Agora Video with ARKit
This quick start enables you to integrate live video chat functionality from the Agora Video SDK using an iOS ARKit sample application.
This sample application demonstrates the following basic Agora SDK functionality:
- Sending a captured ARFrame image to a live video channel
- Rendering remote user ARSession video frames as SCNNodes
Prerequisites
- Agora.io developer account
- Xcode 9.0+
- Physical iPhone or iPad device (iOS simulator is not supported)
Quick Start
This section shows you how to prepare and build the Agora Video with the ARKit sample app.
Create an Account and Obtain an App ID
To build and run the sample application, first obtain an app ID:
- Create a developer account at agora.io. Once you finish the sign-up process, you are redirected to the dashboard.
- Navigate in the dashboard tree on the left to Projects > Project List.
- Copy the app ID that you obtained from the dashboard into a text file. You will use this when you launch the app.
Update and Run the Sample Application
-
Open
Agora-Video-With-ARKit.xcodeprojand edit theViewController.swiftfile. In theagoraKitdeclaration, update<#Your AppId#>with your app ID.fileprivate let agoraKit: AgoraRtcEngineKit = { let engine = AgoraRtcEngineKit.sharedEngine(withAppId: <#Your AppId#>, delegate: nil) ... return engine }()
-
Download the Agora Video SDK. Unzip the downloaded SDK package and copy the
libs/AograRtcEngineKit.frameworkfile into theAgora-Video-With-ARKitfolder.Note: Custom media device protocols are available in the Agora SDK 2.1.0.
-
Connect your iPhone/iPad device and run the project. Ensure a valid provisioning profile is applied or your project will not run.
Using the Sample Application
This sample application requires two devices and works in conjunction with the OpenLive sample application.
-
Run the sample application. The device will display a flashing red plane indicator. Move the device until you find a horizontal surface.
-
Touch the plane indicator to add a virtual display screen to your AR session. The virtual display screen streams the video from the remote user.
-
On a different device, launch the OpenLive sample application using the app ID and join the channel
agoraaras a broadcaster. The virtual display screen from the previous step displays the video broadcast sent from this OpenLive application.
Steps to Create the Sample
The iOS ARKit sample application manages the Agora SDK and ARKit functionality through three main Swift files: ViewController, ARVideoSource, and ARVideoRenderer.
- Add Assets
- Create the Storyboard
- Add Frameworks
- Create the ViewController
- Create the ARVideoSource
- Create the ARVideoRenderer
Add Assets
Create a folder named art.scnassets and add the displayer.scn scene file. The scene in displayer.scn contains a rectangular plane, which is used to display the video.
Create the Storyboard
Open the main.storyboard file in XCode's Interface Builder.
-
Add an
ARSCNViewobject to the stage. This will be the main view for the ARKit application.Note: This
ARSCNViewconnects to thesceneViewvariable inViewController. -
Add the
TapGestureRecogniserto theViewController. Set the referencing outlet connection to theARSCNViewobject created in Step 1.Note: The
TapGestureRecogniserconnects to thedoSceneViewTapped()selector method inViewController.
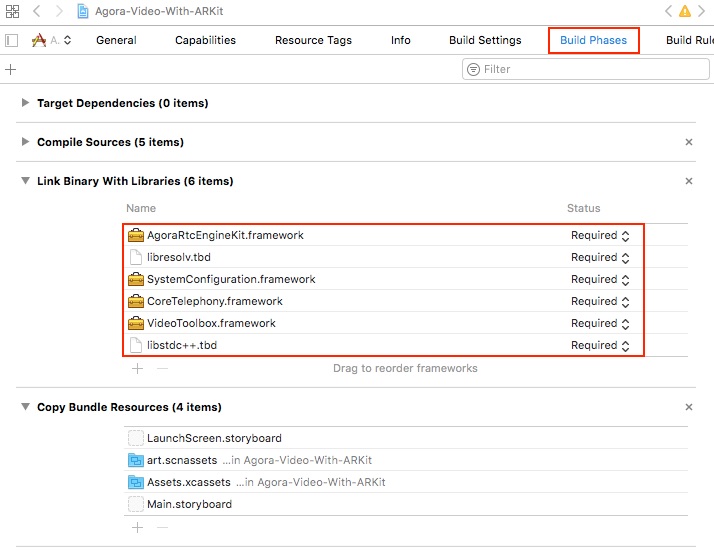
Add Frameworks
In the project's Build Phases window, ensure the following frameworks are added to the project:
AgoraRtcEngineKit.frameworklibresolv.tbdSystemConfiguration.frameworkCoreTelephony.frameworkVideoToolbox.frameworklibstdc++.tbd
Create the ViewController
The ViewController handles the main functionality for the sample application.
