Unofficial tensorflow implementation of Active Bias. Specifically, we implemented SGD-WPV (SGD Weighted by Prediction Variance), which is one of the methods using the concept of high variance in the paper. In this repository, we call it Active Bias for convenience.
Publication
Chang, H. S., Learned-Miller, E., & McCallum, A., Active Bias: Training More Accurate Neural Networks by Emphasizing High Variance Samples," Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), pp. 1002–1012, 2017.
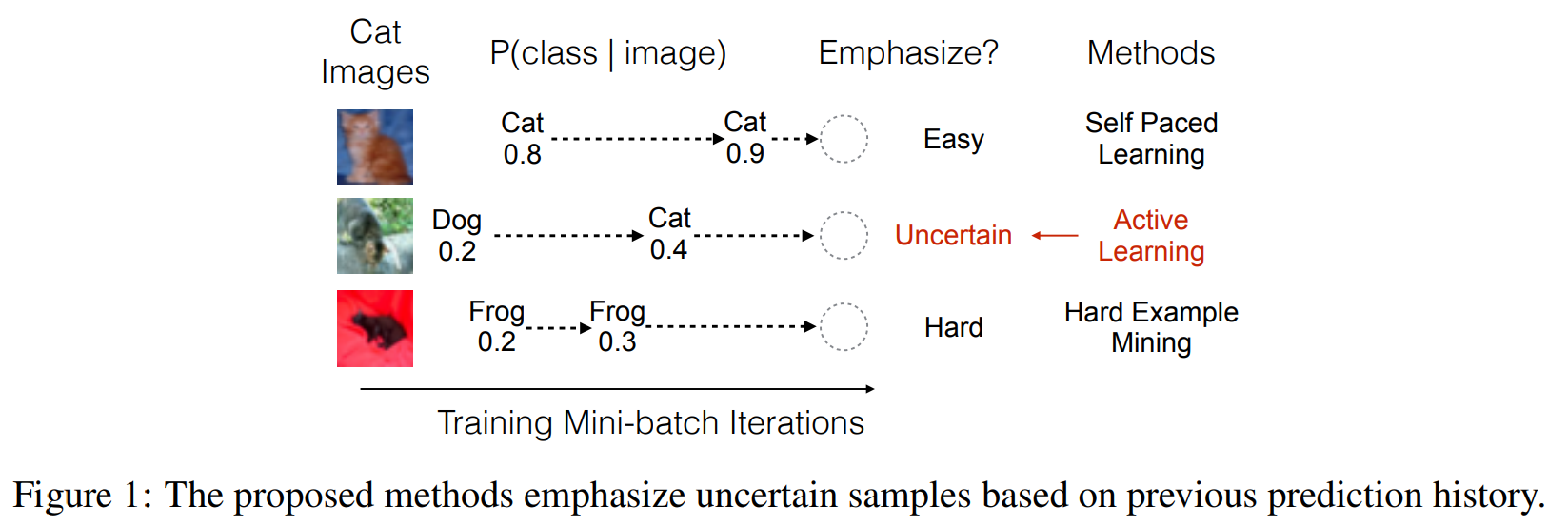
For more accurate training, Active Bias emphasizes uncertain samples with high prediction variances. As shown in below figure borrowed from the original paper, samples with low variances are too easy or too hard for training, therefore Active Bias focuses on uncertain samples with high variance. That is, the sample having highly variate prediction history is preferred to construct next mini-batch. In detail, Active Bias maintains a history structure to store all softmax outputs (or probabilities) of true labels, and computes the variance of accumulated prababilities for each sample. Then, based on the variance, it reweights the backward loss of the samples in each mini-batch before backward propagation.
- To validate the superiority of Active Bias, we showed the test error on a simulated noisy CIFAR-10, which has mislabeled samples.
- To inject noisy labels, the true label i was flipped to the randomly chosen label j with a probability tau. That is, tau is a given noise rate that determines the degree of noiseness on dataset.
- A densely connected neural networks (L=40, k=12)(Huang et al./ 2017) was used to train the noisy CIFAR-10.
- For the performance comparison, we compared the test loss of Active Bias with that of Default. Defualt trained the noisy CIFAR-10 without any processing for noisy labels.
