-
Full integration with
aptas every binary resolves all dependencies: No more installations (of pre-built archives) only to discover that a shared library is missing. No more surprises. -
Full integration with
aptso that an update of a system library cannot break an R package: if a (shared) library is used by a CRAN, the package manager knows and will not remove it. No more (R package) breakage from (system) library updates. -
Installations are fast, automated and reversible thanks to package management layer.
-
Complete coverage with (currently) ~ 19,000 CRAN packages (and 200+ from BioConductor).
-
Complete support for both Ubuntu 20.04 ("focal") and Ubuntu 22.04 ("jammy").
-
Optional (but recommeded) use with bspm automagically connects R functions like
install.packages()toaptfor access to binaries and dependencies.
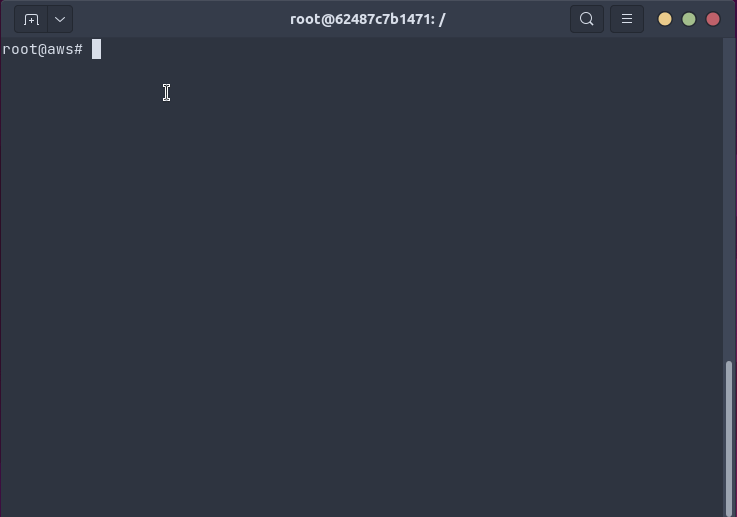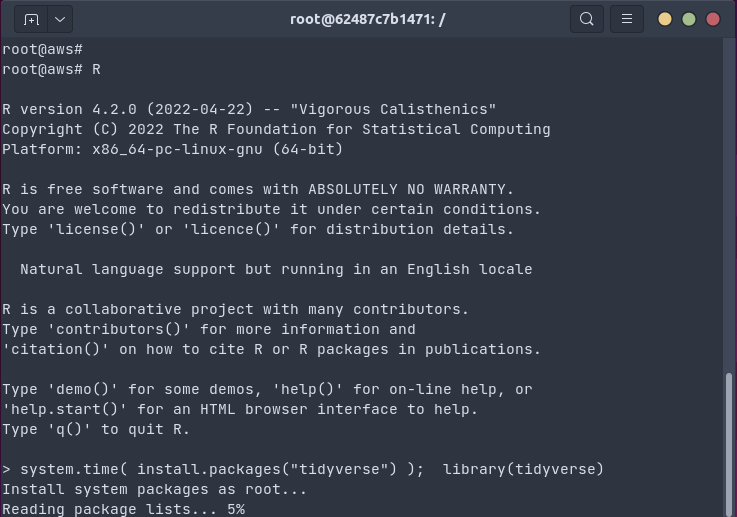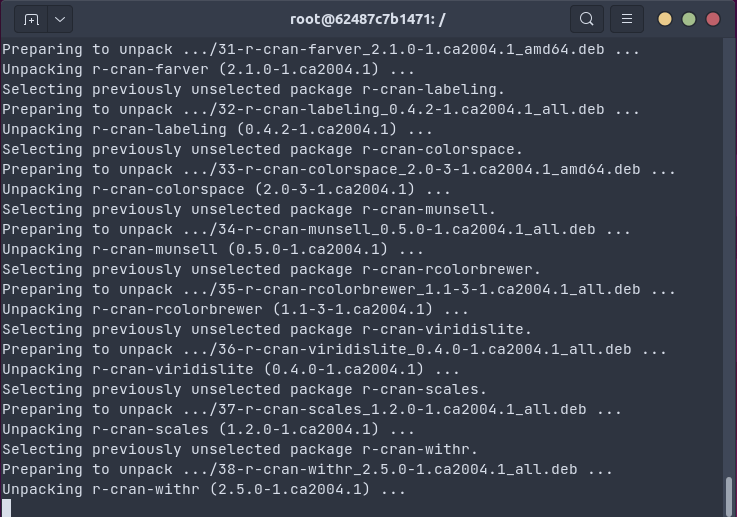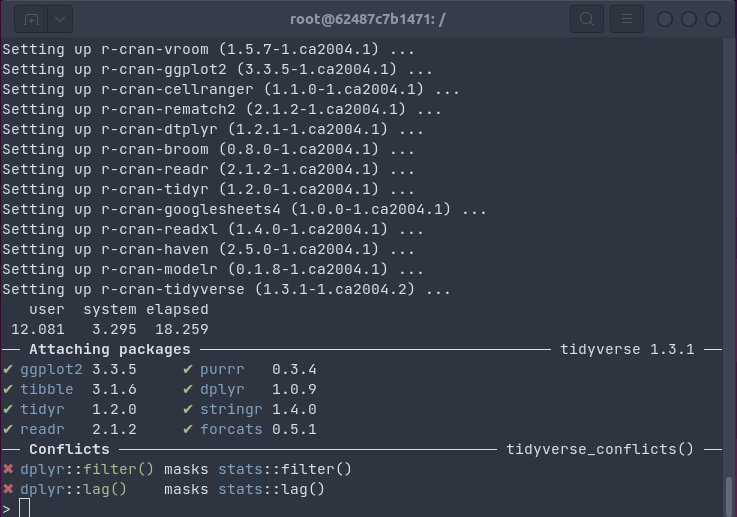
The gif shows how one install.packages("tidyverse") command on an Ubuntu
20.04 system installs all packages as binaries in 18 seconds (by passing the
R package installation to apt using bspm).