- Add Import Statements and Add Global Variables
- Initialize the Scene View and the Agora Kit
- Create Configuration, Run, and Pause ARSCene
- Handle the Tap Gesture Recognizer and Add the Agora Screen Display
- Handle the Unsupported Device Error
- Extend the ARSCNView Delegate
- Extend the ARSession Delegate
- Extend the Agora RTC Engine Delegate
Add Import Statements and Add Global Variables
Add Import Statements
Add the following frameworks to access the iOS UI components, AR features, and Agora SDK:
import UIKit
import ARKit
import AgoraRtcEngineKit| Framework name | Description |
|---|---|
UIKit |
Provides access to the iOS UI components |
ARKit |
Provides access to the iOS AR functionality |
AgoraRtcEngineKit |
Provides access to the Agora SDK |
Add and Initialize Global Variables
Initialize the AR video source videoSource and unusedScreenNodes, an array of unused scene nodes within the application.
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var sceneView: ARSCNView!
...
fileprivate let videoSource = ARVideoSource()
fileprivate var unusedScreenNodes = [SCNNode]()
...
}Initialize the Agora RTC engine agoraKit. Configure the Agora engine with:
| Configuration type | Method |
|---|---|
| Agora app ID | AgoraRtcEngineKit.sharedEngine() creates and initializes the Agora engine. Replace <#Your AppId#> with the app ID from the Agora website dashboard. |
| Video profile | engine.setVideoProfile() sets the video profile as a portrait view with 360P resolution .portrait360P. |
| Channel profile | engine.setChannelProfile() sets the channel profile to live broadcasting .liveBroadcasting. |
| Client role | engine.setClientRole() sets the role of the client as a broadcaster .broadcaster. |
| Enable video | engine.enableVideo() enables video. |
fileprivate let agoraKit: AgoraRtcEngineKit = {
let engine = AgoraRtcEngineKit.sharedEngine(withAppId: <#Your AppId#>, delegate: nil)
engine.setVideoProfile(.portrait360P, swapWidthAndHeight: false)
engine.setChannelProfile(.liveBroadcasting)
engine.setClientRole(.broadcaster)
engine.enableVideo()
return engine
}() Initialize the Scene View and the Agora Kit
In the application viewDidLoad() method, add the scene view settings.
Set the scene view delegate and scene view session delegate to self using sceneView.delegate and sceneView.session.delegate.
Enable the statistics for the scene view using sceneView.showsStatistics.
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
sceneView.delegate = self
sceneView.session.delegate = self
sceneView.showsStatistics = true
...
}Set the Agora SDK delegate to self using agoraKit.delegate and set its video source to videoSource using agoraKit.setVideoSource().
Join the Agora channel using agoraKit.joinChannel() and disable the application's idle timer using UIApplication.shared.isIdleTimerDisabled.
Note: The idle timer is disabled so the user stays connected, and the screen remains on.
agoraKit.delegate = self
agoraKit.setVideoSource(videoSource)
agoraKit.joinChannel(byToken: nil, channelId: "agoraar", info: nil, uid: 0, joinSuccess: nil)
UIApplication.shared.isIdleTimerDisabled = trueCreate Configuration, Run, and Pause ARSCene
The sample application requires the ARWorldTrackingConfiguration. This configuration uses the back-facing camera, tracks a device's orientation and position, and detects real-world surfaces.
Ensure that the AR tracking configuration is supported in the viewDidAppear() method using ARWorldTrackingConfiguration.isSupported.
