PEFT-SP: Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning on Large Protein Language Models Improves Signal Peptide Prediction
PEFT-SP: Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning on Large Protein Language Models Improves Signal Peptide Prediction
Shuai Zeng, Duolin Wang, Dong Xu
Paper: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.11.04.565642v1
This repository contains code and well-trained weights for PEFT-SP using LoRA, Prompt Tuning and Adapter Tuning with ESM-2 model family. The PEFT-SP using LoRA and ESM2-3B backbone outperforms all existing models in Signal Peptide prediction task.
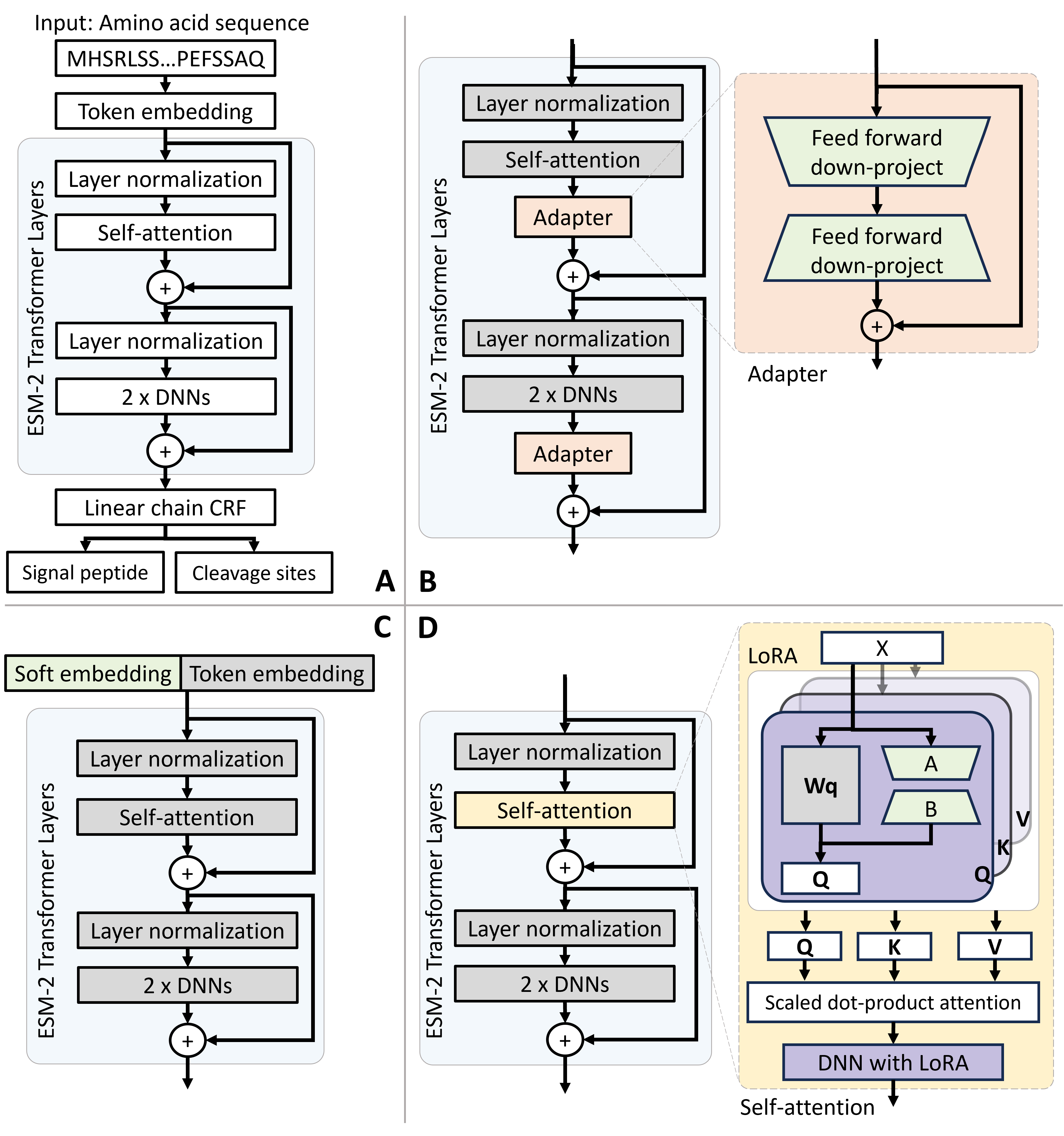 Fig. 1. The architectures for the ESM-2 model and PEFT-SP using different PEFT modules. The light green modules are tunable during training, while the grey modules are fixed. (A) The ESM-2 backbone model uses amino acid sequences to SP and CS. (B) PEFT-SP using Adapter Tuning contains a bottleneck architecture. (C) PEFT-SP using Prompt Tuning appends soft embedding into token embedding. (D) PEFT-SP using LoRA adds trainable rank decomposition matrices into the selfattention layer.
Fig. 1. The architectures for the ESM-2 model and PEFT-SP using different PEFT modules. The light green modules are tunable during training, while the grey modules are fixed. (A) The ESM-2 backbone model uses amino acid sequences to SP and CS. (B) PEFT-SP using Adapter Tuning contains a bottleneck architecture. (C) PEFT-SP using Prompt Tuning appends soft embedding into token embedding. (D) PEFT-SP using LoRA adds trainable rank decomposition matrices into the selfattention layer.