This uses the Docker container referenced below, which has been set up with the five easy setup steps detailed here.
We currently support amd64 (i.e. standard Intel/AMD cpus) for both the 'focal' 20.04 LTS and 'jammy' 22.04 LTS releases. Support for other cpu architectures is certainly possible but somewhat unlikely due to a lack of (additional hardware) resources and time.
Support for other distributions is possible but unlikely right now (due to a lack of resources and time). We hope to cover Debian at some point.
R 4.2.0 is used, and BioConductor 3.15 packages are provided as required by CRAN packages.
Everything :)
We started from cran-logs by picking the N most-downloaded packages, along with their dependencies from BioConductor. (It should be noted that for example the first 100 packages already account for approximately half the total downloads: it is a very skewed distribution.) We iterated, and fairly soon arrived of full coverage of CRAN.
So we now cover
- all CRAN packages (modulo a handful of blacklisted ones) including all packages needing compilation
- all BioConductor package that are implied by these (and build for us).
This currently resuls in 19066 and 18921 binary packages from CRAN in "focal" and "jammy", respectively, and 207 and 215 BioConductor packages, respectively, from the 3.15 release.
The sole exception are two packages we cannot build (as we do not have the required commercial software it accessess) plus less than a handful of 'odd build' that fail.
For the CRAN binaries we either repackage RSPM builds (where available) or build natively. All selected BioConductor 3.15 packages are built natively. For all of these, full dependency resolution and integration with the system is a key feature.
Everything is provided as .deb binary files with proper dependency
resolution by using a proper apt repo which also has a signed Release file.
(Note that you could use this script
add_cranapt_focal.sh
or the variant for
jammy
to facilitate the setup but you may prefer to execute the steps outlined here
by hand.)
First add the repository key so that apt knows it (this is optional but recommended)
apt install --yes --no-install-recommends wget # to add the key
wget -q -O- https://eddelbuettel.github.io/r2u/assets/dirk_eddelbuettel_key.asc \
| tee -a /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/cranapt_key.asc
Second, add the repository to the apt registry:
echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://dirk.eddelbuettel.com/cranapt focal main" \
> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cranapt.list
apt update
(Replace focal with jammy for use with Ubuntu 22.04.)
Third, and optionally, if you do not yet have R 4.2.0 run these two lines (or use the standard CRAN repo setup)
wget -q -O- https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/ubuntu/marutter_pubkey.asc \
| tee -a /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/cran_ubuntu_key.asc
echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/ubuntu focal-cran40/" \
> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cran-ubuntu.list
(Again, replace focal with jammy for use with Ubuntu 22.04.)
Fourth, add repository 'pinning' as apt might get confused by some older
packages (in the Ubuntu distro) which accidentally appear with a higher
version number. See the next section to ensure 'CRANapt' sorts highest.
After that the package are known (under their r-cran-* and r-bioc-*
names). You can install them on the command-line using apt and apt-get,
via aptitude as well as other front-ends.
Fifth, and also optional, install and enable the
bspm package so that CRANapt and
other packages become available via install.packages() and
update.packages().
Because we let apt (and related tools) pick the packages, we have to ensure
that the CRANapt repo sorts higher than the default repo as (older)
package builds in the distribution itself may appear (to apt) to be
newer. A case in point was package gtable whose version in Ubuntu was
0.3.0+dfsg-1 which accidentally sorts higher than the rebuild we made under
a newer and more consistent version number 0.3.0-1.ca2004.1. One possible
fix is 'apt pinning'. Place a file /etc/apt/preferences.d/99cranapt with content
Package: *
Pin: release o=CRAN-Apt Project
Pin: release l=CRAN-Apt Packages
Pin-Priority: 700
which will now give packages from this repo a higher default priority of 700 overriding the standard value of 500.
There are also two Docker containers for Ubuntu 20.04 'focal' and 22.04 'jammy', respectively, at eddelbuettel/r2u that have the above, including pinning and bspm support, already set up.
Use this link below (after possibly signing up for gitpod.io first)
and run one of the three example scripts, or just start R in the terminal window.
The gif below display running one such example to install brms from binaries in a few seconds. Using this requires only (free) GitHub and GitPod accounts.
Please file issues at the GitHub issues for r2u.
As of early May:
-
Some geospatial packages do not currently install on 20.04, adding the UbuntuGIS PPA as a base may help. This is not an issue on 22.04.
-
The littler package reflects build-time configuration, the RSPM binary is then expecting a different R location so it needs a binary rebuild. Added a 'force' flag, may need a list similar to the blacklist to always compiled.
-
A small number of packages do not build for lack required components; examples are ROracle and Rcplex. They, and their reverse dependencies, are are blacklisted and not built.
-
[DONE] The BioConductor release is still at 3.14 and should be upgraded to the now-current 3.15.
-
[DONE] Support for Ubuntu 22.04 has been added as well.
-
[DONE] Package nlme needed special treatment because the Debian/Ubuntu binary changed the 'hyphenated' version to a 'dot-separated' one leading to an inverted sorting order (see issue #7, as well as the FAQ, for more on this).
Dirk Eddelbuettel
The repository-building code in this package is released under the GPL (>= 2).
All CRAN and BioConductor packages are released under their respective licenses.
This was made possible by the generous support of endless coffee thanks to my GitHub Sponsors.