For today’s activity, you are going to be walking through all of the steps required for your first Core assignment, but with a different database.
-
Fork and clone this GitHub repository using GitHub Desktop.
- The owner of the repository is displayed as part of the repo name on GitHub.com. If it says "coding-dojo-data-science", you are looking at the original repo. Click on the "Fork" button on the top-right.
- You will see the name of the repo will change and should now start with YOUR GitHub username. It will also indicate that it is a fork of the original repository.
-
Open the repo with Jupyter Notebook and create a new Notebook using dojo-env for your analysis. Lesson Link (See the "Open the Repository with Jupyter Notbeook" section.)
- Don't see Python (dojo-env) as an option?
- Make sure you ran the following line in your terminal/GitBash from Python Installation Step 2 after creating your dojo-env:
python -m ipykernel install --user --name dojo-env --display-name "Python (dojo-env)"
- Make sure you ran the following line in your terminal/GitBash from Python Installation Step 2 after creating your dojo-env:
- Don't see Python (dojo-env) as an option?
-
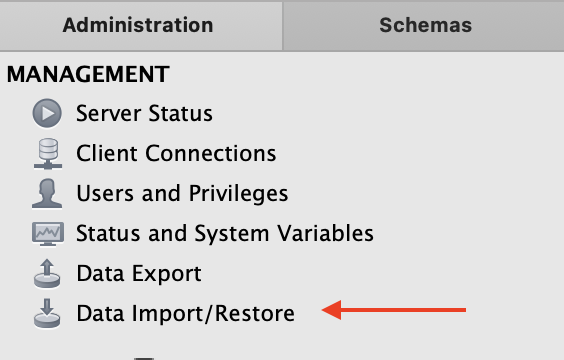
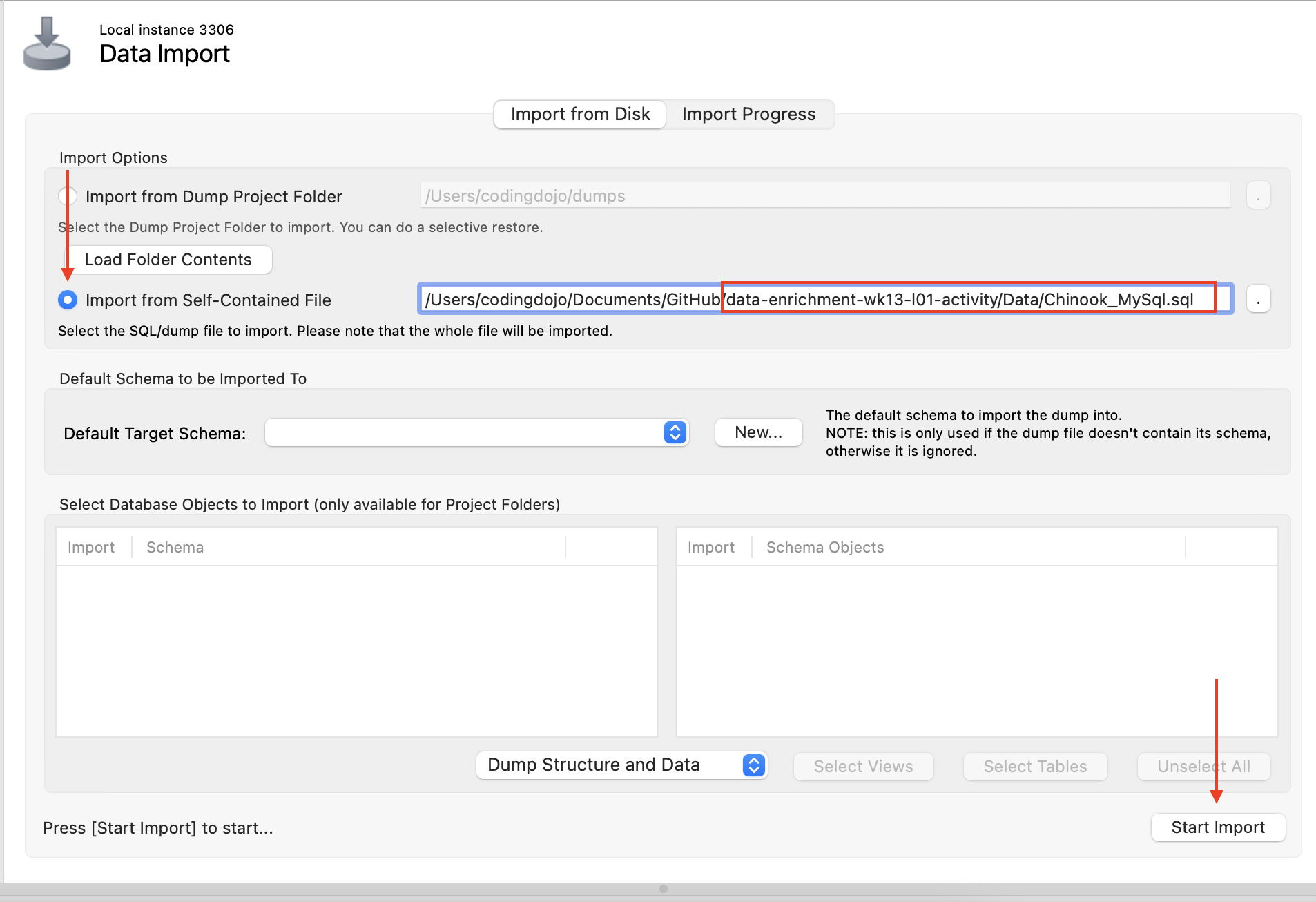
Install the included database in the Data folder (Chinook_MySql.sql) into your MySQL Server.
- Either double-click on the .sql file in the Data folder using Windows' File Explorer or Mac Finder
- OR Open MySQL Workbench and use the Data Import tool and then run with MySQL Workbench).
-
Use Reverse Engineering in MySQL Workbench to create an ERD for the Chinook database you just installed. Lesson Link
- Export the ERD into your repostory as a png file in your Data folder.
- Insert the ERD into a Markdown cell in your notebook using the following syntax (make sure to change the filename to match yours, if you used something other tha "ERD.png")

-
In your Jupyter Notebook, use pymysql and sqlalchemy to connect your database. Lesson Link
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import pymysql
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
## Change username and password to match your personal MySQL Server settings
username = 'root' # default username for MySQL db is root
password = 'YOUR_PASSWORD' # whatever password you chose during MySQL installation.
connection = f'mysql+pymysql://{username}:{password}@localhost/Chinook'
engine = create_engine(connection)-
In your notebook, run the queries necessary to answer the following questions:
- What is the most a customer has spent on a single purchase and what is their customerId?
- What country is the customer with the largest total bill from (from question 2)?
- Which customerID made the fewest purchases (invoices)?
- Retrieve the id, name, and # of playlists for tracks that appear on playlists more than 4 times?
-
Save your notebook and close Jupyter.
-
Save your work in a new commit with GitHub desktop and push it to GitHub.