- Anaconda3 required (tested on version 4.12.0)
- Download and unzip this GitHub repo.
- Create and activate the conda environment.
conda env create -f PEFT_SP_env.yaml
conda activate PEFT_SP_env
The training script is in scripts/predict.py. The examples for the prediciton of PEFT-SP are in ./run_prediction.sh
An example to prediction of PEFT-SP using LoRA with ESM2-150M is shown below:
python scripts/predict.py --data data/prediction_testcase.fasta --output_file ./prediction.csv --model_architecture esm2_t30_150M_UR50D --model_filename testruns/BestLora/ESM2-150M/test_0_valid_1/model.pt --constrain_crf --average_per_kingdom --sp_region_labels --prompt_method NoPrompt --prompt_len 0 --num_end_lora_layers 33 --num_lora_r 8 --num_lora_alpha 8
An example of test data is in data/prediction_testcase.fasta and also shown in below:
>O28846|ARCHAEA|NO_SP|0
MTMTLAKRFTAEVVGTFILVFFGPGAAVITLMIANGADKPNEFNIGIGALGGLGDWFAIGMAFALAIAAV
>Q12UD6|ARCHAEA|SP|1
MKTKGIRMAALFMAMLVVSMFAVAPAMACAPQEPIDKSDEKKVLKVVSDEISLPEEYTISNNPDTDGFIF
>P58300|ARCHAEA|LIPO|0
MRRATYAFALLAILVLGVVASGCIGGGTTTPTQTSPATQPTTTQTPTQTETQAVECGSGKVVIWHAMQPN
Its prediction results is shown in below:
sp_type_id sp_type_name cv_position sp_type_probabilities
0 0 NO_SP -1 [1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
1 1 SP 8 [0.005, 0.975, 0.005, 0.005, 0.008, 0.002]
2 1 LIPO 32 [0.003, 0.336, 0.652, 0.003, 0.005, 0.002]
The training script is in scripts/train.py. The ESM-2 model would be downloaded in ESM2_models. The examples to train the PEFT-SP using LoRA, Prompt Tuning and Adapter Tuning using ESM-2 model family are in ./run_peft_sp.sh.
An example to train PEFT-SP using LoRA with ESM2-150M is shown below:
python scripts/train.py --data data/small_data/small_dataset_30.fasta --test_partition 0 --validation_partition 1 --output_dir testruns --experiment_name ESM2-150M --remove_top_layers 1 --sp_region_labels --region_regularization_alpha 0.5 --constrain_crf --average_per_kingdom --batch_size 20 --epochs 3 --optimizer adamax --lr 0.005 --freeze_backbone --prompt_len 0 --num_end_lora_layers 25 --num_lora_r 8 --num_lora_alpha 8
The evaluation script is in scripts/cross_validate.py. The examples for the evaluation of PEFT-SP are in ./run_cross_validation.sh
An example to evaluate PEFT-SP using LoRA with ESM2-150M is shown below:
python scripts/cross_validate.py --data data/small_data/small_dataset_30.fasta --model_base_path testruns/BestLora/ESM2-150M --n_partitions 3 --output_file testruns/BestLora/ESM2-150M/crossval_metrics.csv --model_architecture esm2_t30_150M_UR50D --constrain_crf --average_per_kingdom --sp_region_labels --prompt_method NoPrompt --prompt_len 0 --num_end_lora_layers 25 --num_lora_r 8 --num_lora_alpha 8
If you find PEFT-SP useful in your research, we ask that you cite the paper:
@article {Zeng2023.11.04.565642,
author = {Shuai Zeng and Duolin Wang and Dong Xu},
title = {PEFT-SP: Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning on Large Protein Language Models Improves Signal Peptide Prediction},
elocation-id = {2023.11.04.565642},
year = {2023},
doi = {10.1101/2023.11.04.565642},
publisher = {Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory},
abstract = {Signal peptides (SP) play a crucial role in protein translocation in cells. The development of large protein language models (PLMs) provides a new opportunity for SP prediction, especially for the categories with limited annotated data. We present a Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) framework for SP predic- tion, PEFT-SP, to effectively utilize pre-trained PLMs. We implanted low-rank adaptation (LoRA) into ESM- 2 models to better leverage the protein sequence evolutionary knowledge of PLMs. Experiments show that PEFT-SP using LoRA enhances state-of-the-art results, leading to a maximum MCC2 gain of 0.372 for SPs with small training samples and an overall MCC2 gain of 0.048. Furthermore, we also employed two other PEFT methods, i.e., Prompt Tunning and Adapter Tuning, into ESM-2 for SP prediction. More elaborate ex- periments show that PEFT-SP using Adapter Tuning can also improve the state-of-the-art results with up to 0.202 MCC2 gain for SPs with small training samples and an overall MCC2 gain of 0.030. LoRA requires fewer computing resources and less memory compared to Adapter, making it possible to adapt larger and more powerful protein models for SP prediction.Competing Interest StatementThe authors have declared no competing interest.},
URL = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2023/11/05/2023.11.04.565642},
eprint = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2023/11/05/2023.11.04.565642.full.pdf},
journal = {bioRxiv}
}This source code is licensed under the MIT license found in the LICENSE file
in the root directory of this source tree.