Number Server is a stand-alone application able to accept multiple socket connections over TCP/IP for writing numbers in a single log file free from duplicates.
In order to run Number Server on your machine you need:
The easiest way to start Number Server is typing from the project folder the command:
mvn clean install exec:java
It will start the application, create the logging file (by default numbers.log) and listen the port (by default 4000) for
numbers to write in the file; if the file already exists it will be cleared.
The maximum number of connections is set to five by default.
Periodically (by default 10 sec) the application prints on standard output a report containing:
- The difference since the last report of the count of new unique numbers that have been received;
- The difference since the last report of the count of new duplicate numbers that have been received;
- The total number of unique numbers received for this run of the Application.
An example of report could be the following:
Received 50 unique numbers, 2 duplicates. Unique total: 567231
It is possible to pass some arguments at the startup to modify some default behaviors by running the command:
mvn clean install exec:java -Dexec.args="arg0=value0 arg1=value1 ..."
The accepted arguments are:
port(default4000) - define the listening port;logFile(defaultnumbers.log) - define the file's path where logging the numbers;maxConnections(default5) - define the maximum number of connections accepted;reportPeriod(default10000) - define how long is the period (in milliseconds) between each report.
It is possible to send numbers to the Number Server by using telnet (or PuTTY for windows) clients.
For example by typing on your terminal telnet localhost 4000.
Once the client session is created, a number can be sent by simply typing it and press enter. There are few rules to follow by the way:
- A number can be composed by at most 9 digits (e.g.
314159265or007007009); - If a number is composed by less than 9 digits, it must include leading zeros till reach 9 digits;
- Any invalid sent number will disconnect the client;
- Typing
terminatefollowed by enter will stop Number Server and disconnect all the clients.
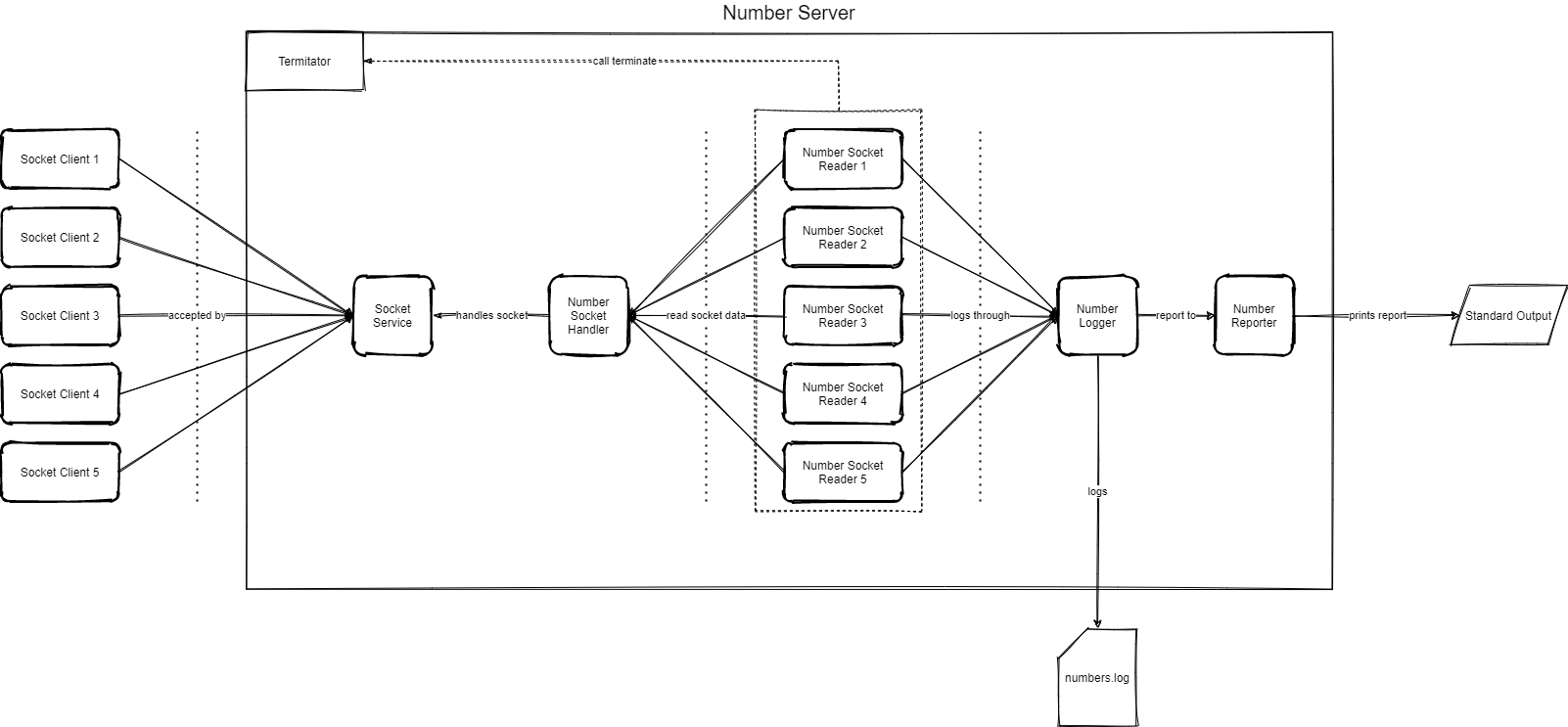
There are five main component in the design:
SocketService- its function is to accept socket connections by listening the specified port;NumberServiceHandler- once the socket connection is accepted, the socket is passed to this handler that tries to dispatch the socket stream to any freeNumberSocketReader; it is also responsible to manage the lifecycle of the socket.NumberSocketReader- it reads the data sent through the socket; if the data is a valid number then it is passed toNumberLogger; the read continues till an invalid number is received; if the special keywordteminationis received theTerminatioris called;NumberLogger- it is a thread safe module with the responsibility of writing to the log file; it ensures that those numbers are not duplicated. It also notifies theNumberReporterif the received number was a duplicated or not;NumberReporter- it keeps the count of uniques, duplicates and total uniques numbers between each report and print them to standard output.
Number server has been tested on a Windows 10 laptop with 1.6 GHz intel i5 8th gen processor and 16 GB of RAM. The implementation proved to be able to handle more than 2M of numbers per 10 seconds.
Following a table containing the average performance resulted from 100 runs of stress tests. It shows the type of test, the elapsed time for processing 2M number for each socket client connected, the average throughput of processing numbers.
| Test | 2M of numbers (sec) | Throughput (numbers/sec) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 socket client | 1,87 | 1,06 M |
| 5 socket clients all duplicates | 4,60 | 0,43 M |
| 5 socket clients no duplicates | 5,59 | 0,35 M |
Number Server has been developed following as much as possible SOLID and TDD principles. It has a final
code coverage of 87%. The number of classes has been kept as much as possible close to the architectural design
for improving the readability.
- The socket stream is read using a
java.io.BufferedReaderwhich proved better performance respect tojava.util.Scanner; - The file log is written using
java.io.FileWriterbecause of its performance; - The numbers logged are plain numbers without leading zeros because it was not specified in the requirements.
The current architecture work just fine with a reduced and limited number of connection. On the other hand, it has a potential limit on the scalability if the number of connections increase a lot.
In fact, each reader is running on its own thread and could lead to memory limitations. It should be possible
overcome this limitation by taking advantage of the non-blocking I/O provided by java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel
(instead of java.net.ServerSocket) and reading the channel stream with a single reader.
By the way, using a single reader could potentially reduce the throughput of the application.
Now that you know everything enjoy the Number Server :)