A Python implementation of virtual serial ports. Useful for developing and testing programs which need to talk to a serial port.
Example uses:
- Create a virtual port which echoes back any data sent to it.
- Create a two or more ports; sending data to one sends data to the others.
Has no dependencies other than the Python standard library.
Only works on *nix type systems. Tested on Debian Linux, but should work on others (macOS, BSD, etc.). For Windows, look at com0com or Virtual Serial Port Driver.
$ pip3 install PyVirtualSerialPorts
$ sudo pip3 install PyVirtualSerialPorts
If the script install folder is in your PATH (almost certainly the case if
installed as root), you can simply run:
$ virtualserialports ...
Otherwise, you can use it as a module:
$ python3 -m virtualserialports ...
usage: virtualserialports [-h] [-l] [-d] num_ports
positional arguments:
num_ports number of ports to create
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-l, --loopback echo data back to the sending device too
-d, --debug log received data to stderr
$ virtualserialports -l 1
The created port will be printed on the command line e.g. /dev/pts/0, and can
be used with any serial program, e.g. minicom:
$ minicom -D /dev/pts/0
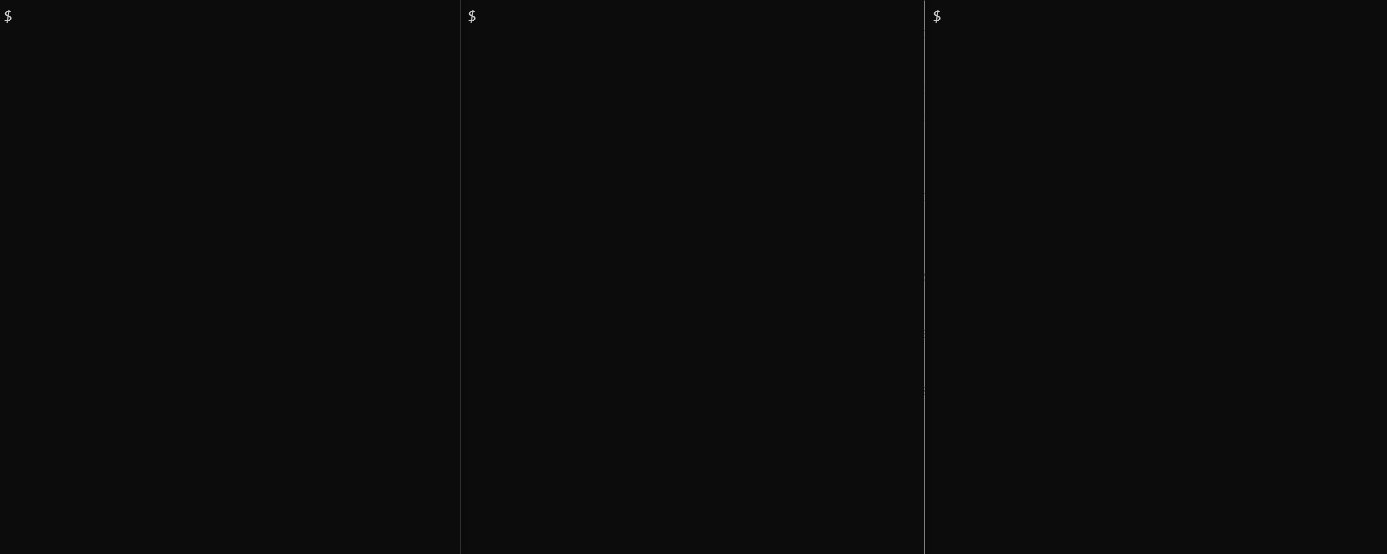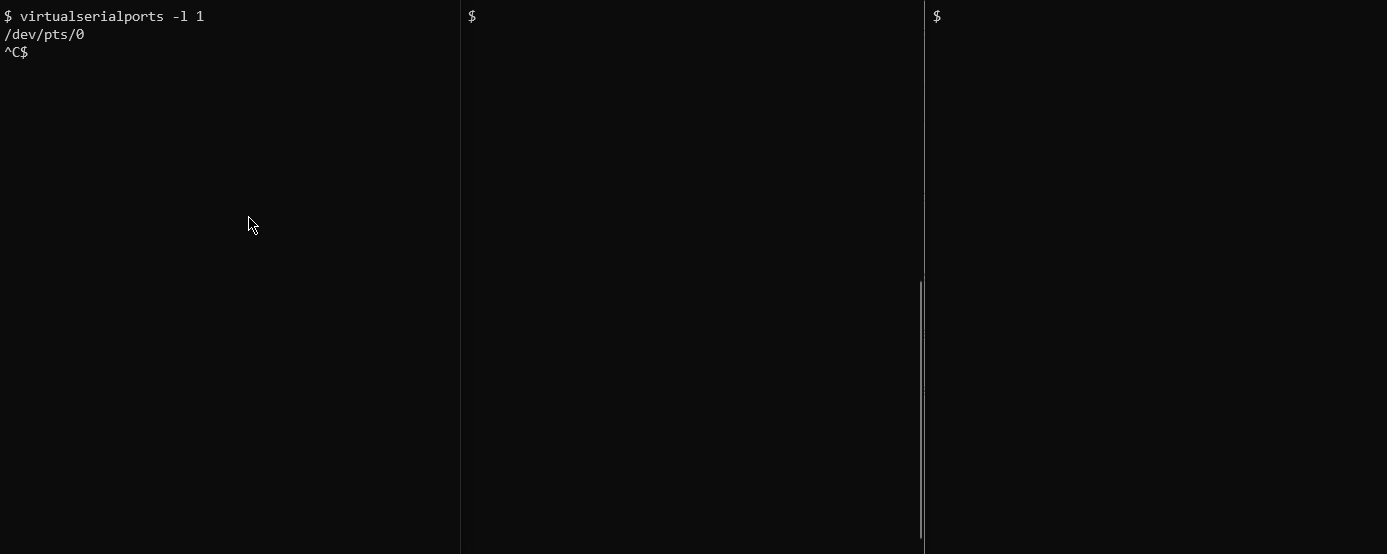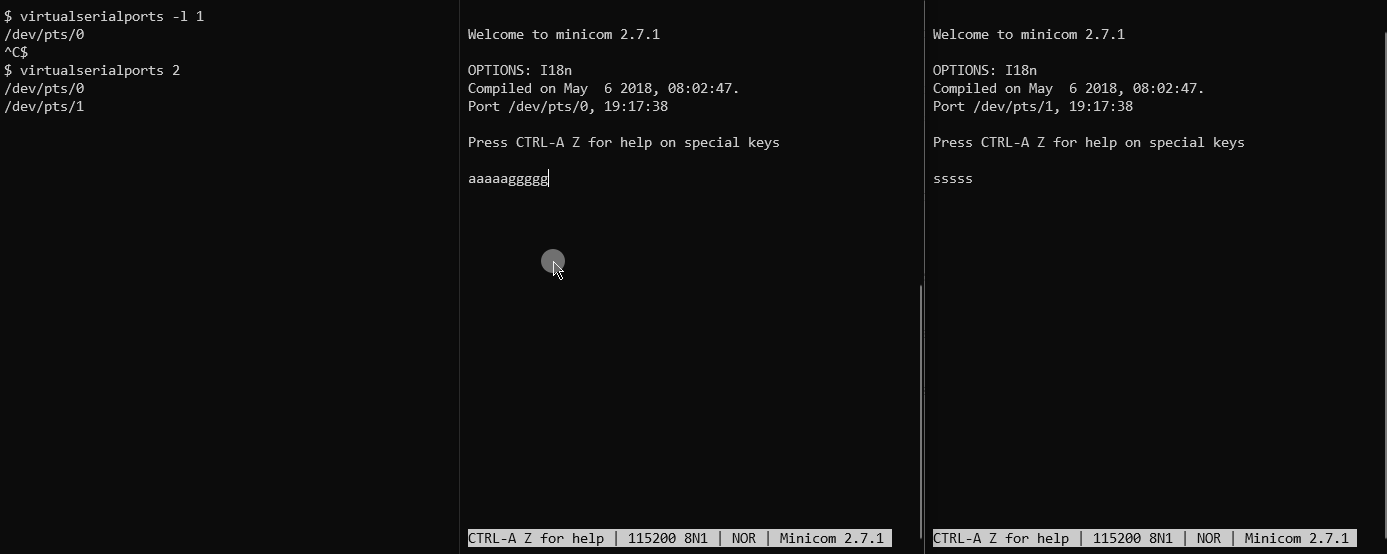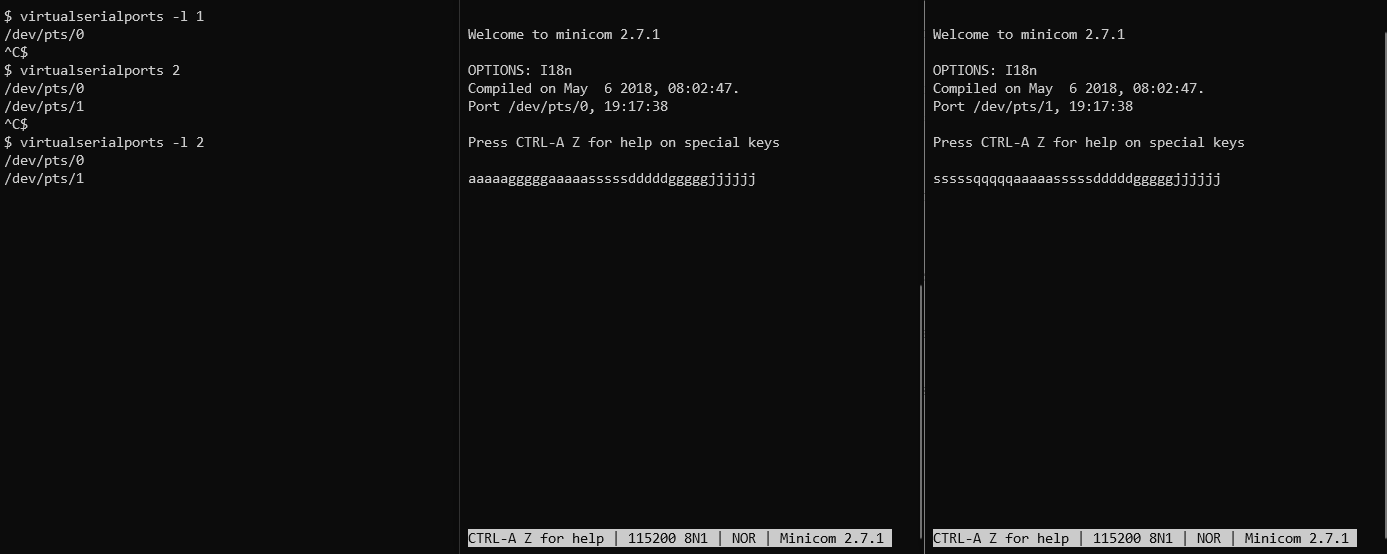
$ virtualserialports 2
The two created ports will be printed, and again can be used with any serial program. E.g. in one terminal window:
$ minicom -D /dev/pts/0
and in a second:
$ minicom -D /dev/pts/1
Now typing data on one terminal will appear in the other.
$ virtualserialports -l 3
virtualserialports.run(num_ports, loopback=False, debug=False)
- num_ports: number of ports to create.
- loopback: whether to echo data back to the sender.
- debug: whether to print debugging info to stdout.
import virtualserialports
virtualserialports.run(2, loopback=True, debug=False)