-
If the configuration is not supported, display an error to the user using
showUnsupportedDeviceError(). -
If the configuration is supported, create the configuration and set the plane detection to horizontal using
configuration.planeDetection = .horizontal.Run the scene view session with the configuration using
sceneView.session.run().
override func viewDidAppear(_ animated: Bool) {
super.viewDidAppear(animated)
guard ARWorldTrackingConfiguration.isSupported else {
showUnsupportedDeviceError()
return
}
let configuration = ARWorldTrackingConfiguration()
configuration.planeDetection = .horizontal
sceneView.session.run(configuration)
}
In the viewWillDisappear() method, pause the scene view session using sceneView.session.pause():
override func viewWillDisappear(_ animated: Bool) {
super.viewWillDisappear(animated)
sceneView.session.pause()
}
Handle the Tap Gesture Recognizer and Add the Agora Screen Display
The doSceneViewTapped() method adds the Agora display view to the AR scene. This method is applied to the tap gesture recognizer created in the storyboard.
@IBAction func doSceneViewTapped(_ recognizer: UITapGestureRecognizer) {
...
}Conduct a hit test on the tap, to ensure it hits a real-world existing plane using the sceneView.hitTest(). If the tap is unsuccessful, terminate the method with a return.
let location = recognizer.location(in: sceneView)
guard let result = sceneView.hitTest(location, types: .existingPlane).first else {
return
}If the tap is successful:
- Create a
SCNScenewith thedisplayer.scnasset. - Set the root node of the scene.
Apply the worldTransform of the tapped result to the scene's rootNode using rootNode.simdTransform = result.worldTransform. This aligns rootNode with the real-world scene.
let scene = SCNScene(named: "art.scnassets/displayer.scn")!
let rootNode = scene.rootNode
rootNode.simdTransform = result.worldTransform
sceneView.scene.rootNode.addChildNode(rootNode)Find the scene's displayer node and append its screen to the unused screen nodes array unusedScreenNodes.append():
let displayer = rootNode.childNode(withName: "displayer", recursively: false)!
let screen = displayer.childNode(withName: "screen", recursively: false)!
unusedScreenNodes.append(screen) Handle the Unsupported Device Error
The showUnsupportedDeviceError() method ensures the device supports 6DOF world tracking and alerts the user if world tracking is not supported.
Create a UIAlertController, apply an OK button, and display the alert to the user using present().
private func showUnsupportedDeviceError() {
// This device does not support 6DOF world tracking.
let alertController = UIAlertController(
title: "ARKit is not available on this device.",
message: "This app requires world tracking, which is available only on iOS devices with the A9 processor or later.",
preferredStyle: .alert
)
alertController.addAction(UIAlertAction(title: "OK", style: .default, handler: nil))
present(alertController, animated: true, completion: nil)
}Extend the ARSCNView Delegate
Create an extension to the ARSCNViewDelegate. The renderer() method triggers when a node is added to the scene.
extension ViewController: ARSCNViewDelegate {
func renderer(_ renderer: SCNSceneRenderer, didAdd node: SCNNode, for anchor: ARAnchor) {
...
}
}When a node is added, create a SCNBox and apply a red texture using plane.firstMaterial?.diffuse.contents = UIColor.red:
guard let planeAnchor = anchor as? ARPlaneAnchor else {
return
}
let plane = SCNBox(width: CGFloat(planeAnchor.extent.x),
height: CGFloat(planeAnchor.extent.y),
length: CGFloat(planeAnchor.extent.z),
chamferRadius: 0)
plane.firstMaterial?.diffuse.contents = UIColor.red Create a new SCNNode using the geometry from the plane and add this planeNode as a child node to node.
Complete the render() method by animating a fade-out action on planeNode using planeNode.runAction().
let planeNode = SCNNode(geometry: plane)
node.addChildNode(planeNode)
planeNode.runAction(SCNAction.fadeOut(duration: 1))Extend the ARSession Delegate
Create an extension to the ARSessionDelegate. The session() method triggers when an ARFrame is updated within an ARSession.
