In the present repository, you can find the materials for the paper
Ayzel G., Heistermann M. The effect of calibration data length on the performance of conceptual versus data-driven hydrological models.
which was revised and re-submitted to Computers & Geosciences. The initially submitted version of the paper and the corresponding repository are located here.
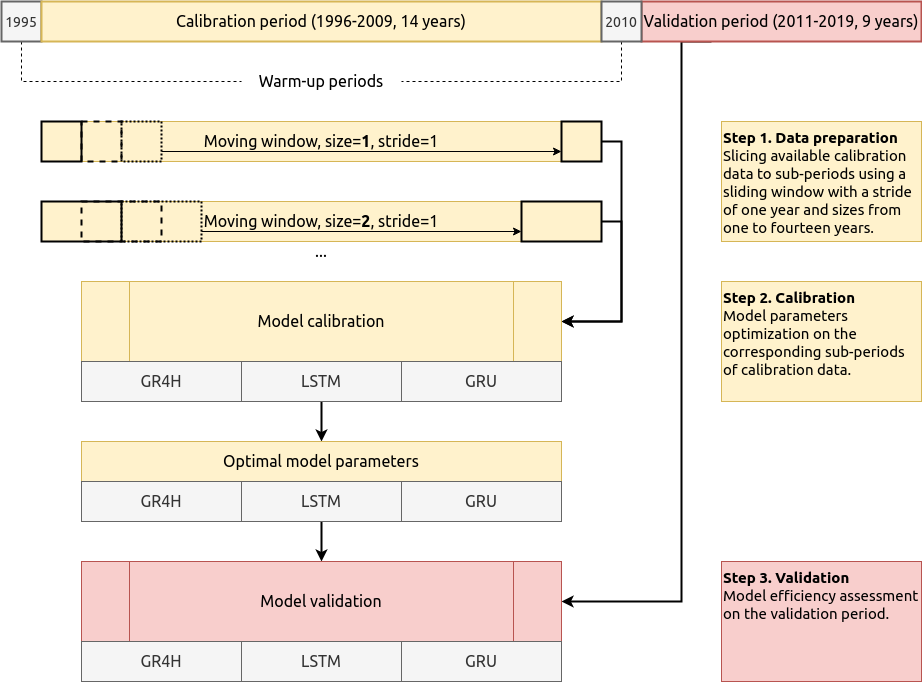
In this study, we want to investigate the effect of calibration data length on the validation performance of different rainfall-runoff models. To this aim, we consequently increase the calibration data length from one to twenty calendar years and investigate how that affects the model skill on a hold-out (validation) period.
We use three models for runoff prediction at hourly temporal resolution:
one conceptual
- GR4H -- a conceptual hydrological model. It is a derivative from the GR4J model -- the version for runoff prediction at daily temporal resolution.
and two data-driven models which differ by the type of the computational layer used
- Long Short-Term Memory Network (LSTM)
- Gated Recurrent Units Network (GRU)
The code is written in Python programming language (v3.6) using open-source software libraries, such as numpy, pandas, scipy, numba, tensorflow, and keras. The analysis of obtained results was done also using jupyter notebooks and matplotlib plotting library.
You can install all the required dependencies using conda -- an open-source package management system. First, install conda itself, then use the provided environment.yml file to create the isolated environment:
conda env create -f environment.ymlThe code directory consists the following files:
gr4h.py
- holds the code for the GR4H hydrological model.
gr4h_script.py
- describes the workflow for the main calibration/validation experiment for the GR4H model.
ann_script.py
- describes the workflow for the main calibration/validation experiment for LSTM and GRU models.
run_$model_name$_experiment.sh
- bash scripts that run the main calibration/validation experiment for the selected river basins.
There are three files (Jupyter notebooks) in the analysis directory:
00_results_summary_calculation.ipynb
- calculates and aggregates the evaluation metrics based on obtained results of streamflow simulation .
01_results_visualization.ipynb
- represents the visual analysis of the effect of calibration data length on the performance of hydrological models.
02_hydrograph_plotting.ipynb
- consists the code for plotting hydrographs (observed and simulated runoff time series).
The full results of the conducted experiment can be found in the respective data repository .
Two files aggregate evaluation metrics for the calibration and validation periods: summary_calibration.npy and summary_validation.npy, respectively.
The figures subfolder consists of figures that were generated using the 01_results_visualization.ipynb Jupyter notebook.
Input data (discharge and meteorological forcing time series) for the selected set of basins is located in the forcing directory.
We used the following sources for the input data compilation:
- National Water Information System (NWIS) -- to retrieve discharge time series.
- NLDAS reanalysis -- to retrieve precipitation and air temperature data.