In this workshop, you will create a microservices app (written in Python) out of AWS Lambda functions, using the CloudFormation template provided. You will then instrument the functions to get visibility through Splunk APM. No coding experience necessary!
- Requirements
- Steps
- Create the microservices environment
- Instrument the Lambda functions
- Run the app to generate APM data
- [Optional] Add custom span tags for additional info
- Conclusion
- Troubleshooting
- Access to a Splunk Observability Cloud organization with APM enabled
- Permissions to view APM access tokens in Splunk Observability Cloud
- AWS account
- Permissions to create Lambda functions and S3 buckets in the 'us-east-1' (N. Virginia) region on AWS
Two specific AWS resources are required to run this demo/workshop that are outside the scope of this demo:
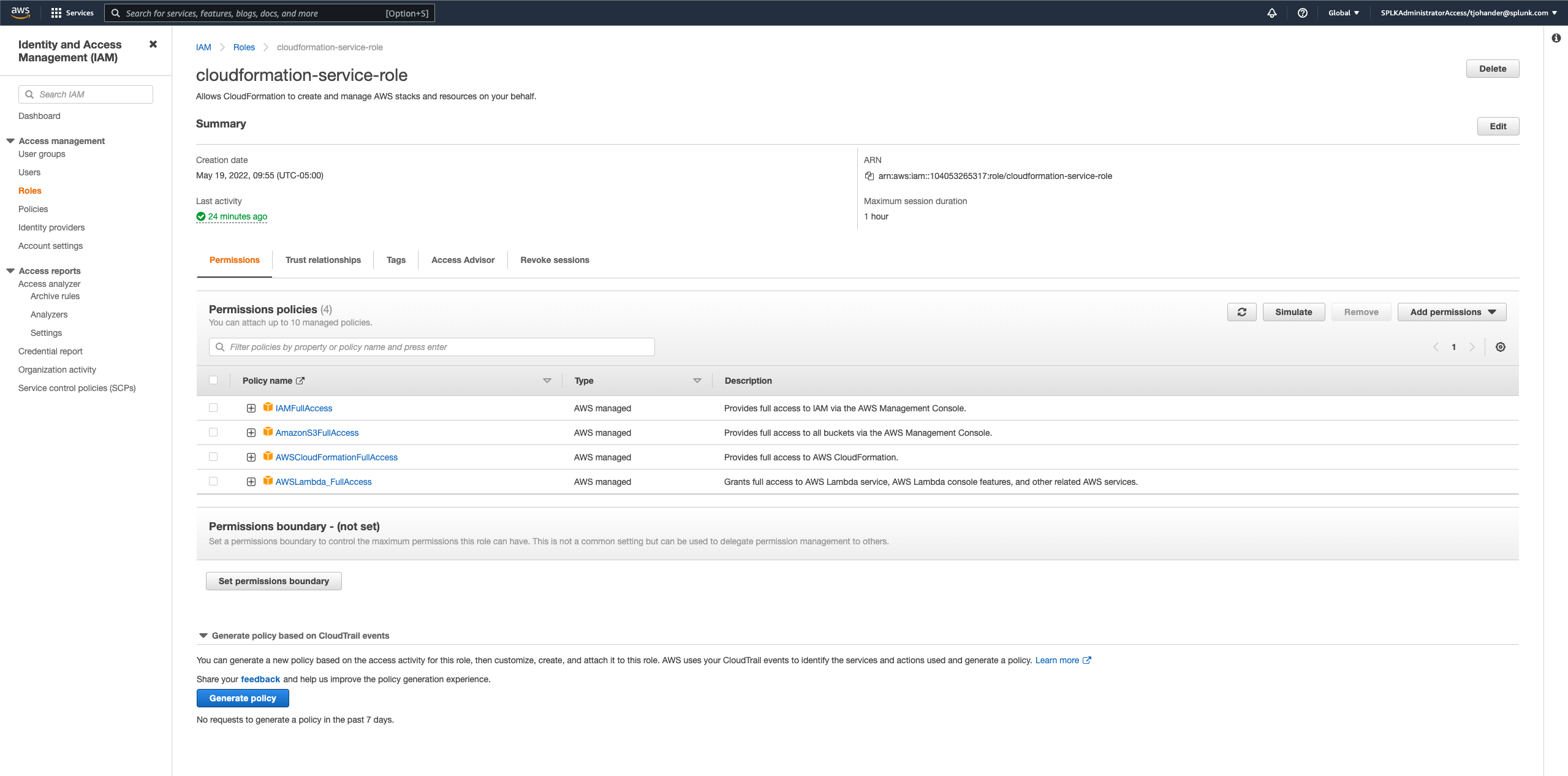
- An IAM Role that the Cloudformation service will assume to create the resources described in the Cloudformation templates. This a different role that's used to invoke the lambda functions themselves. This role is created outside of the project templates. Since this IAM "user" is needed to build the other resources, it can't be included in the Cloudformation templates for the Lambda demo. The easiest way to get up and running is to create a Cloudformation Service User Role with the following settings:
After this is created you'll need to note the role ARN to add to the Cloudformation GUI or CLI setup. In other words, you're going to tell Cloudformation to run as this Service Account to generate all the demo resources.