When the frame updates, send a captured image buffer to the video source using videoSource.sendBuffer().
extension ViewController: ARSessionDelegate {
func session(_ session: ARSession, didUpdate frame: ARFrame) {
videoSource.sendBuffer(frame.capturedImage, timestamp: frame.timestamp)
}
}Extend the Agora RTC Engine Delegate
Create an extension to the AgoraRtcEngineDelegate. This delegate handle listeners for the Agora RTC engine through a series of rtcEngine() methods.
extension ViewController: AgoraRtcEngineDelegate {
...
}- didOccurError Listener
- didOccurWarning Listener
- didJoinChannel Listener
- didRejoinChannel Listener
- didJoinedOfUid Listener
didOccurError Listener
The didOccurError event listens for errors from the Agora RTC engine. The sample application logs the error code value specified by errorCode.rawValue.
func rtcEngine(_ engine: AgoraRtcEngineKit, didOccurError errorCode: AgoraErrorCode) {
print("error: \(errorCode.rawValue)")
}didOccurWarning Listener
The didOccurWarning event listens for warnings from the Agora RTC engine. The sample application logs the warning code value specified by warningCode.rawValue.
func rtcEngine(_ engine: AgoraRtcEngineKit, didOccurWarning warningCode: AgoraWarningCode) {
print("warning: \(warningCode.rawValue)")
}didJoinChannel Listener
The didJoinChannel event listens for users that join the channel. The sample application logs the user's ID uid.
func rtcEngine(_ engine: AgoraRtcEngineKit, didJoinChannel channel: String, withUid uid: UInt, elapsed: Int) {
print("did join channel with uid:\(uid)")
}didRejoinChannel Listener
The didRejoinChannel event listens for users that rejoin the channel. The sample application logs a general did rejoin channel text.
func rtcEngine(_ engine: AgoraRtcEngineKit, didRejoinChannel channel: String, withUid uid: UInt, elapsed: Int) {
print("did rejoin channel")
}didJoinedOfUid Listener
The didJoinedOfUid event listens for users that join an Agora session. This event listener sets the display for the user.
-
The sample application logs the user ID
uidof the user and checks if theunusedScreenNodesarray is empty. -
If
unusedScreenNodesis not empty, the first screen node is removed usingunusedScreenNodes.removeFirst(). -
Create an
ARVideoRendererand apply thescreenNodeas therenderNodeusingrenderer.renderNode. -
Set the
rendereras the remote video renderer for the user usingagoraKit.setRemoteVideoRenderer().
func rtcEngine(_ engine: AgoraRtcEngineKit, didJoinedOfUid uid: UInt, elapsed: Int) {
print("did joined of uid: \(uid)")
guard !unusedScreenNodes.isEmpty else {
return
}
let screenNode = unusedScreenNodes.removeFirst()
let renderer = ARVideoRenderer()
renderer.renderNode = screenNode
agoraKit.setRemoteVideoRenderer(renderer, forUserId: uid)
}Create the ARVideoSource
- Add Import Statements and Define Global Variables
- Add Initialization, Start, Stop, and Dispose Methods
- Add Buffer Methods
Add Import Statements and Define Global Variables
Add the UIKit and AgoraRtcEngineKit frameworks. The UIKit framework provides access to iOS components, and the AgoraRtcEngineKit provides access to the Agora SDK functionality.
import UIKit
import AgoraRtcEngineKitDefine the global variable AgoraVideoFrameConsumer to manage video buffering:
class ARVideoSource: NSObject, AgoraVideoSourceProtocol {
var consumer: AgoraVideoFrameConsumer?
...
}Add Initialization, Start, Stop, and Dispose Methods
The sample application adds empty methods for convenience. Use these to debug and add additional functionality to your application.
func shouldInitialize() -> Bool { return true }
func shouldStart() { }
func shouldStop() { }
func shouldDispose() { }| Method | Description |
|---|---|
shouldInitialize() |
Triggers before the Agora engine initializes |
shouldStart() |
Triggers before the Agora engine starts |
shouldStop() |
Triggers before the Agora engine stops |
shouldDispose() |
Triggers before the Agora engine is disposed |
Add Buffer Methods
The bufferType() and sendBuffer() methods handle buffering for the Agora video.
