My first project undertaking in C language
TOPIC: Comparitive analysis of Un-informed Search Algorithms
Implementation of
- DFS
- BFS
- DLS
- IDDFS, all these algorithms in C language and their comparison with respect to time and space complexity.
Set of all possible states for a given problem is known as state space of the problem.
There are two types of search:
- Un-informed Search
- Informed Search
These are such problems where we don't know any domain specific information. So we have to search without any additional knowledge of the target state. Hit and trial method.
In this type of problems we have prior knowledge of our target state like functions to guide the search proceedures. So we will be able to get to the target state.
Note: Knowledge in the previous context means "Derived from experience,Stores experience and change the search rules further"".
For Searching, We need
- Initial state description of problem.
- Set of legal operators[Conditions].
- Final (or) goal state.
- Go through the following links for understanding of the following algorithms.
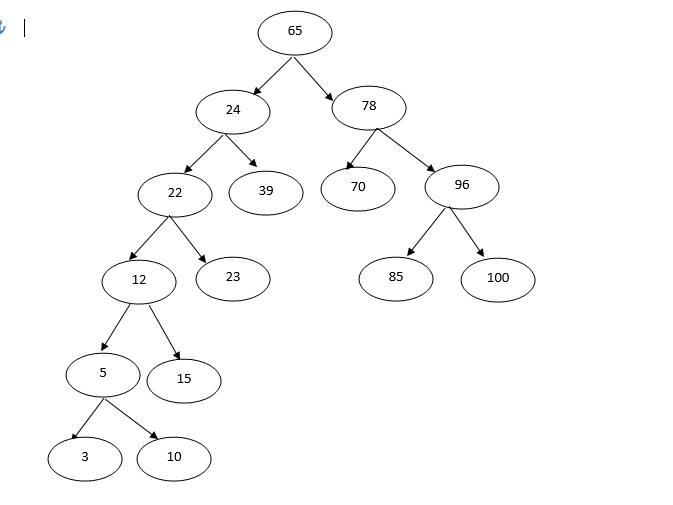
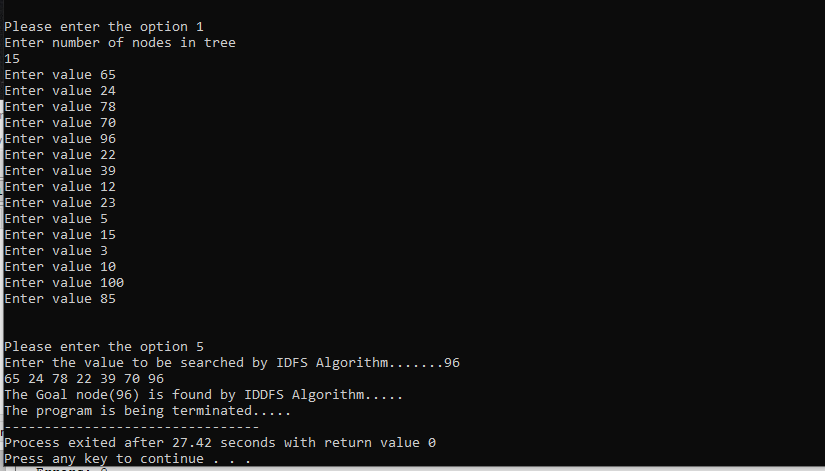
We have entered the following data: 65,24,78,70,96,22,39,12,23,5,15,3,10,100,85.
Now, we will perform search of a particular value with all four of the algorithms.
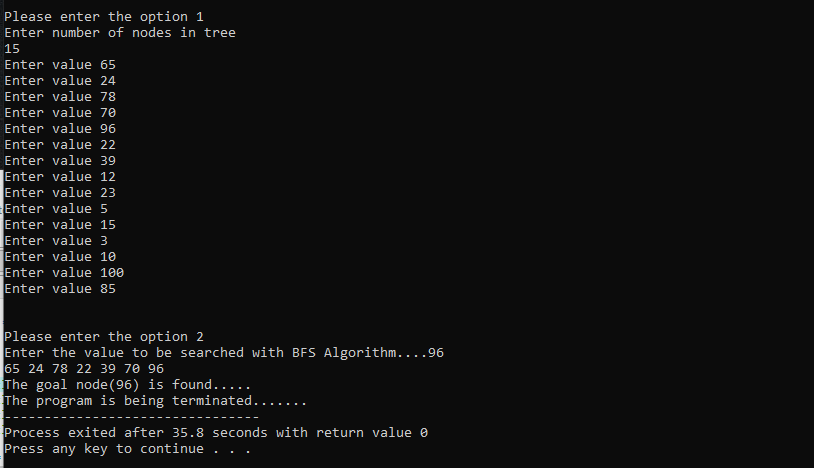
The time taken to find (96) is 35.8 sec with BFS Algorithm.