- Download this CloudFormation template. This template contains all the objects (and code) that are needed for the microservices app that you will instrument.
- Navigate to CloudFormation in the AWS console. Make sure you are in the 'us-east-1' (N. Virginia) region!!! The CloudFormation template is written for that region ONLY.
- At the top-right, click
Create stack>With new resources (standard). - On the 'Create stack' page, select
Upload a template file, and thenChoose fileto select the CloudFormation template you downloaded in Step 1. ClickNext.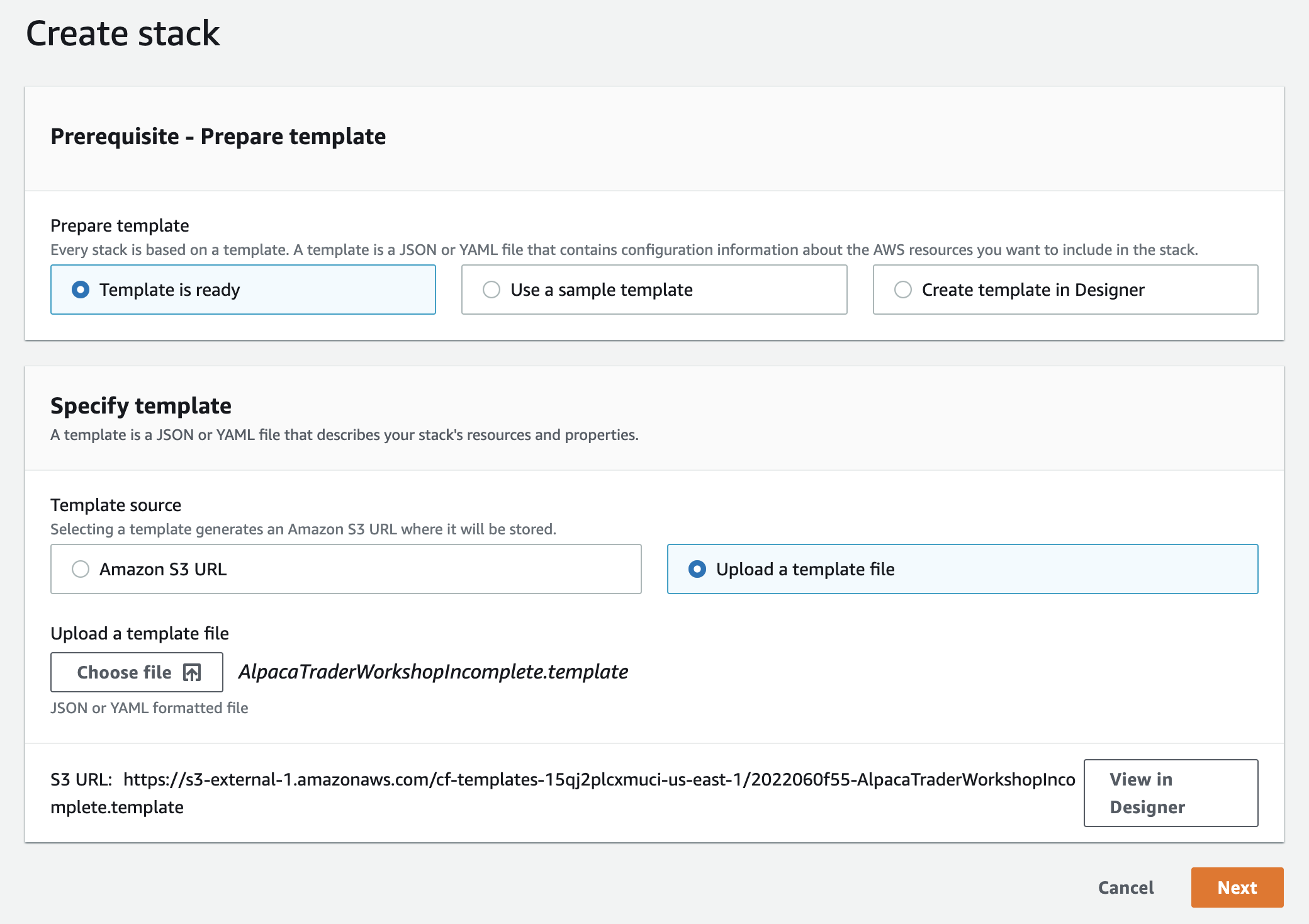
- To complete the CloudFormation stack creation, give the stack a name (e.g.
lambda-stack), and under 'Parameters', enter a name for the S3 bucket to be used by the microservices app. ClickNext. Note that this name must be unique across all of AWS. - On the next page titled 'Configure stack options', scroll all the way down and click
Next. Finally, on the 'Review' page, scroll to the bottom, and select the checkbox that says 'I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resources with custom names.' Then clickCreate stack. - You should now see that your stack has a status of 'CREATE_IN_PROGRESS'. Wait until it says 'CREATE_COMPLETE' (or spam the refresh button, your choice). You now have a microservices app running on AWS Lambda!
- This CLI Command can be executed by either pointing the
--template-bodyparameter to the local path of the Cloudformation template file, or passing--template-url <An URL to an S3-based location of a template file> - Execute the following AWS CLI Command:
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name <some-arbitrary-name> \
--template-body file://<local-path-to-'AlpacaTraderWorkshopIncomplete.template'> \
--region us-east-1 \