The bufferType() returns the AgoraVideoBufferType type with a static value of .pixelBuffer.
func bufferType() -> AgoraVideoBufferType {
return .pixelBuffer
}The sendBuffer() method sends the CVPixelBuffer and associated TimeInterval time stamp to the Agora video frame consumer using consumer?.consumePixelBuffer().
func sendBuffer(_ buffer: CVPixelBuffer, timestamp: TimeInterval) {
let time = CMTime(seconds: timestamp, preferredTimescale: 10000)
consumer?.consumePixelBuffer(buffer, withTimestamp: time, rotation: .rotation90)
}Create the ARVideoRenderer
- Add Import Statements
- Define Global Variables
- Extend the Agora Video Sync Protocol
- Extend the ARVideo Renderer
Add Import Statements
Add the UIKit, MetalKit, SceneKit, and AgoraRtcEngineKit frameworks.
import Foundation
import MetalKit
import SceneKit
import AgoraRtcEngineKit| Framework name | Description |
|---|---|
UIKit |
Provides access to the iOS UI components |
MetalKit |
Provides access to the iOS Metal functionality |
SceneKit |
Provides access to the iOS 3D components and functionality |
AgoraRtcEngineKit |
Provides access to the Agora SDK |
Define Global Variables
Define the global textures yTexture, uTexture, vTexture, and rgbTexture. These are used as textures for rendering.
class ARVideoRenderer : NSObject {
fileprivate var yTexture: MTLTexture?
fileprivate var uTexture: MTLTexture?
fileprivate var vTexture: MTLTexture?
fileprivate var rgbTexture: MTLTexture?
...
}Create a MTLCreateSystemDefaultDevice, which references the system default Metal device.
Define a MTLCommandQueue, which queues buffers for the device to execute.
Define a default MTLLibrary, which contains Metal shading language source code.
fileprivate let device = MTLCreateSystemDefaultDevice()
fileprivate var commandQueue: MTLCommandQueue?
fileprivate var defaultLibrary: MTLLibrary?Define threadsPerThreadgroup and threadgroupsPerGrid sizes using MTLSizeMake.
Define a MTLComputePipelineState object, which contains the compute function and configuration state for the device.
fileprivate var threadsPerThreadgroup = MTLSizeMake(16, 16, 1)
fileprivate var threadgroupsPerGrid = MTLSizeMake(128, 96, 1)
fileprivate var pipelineState: MTLComputePipelineState?Complete the ARVideoRenderer class by defining an optional SCNNode:
var renderNode: SCNNode?Extend the Agora Video Sync Protocol
Create an extension to the AgoraVideoSinkProtocol. This protocol handles listeners for the Agora RTC engine and adds rendering functionality:
extension ARVideoRenderer: AgoraVideoSinkProtocol {
...
}- Listener Methods
- shouldInitialize() Method
- shouldDispose() Method
- bufferType() and pixelFormat() Methods
- renderRawData() Method
Listener Methods
The sample application adds listeners to allow additional functionality to your application.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
shouldInitialize() |
Triggers before the Agora engine initializes |
shouldStart() |
Triggers before the Agora engine starts |
shouldStop() |
Triggers before the Agora engine stops |
shouldDispose() |
Triggers before the Agora engine is disposed |
func shouldInitialize() -> Bool {
...
}
func shouldStart() {
}
func shouldStop() {
}
func shouldDispose() {
...
}shouldInitialize() Method
The shouldInitialize() method sets the default library for the device using device?.makeDefaultLibrary().
The Metal shading language source code from defaultLibrary is applied to the device using device.makeComputePipelineState() and creates the device's commandQueue.
func shouldInitialize() -> Bool {
defaultLibrary = device?.makeDefaultLibrary()
if let device = device, let function = defaultLibrary?.makeFunction(name: "writeRGBFromYUV") {
pipelineState = try? device.makeComputePipelineState(function: function)
}
commandQueue = device?.makeCommandQueue()
return true
}shouldDispose() Method
The shouldDispose() method clears all the global textures, setting them to their default states:
func shouldDispose() {
yTexture = nil
uTexture = nil
vTexture = nil
rgbTexture = nil
}bufferType() and pixelFormat() Methods
The bufferType() and pixelFormat() methods define the type of buffer and pixel format for the Agora engine.