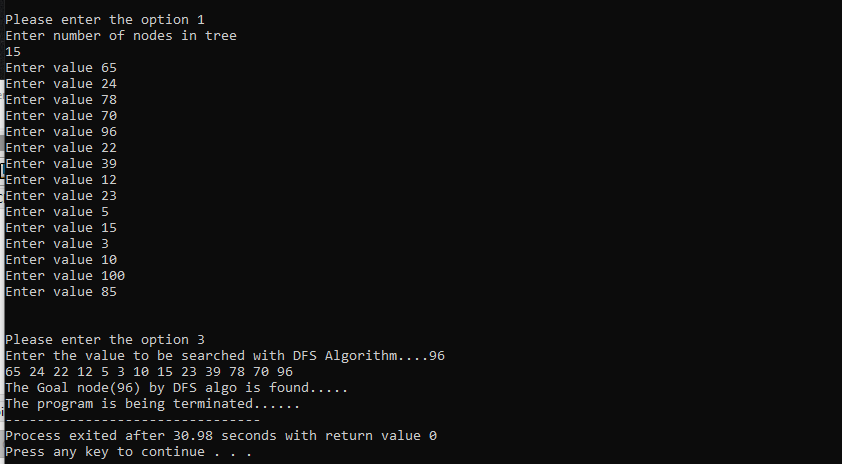
The time taken to find(96) is 30.98 sec with DFS Algorithm.
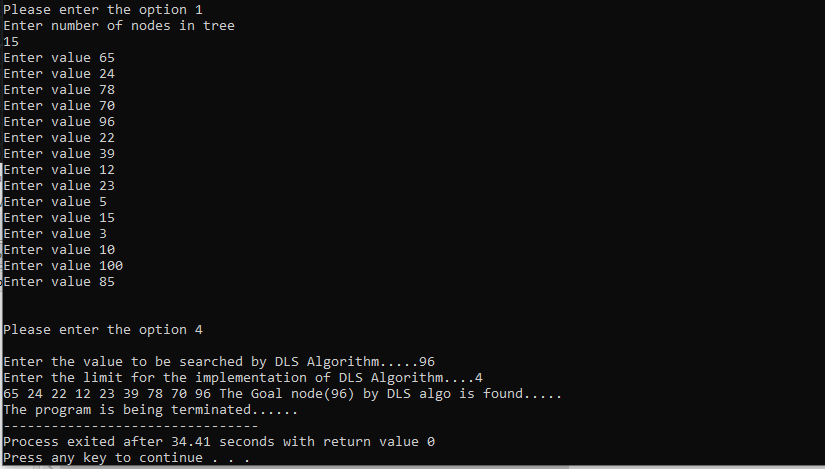
The time taken to find(96) is 34.41 sec with DLS Algorithm.
The time taken to find(96) is 27.42 sec with IDDFS Algorithm.
Alright, By seeing the different time taken by different algorithms you can see the optimized algorithm, but it's not necessary that IDDFS algorithm will give you the optimized result always.
- This was applied for large datasets where there may be infinite long trees and might take a lot of time to traverse in such cases IDDFS algorithm will give you the best result.
- For small size of data you can use DFS, and if you know the goal whether it lies on left branch (or) right branch you can select the corresponding algorithm.
- If the goal lies on left side then select DFS Algorithm, else you can select the BFS Algorithm to get the optimized result. And again BFS has a higher space complexity compared to DFS algorithm, So if space is a constraint then avoid using BFS Algorithm.
Note: If you have any more insight on this you can pull request. Will be happy to see your contribution :)
This is an open project and contribution in all forms are welcomed. Please follow these Contribution Guidelines
Adhere to the GitHub specified community code.