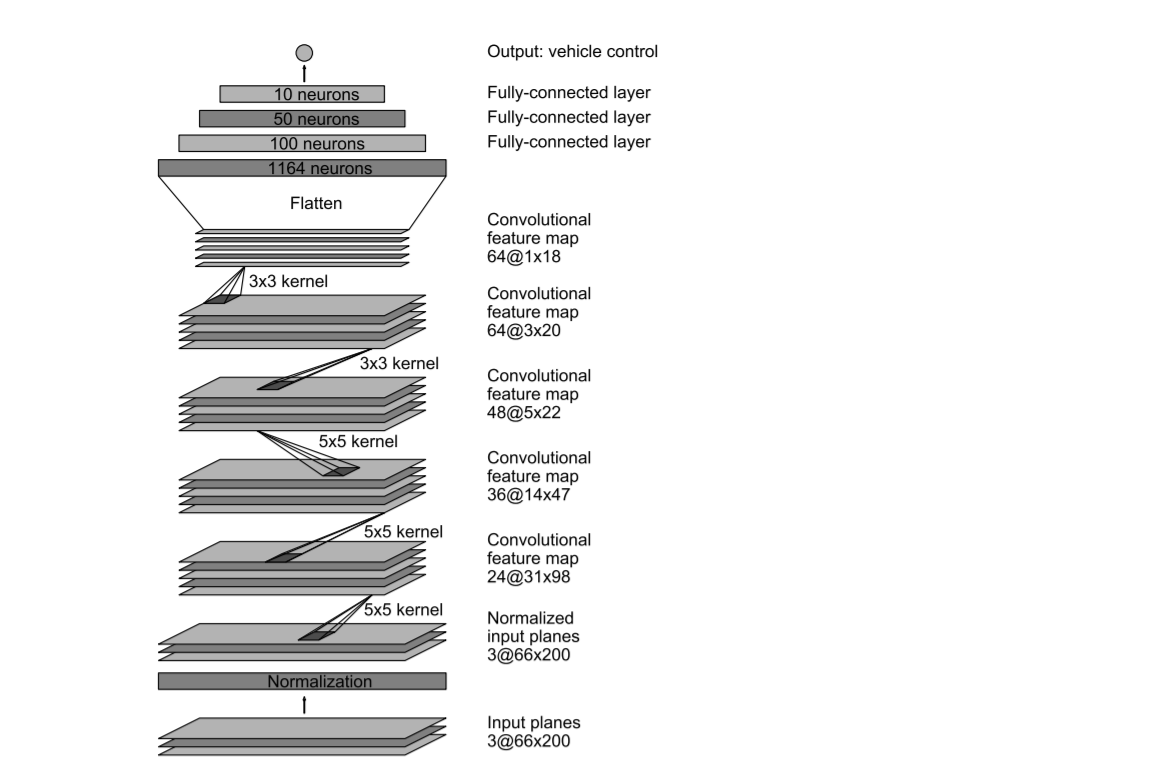
- The underlying architecture used here is based on the NVIDIA paper
- The paper described the network of 9 layers, including a normalization layer, 5 convolutional layers, and 3 fully connected layers.