--parameters ParameterKey=bucketName,ParameterValue=<some-arbitrary-s3-bucket-name> \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--role-arn <the-cfn-serivce-account-role-arn>As an example:
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name lambda-demo-tsj-splunk-100 \
--template-body file:///Users/tjohander/splunk/projects/lambda-apm-workshop/AlpacaTraderWorkshopIncomplete.template \
--region us-east-1 \
--parameters ParameterKey=bucketName,ParameterValue=tsj-splunk-alpaca-bucket-100 \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--role-arn arn:aws:iam::12345678:role/cloudformation-service-role- Navigate to AWS Lambda and take a moment to understand the functions in this app. There are 4 of them: 'watchlistUpdater', 'stockRanker', 'getFinancials', and 'buyStocks'. The architecture of these functions will become clear once you instrument them for APM.
- Navigate to the Splunk O11y 'Data Setup' page, and search for
lambda(you may have to clickExtend search across all integrations). SelectAWS Lambda (Serverless instrumentation), and clickAdd Integration. - For 'Function name', enter the name of the first Lambda function you will instrument (e.g.
watchlistUpdater). Select your Splunk access token (make sure it has the right permissions for APM), and enter a name for this app's environment (e.g.lambda-app). Click 'Next'. Make sure the environment name is the same for all your functions in this app. - On the 'Install Integration' page, select
Python. Follow the steps on this page to add the Splunk OTel layer and set the environment variables. For the ARN, usearn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:254067382080:layer:splunk-apm:51.





- Phew! That was a lot. Now repeat Step 11 for all 4 Lambda functions. (You do not need to go through the Splunk O11y GDI wizard again; simply make the changes necessary in AWS.)
