There is an order of operations with running an NFS server in Kubernetes.
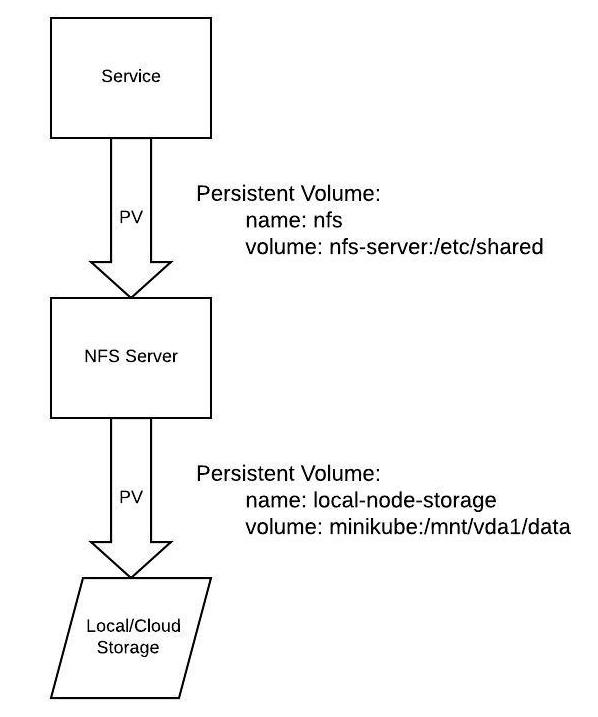
Below is an architecture overview of the setup, which is based off of the example in the kubernetes git repo.
NOTE: The persistent volume for local-node-storage runs out of space pretty quickly when mounted within minikube, so I have adjusted the mount point for local development to be outside of the minikube vm on the host computer. Continue reading and/or view nfs/set_local_pv for more details.
All the commands used to run the NFS server, as well as some other helper commands, can be found in the Makefile.
Run these commands using the make command, proceeded by the command you want to run in the Makefile.
Continue reading for how to run the NFS server.
These commands automate the manual steps in the Step-by-step section.
Setup:
make deploy_nfs-allTear down:
make delete_nfs-allTo not run into errors, you will want to make sure the make command is on your system, as well as install minikube and docker
A small test file is also included, located in nfs/nfs_test. This is used to verify that the service can install and run.
Run it with the following command: make test_nfs
- The first step is to generate the local persistent volume and persistent volume claim that will be consumed by the NFS server.
make deploy_local-pvThis first persistent volume (PV) is a local hostPath volume that mounts within minikube. This is for development use only and should be replaced by a cloud-backed storage persistent volume claim when run in production. This local PV is mounted to the NFS server pod as the main volume storage for the NFS server.
- The next step is to deploy the NFS server:
make deploy_nfs-serverThis generates an NFS-server based on the Dockerfile and init script in this directory, as well as a corresponding service for the pod.
- Now it is time to create the second PV, which is specifically an NFS persistent volume that takes in a running NFS server IP and file mount location to expose to other services.
make deploy_nfs-pvA look at what is happening in this command:
Because we are running our own NFS server within Kubernetes, we only know the IP of the server after it is running, so at this step we need to get the server IP, you can do this manually by running:
kubectl get svcThe server IP for the nfs-server will be listed under the ClusterIP column. This is then copied into the deployment/nfs-pv.yml file in the nfs server field, replacing {{nfs-server.default.svc.cluserIP}}.
The make command (make deploy_nfs-pv) for applying the deployment/nfs-pv.yml file programmatically grabs the Cluster IP of the running nfs-server and creates a tmp file to apply. Similarly the make delete_nfs-pv command removes this tmp file and deletes the k8 resources in that file.
A note about Persistent Volume Claims (PVC) that are grouped with the persistent volumes; they are the method by which pods make requests to access volumes.
- The final step to apply the NFS server system to work with a pod is to add the PVC to the pod setup as a volume mount:
spec:
containers:
- name: <pod-name>
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs
mountPath: "/etc/shared" #choose whatever mount path for the pod
volumes:
- name: nfs
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: nfsIt is important to verify that the system is working as expected, but how do you do that?
- Check that the local persistent volume is mounted to the NFS server by logging into the NFS server and create a file.
# log into the nfs-server pod (get the full name from `kubectl get pod` command)
kubectl exec -it <nfs-server-full-pod-name> -- sh
cd /etc/shared
touch unicorns.txtunicorns.txt was just created in the nfs-server mount point, now verify that it is also visible from the local mount point on your computer.
The local mount point was generated from the nfs/set_local_pv script. The location is one of the following, depending on OS:
mount_point=
/Users/${user_id}/mounted-pv-data (mac)
/home/${user_id}/mounted-pv-data (linux)Check this location:
ls $mount_point
# you should see the following output if all was set up correctly:
unicorns.txtSubsequent pods that are generated can now add this volume mount and have access to this shared location across pods.
volumeMounts:
- name: local
mountPath: "/etc/shared"Swap out the local-pv.yml for a cloud backend when moving off of local development.
Checking running kubernetes services:
kubectl get pod
kubectl get svc
kubectl get pv
kubectl get pvcGet more details on a specific service:
kubectl describe pod <pod-name>
kubectl describe svc <svc-name>
...etcLogging into a pod to run commands and check things out:
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> shIf a PV or PVC hangs during deletion, you can manually edit and remove the finalizers to release them:
kubectl patch pvc pvc_name -p '{"metadata":{"finalizers":null}}'
kubectl patch pv pv_name -p '{"metadata":{"finalizers":null}}'See this issue thread for more details.
Check connectivity to the server and available exports:
# log into server or client pod
showmount -e <nfs-server-ip>Test manual mounting if there are volume mounting issues:
# log into server pod - test that mounting is working at the server network level
mount -v 127.0.0.1:/mnt /client/mnt
# show available mounts
mount# log into client pod - test that mounting can happen from the client pod to the NFS server pod
mount -v <nfs-server-cluster-ip>:/ /etc/shared
# show available mounts
mountCheck that all rpc services are running as expected:
# log into NFS server
rpcinfo -p
# should give output similar to the following:
program vers proto port service
100000 4 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 3 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 4 udp 111 portmapper
100000 3 udp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs
100005 1 udp 48988 mountd
100005 1 tcp 46749 mountd
100005 2 udp 45417 mountd
100005 2 tcp 40393 mountd
100005 3 udp 58823 mountd
100005 3 tcp 50841 mountd
The vers column relates to the NFS version. We are running NFSv4.
You can also check what version is being used by running the mount command.
Also, a helpful article on NFS Troubleshooting. And on NFSv4.