- Python 3.6.4
- Tensorflow-gpu 1.8.0 (pip install tensorflow-gpu==1.8.0)
- Tensorpack (pip install tensorpack)
-
Algorithm parameters
-gpu_id: gpu number which you want to use. -method_name: method in {Default, ActiveBias}. -noise_rate: the rate which you want to corrupt. -log_dir: log directory to save the training/test error. -
Algorithm configuration Data augmentation and distortion are not applied, and training paramters are set to:
# gradient optimizer type optimizer = 'momentum' # total number of training epcohs total_epochs = 200 # batch size batch_size = 128 # learning rates used for training, and the time to use each learning rate. lr_boundaries = [40000, 60000] lr_values = [0.1, 0.02, 0.004] # warm-up epochs warm_up = 15 # smoothness constant smoothness = 0.2 # training algorithms if method_name == "Default": default(gpu_id, input_reader, total_epochs, batch_size, lr_boundaries, lr_values, optimizer, noise_rate, log_dir=log_dir) elif method_name == "ActiveBias": active_bias(gpu_id, input_reader, total_epochs, batch_size, lr_boundaries, lr_values, optimizer, noise_rate, warm_up, smoothness, log_dir=log_dir)
-
Running commend
python main.py gpu_id method_name noise_rate log_dir
This commend includes: (i) CIFAR-10 automatical download, (ii) noise injection, and (iii) neural network training.
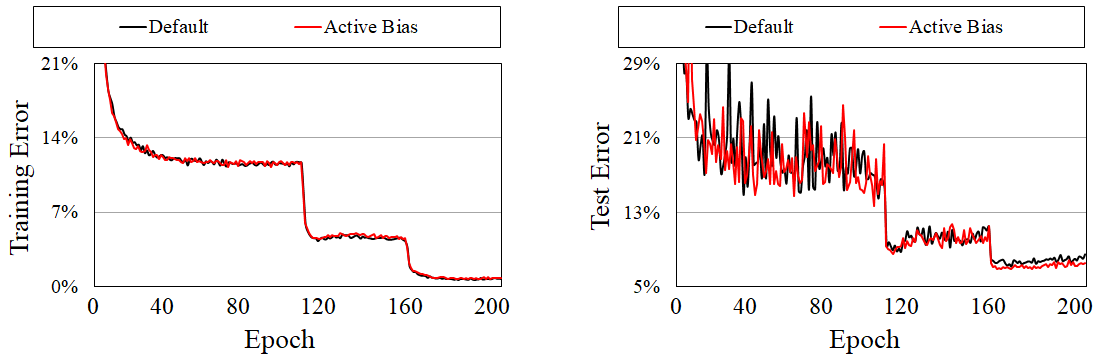
- This tutorial shows the superiority of Active Bias on clean dataset. For a fixed training epochs (i.e., same number of iterations), Active Bias achieved relatively 3.76% lower test error compared with that of Default.
- We set tau to 0.0.
- Running script
#!/bin/sh main.py 0 Default 0.0 tutorial_1/Defulat main.py 0 ActiveBias 0.0 tutorial_1/ActiveBias - Running result
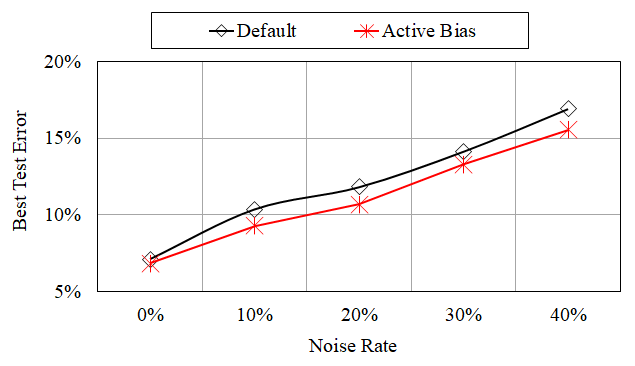
- This tutorial shows the robustness of Active Bias on noisy labels. For all noise rates, Active Bias achieved lower test error compared with that of Default.
- We used tau in {0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4} //from light noise to heavy noise
- Running script
#!/bin/sh for i in 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 do main.py 0 Default $i tutorial_2/Defulat/$i main.py 0 ActiveBias $i tutorial_2/ActiveBias/$i done
- Running result