- Time to finally run the code and see some data! Manually run these 3 functions in order: 'watchlistUpdater', 'stockRanker', and 'buyStocks'. To run them, open up each function, and under the 'Function overview' section, click on the
Testtab. Enter an event name (e.g.test), and at the top right, click the orangeTestbutton.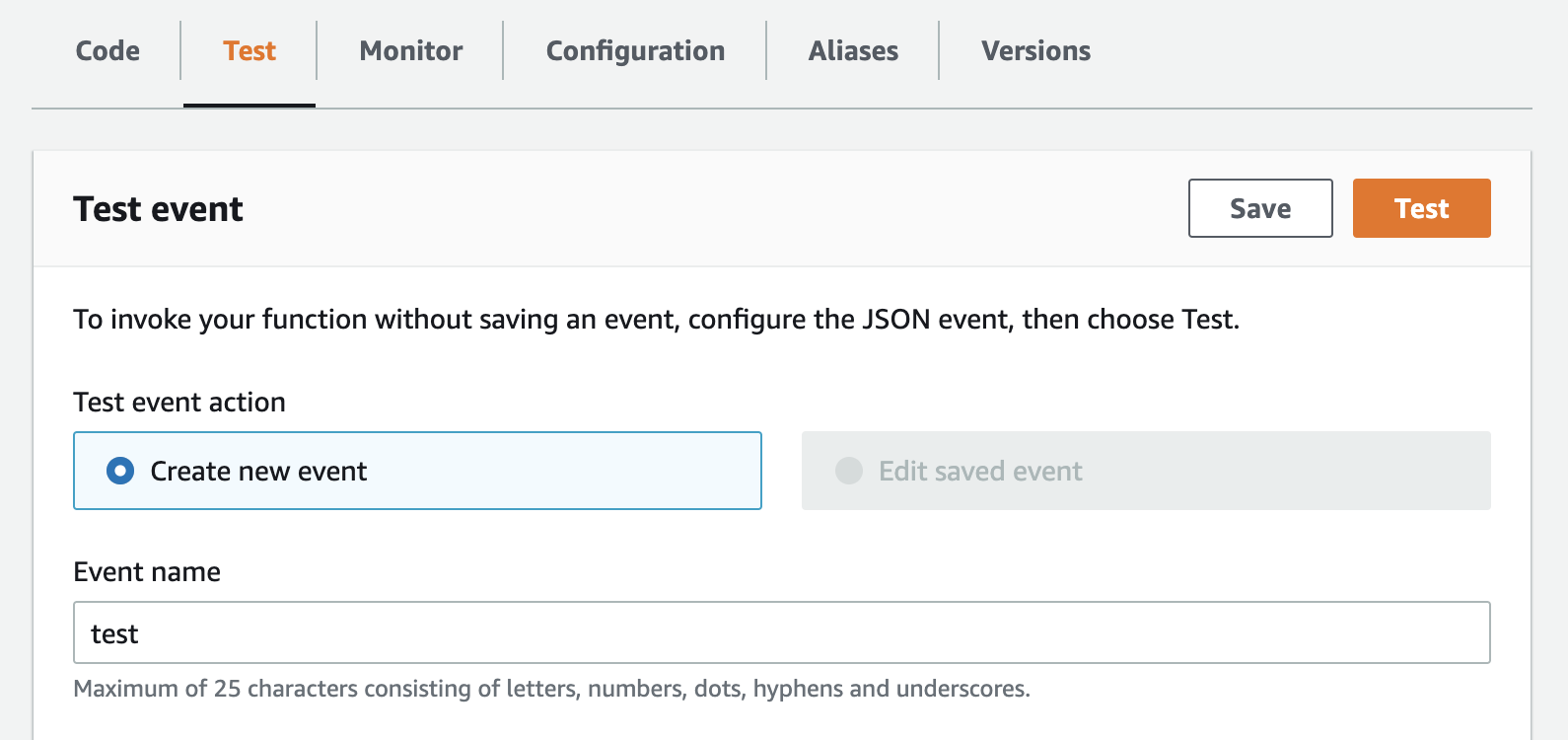
- If 'watchlistUpdater' and 'stockRanker' run as expected, you should see 'Execution result: succeeded'.