The bufferType() returns a static value of .pixelBuffer.
The pixelFormat() returns a static value of .I420.
func bufferType() -> AgoraVideoBufferType {
return .rawData
}
func pixelFormat() -> AgoraVideoPixelFormat {
return .I420
}renderRawData() Method
The renderRawData() method creates the global textures yTexture, uTexture, vTexture, and rgbTexture.
rgbTexture is applied to the geometry of the renderNode using node.geometry?.firstMaterial?.diffuse.contents = rgbTexture.
Render the node with the rgbTexture by calling the renderRGBTexture() method.
func renderRawData(_ rawData: UnsafeMutableRawPointer, size: CGSize, rotation: AgoraVideoRotation) {
guard let node = renderNode else {
return
}
let width = Int(size.width)
let height = Int(size.height)
yTexture = createTexture(withData: rawData,
width: width,
height: height)
uTexture = createTexture(withData: rawData + width * height,
width: width / 2,
height: height / 2)
vTexture = createTexture(withData: rawData + width * height * 5 / 4,
width: width / 2,
height: height / 2)
rgbTexture = createEmptyRGBTexture(width: width, height: height)
node.geometry?.firstMaterial?.diffuse.contents = rgbTexture
renderRGBTexture()
}Extend the ARVideo Renderer
Create an extension to the ARVideoRenderer. This renderer creates textures for video rendering.
private extension ARVideoRenderer {
...
}createTexture() Method
The createTexture() method creates a MTLTexture from a MTLTextureDescriptor using device?.makeTexture().
The texture is updated with the UnsafeMutableRawPointer information from the createTexture() method using texture?.replace().
func createTexture(withData data: UnsafeMutableRawPointer, width: Int, height: Int) -> MTLTexture? {
let descriptor = MTLTextureDescriptor.texture2DDescriptor(pixelFormat: .r8Uint,
width: width,
height: height,
mipmapped: false)
let texture = device?.makeTexture(descriptor: descriptor)
texture?.replace(region: MTLRegionMake2D(0, 0, width, height),
mipmapLevel: 0,
withBytes: data,
bytesPerRow: width)
return texture
}createEmptyRGBTexture() Method
The createEmptyRGBTexture() method creates and returns an empty MTLTexture of a specified width and height.
A MTLTextureDescriptor with a usage of .shaderWrite and .shaderRead is created, allowing for the texture to be read and written to.
The rgbTexture is created from a rgbaDescriptor using device?.makeTexture().
func createEmptyRGBTexture(width: Int, height: Int) -> MTLTexture? {
let rgbaDescriptor = MTLTextureDescriptor.texture2DDescriptor(pixelFormat: .rgba16Float,
width: width,
height: height,
mipmapped: false)
rgbaDescriptor.usage = [.shaderWrite, .shaderRead]
let rgbTexture = device?.makeTexture(descriptor: rgbaDescriptor)
return rgbTexture
}renderRGBTexture() Method
The renderRGBTexture() method encodes the textures for the buffer.
The encoder is created from the commandQueue buffer using the buffer.makeComputeCommandEncoder().
The encoding process for the encoder includes:
- Applying the
stateusingencoder.setComputePipelineState() - Applying textures using
encoder.setTexture() - Dispatching thread groups using
encoder.dispatchThreadgroups()
Complete the encoding process with the encoder.endEncoding() method and commit the buffer using buffer.commit().
func renderRGBTexture() {
guard let state = pipelineState,
let buffer = commandQueue?.makeCommandBuffer(),
let encoder = buffer.makeComputeCommandEncoder() else {
return
}
encoder.setComputePipelineState(state)
encoder.setTexture(yTexture, index: 0)
encoder.setTexture(uTexture, index: 1)
encoder.setTexture(vTexture, index: 2)
encoder.setTexture(rgbTexture, index: 3)
encoder.dispatchThreadgroups(threadgroupsPerGrid,
threadsPerThreadgroup: threadsPerThreadgroup)
encoder.endEncoding()
buffer.commit()
}Resources
- Complete API documentation is available at the Document Center.
License
This software is licensed under the MIT License (MIT). View the license.