- They trained the weights of our network to minimize the mean squared error between the steering command output by the network and the command of either the human driver or the adjusted steering command for off-center and rotated images
- They used a striding window of 2x2 stride in the first three layers and a kernel of size 5x5. The last two convolution layers had 3x3 kernel size and no striding. The fully connected layers are designed to function as a controller for steering
- They achieved great results through this model. However, this sophisticated architecture would be excessive for the dataset I am working with. Hence, I would focus on a simpler network of fewer convolution layers
- The model training based on the images captured from driving the car
- The output that model trains on is the steering angle
- Here, I am keeping the evaluation metrics simple to MSE (Mean Squared Error)
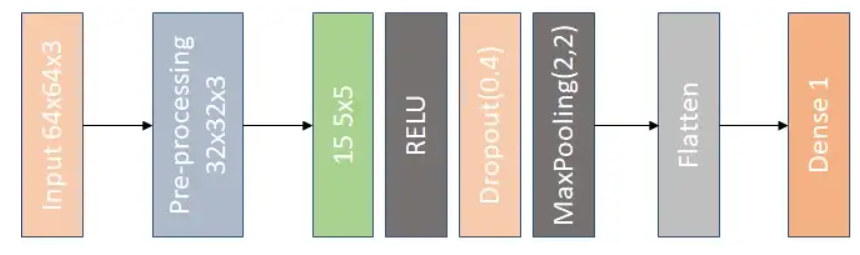
- Originally I planned to use the NVIDIA architecture but I was taking a long time to train even on just 1 epoch. It actually broke my Google Colab limits. So, I used the modified architecture -
- For a car to identify steering angles, it is important to identify features like road edges. In CNN such high-level features are extracted at initial layers hence, the layers have been reduced from the NVIDIA CNN model to first a three dense layers, then to two convolution layers and two dense layers and finally to finally to one convolution layer and one dense layer without compromising performance but reducing the training time of around 10- 15 minutes
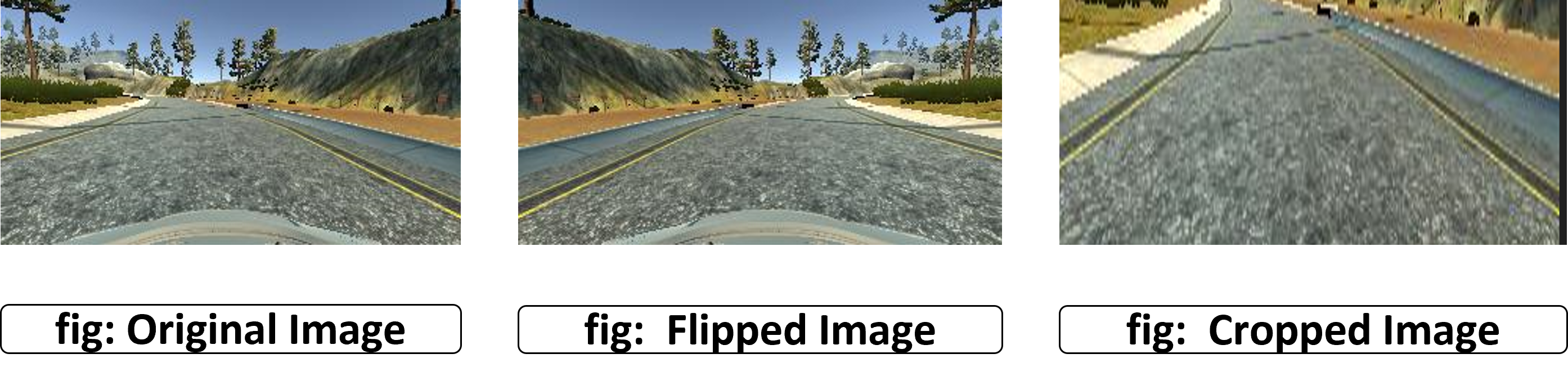
- I used basic data augmentation techniques, such as cropping, flipping etc.
- For flipping, I used the generated center camera images, flipped them and used them with a negative steering angle of that of the original steering angle of the center image. This flipping of the images technique helped to balance the dataset so that model will not be biased towards any specific condition.
- For cropping step, I removed 60px from the top and 20px from the bottom keeping the original steering angel values. Since model training does not require surrounding details such as natural scenarios, sky, etc. reduced image ratio helped with model training efficiency
- I spent this week on trying different neural network architechture and improving the model performance
| Hyper-Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Epochs | 5 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Learning Rate | 0.001 |
| Train-Test Split | 80-20% |
| Batch Size | 64 |
| Loss Function | MSE |
| Activation Function | RELU |
| Dropout | 35% |
- Here is the result
output.mp4
- Here is the report attached MS_Independent_Study_Fall_2022_Report.pdf