- When running the 'buyStocks' function, you will get an error--this is expected! If you go into the service map in Splunk APM, you will now see that all 4 of our functions are there, as well as the S3 bucket that some of them are talking to. There will be a red circle for 'buyStocks', indicating that an error occurred! This is especially useful if Lambda functions are scheduled to run automatically, in which case errors won't be immediately apparent without APM.

- In the APM service map, click on
buyStocksand selectTraceson the right. Find the trace with the error we just saw, and see if you can find the issue. If not, go to the next step. - Go back to the AWS Lambda page for 'buyStocks' and in 'index.py', uncomment line 13. Click
Deployto save your changes.
def lambda_handler(event, context):
s3 = boto3.client('s3')
alpaca_id = "PK6MU6XGW0KY0SSI402E"
alpaca_secret = "ZBvSlwEB8mk1DnbFZHCm18mkmeYdxVLu5nw6c8cR"
headers = {'APCA-API-KEY-ID':alpaca_id, 'APCA-API-SECRET-KEY':alpaca_secret}
rankings_file = s3.get_object(Bucket=os.environ['BUCKET_NAME'], Key='rankings.txt')
#stock_ranking = rankings_file['Body'].read().decode('utf-8').split(' ')
# ^^^ UNCOMMENT THE LINE ABOVE- Go to the
Testtab and run this function again. You should now see 'Execution result: succeeded', and another trace should pop up in Splunk APM as well (this time without any errors).
- Custom span tags are already added for 3 of the functions. Let's take a look at how to add custom span tags in the 4th one, 'getFinancials'. Open up the 'getFinancials' Lambda function.
- Under line 2, add a new line and write
from opentelemetry import trace. Under line 6, add with proper indentation
customizedSpan = trace.get_current_span()
customizedSpan.set_attribute("symbol", ticker);
customizedSpan.set_attribute("finnhub.token", "brqivm7rh5rc4v2pmq8g");The final result should look like this:
import json
import requests
from opentelemetry import trace
def lambda_handler(event, context):
ticker = event['symbol']
customizedSpan = trace.get_current_span()
customizedSpan.set_attribute("symbol", ticker);
customizedSpan.set_attribute("finnhub.token", "brqivm7rh5rc4v2pmq8g");Source: Instrument your application code to add tags to spans
- Click
Deployto save your changes. Now if you run 'stockRanker' and look at the traces for 'getFinancials' in Splunk APM, you'll see that each span has tags for the stock symbol being analyzed and the API token being used. This can help with troubleshooting, in case of any errors.
At this point, you've created a microservices app in AWS using a CloudFormation template, and instrumented it for Splunk APM. As you probably noticed, the process of instrumenting Lambda functions for APM is simple, but tedious. This is where CloudFormation can help. For this workshop, the process of creating the app was automated, but the instrumentation can be automated too.
To see what the final result should look like if you did everything correctly (and how the instrumentation process can be automated), create a stack with this CloudFormation template and run the 3 functions in the same order: 'watchlistUpdater', 'stockRanker', and 'buyStocks'.
Alternatively, the final state can be deployed with the following AWS CLI Command, executed from the root of this project directory:
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name <some-arbitrary-name> \
--template-body <local-path-to-'AlpacaTraderWorkshop.template'> \
--region us-east-1 \
--parameters ParameterKey=bucketName,ParameterValue=<some-arbitrary-s3-bucket-name> \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--role-arn <the-cfn-serivce-account-role-arn>S3 bucket names must be unique across the entirety of AWS, so make sure that when you create your CloudFormation stack, you enter a unique name in the 'bucketName' parameters field.
Ensure that the Splunk access token you have used has the right permissions for APM data.
Don't forget to indent your code the proper amount when adding custom span tags, or the Python code won't be able to run.
Make sure the environment name (OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES environment variable in Lambda configuration) is the same for all your functions in this app.