Adriano D'Alessandro, Ali Mahdavi-Amiri & Ghassan Hamarneh
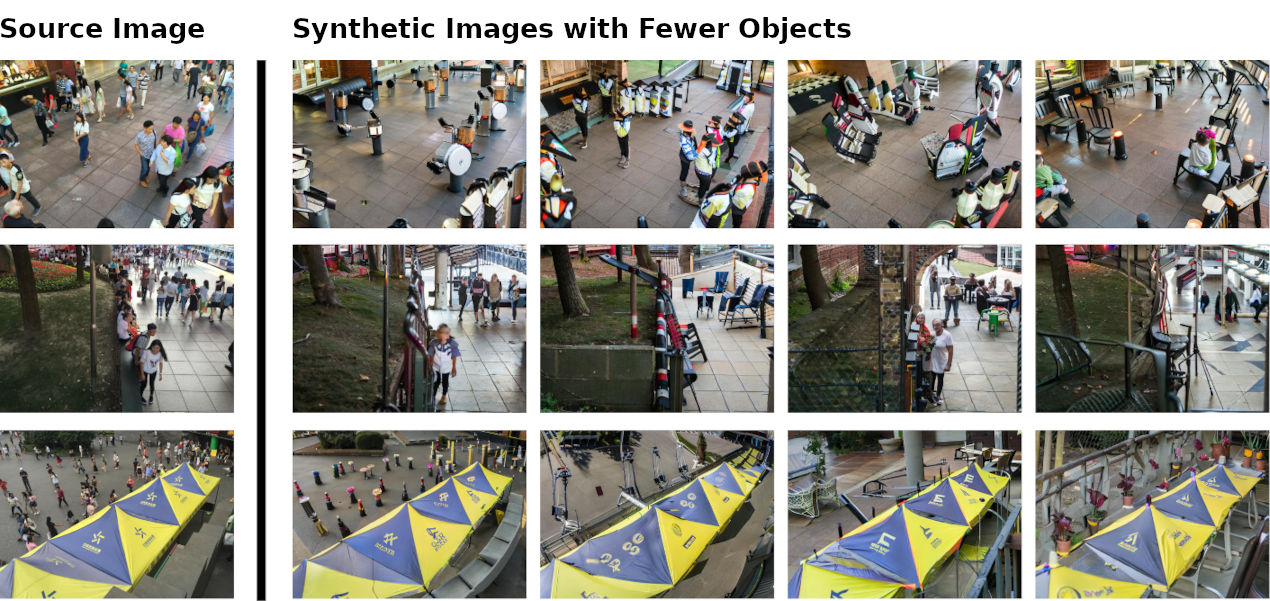
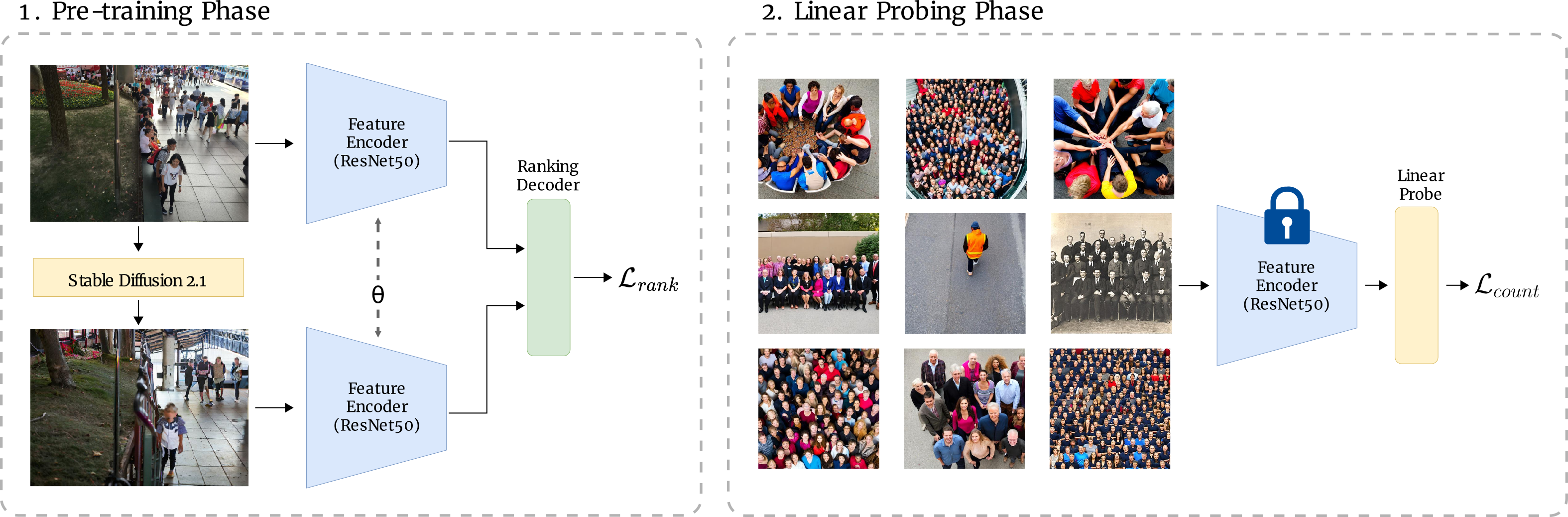
Crowd counting is a critical task in computer vision, with several important applications. However, existing counting methods rely on labor-intensive density map annotations, necessitating the manual localization of each individual pedestrian. While recent efforts have attempted to alleviate the annotation burden through weakly or semi-supervised learning, these approaches fall short of significantly reducing the workload. We propose a novel approach to eliminate the annotation burden by leveraging latent diffusion models to generate synthetic data. However, these models struggle to reliably understand object quantities, leading to noisy annotations when prompted to produce images with a specific quantity of objects. To address this, we use latent diffusion models to create two types of synthetic data: one by removing pedestrians from real images, which generates ranked image pairs with a weak but reliable object quantity signal, and the other by generating synthetic images with a predetermined number of objects, offering a strong but noisy counting signal. Our method utilizes the ranking image pairs for pre-training and then fits a linear layer to the noisy synthetic images using these crowd quantity features. We report state-of-the-art results for unsupervised crowd counting.
We release our code for reproducing the experiments conducted within our paper.
tensorflow==2.8
tensorflow_addons==0.16.1
protobuf==4.21.5
scikit_image==0.18.1
tifffile==2023.4.12# Example installation steps
$ git clone https://github.com/adrian-dalessandro/SYRAC.git
$ cd SYRAC
$ pip install -r requirements.txtBefore fine-tuning on noisy synthetic crowd counting data, you need to pre-train the model on ranking data. Use the following command:
# Training from scratch
$ python train_wrapper.py --experiment training/baseline \
--params_dir "./config/" \
--dataset "YOUR_DATASET" \
--data_dir "path/to/dataset" \
--experiment_dir "path/to/experiments" \
--experiment_name "name_your_experiment"--experiment: the path to the training procedures (currently only training/baseline but you could write your own)--params_dir: Path to the directory containing model configuration parameters.--dataset: Name of the synthetic ranking dataset top-level directory (e.g. "DS_SYNTH_JHU")--data_dir: Path to the directory where your ranking data directory is located.--experiment_dir: Path to the directory where pre-training experiment results will be saved.--experiment_name: Name your pre-training experiment for identification.
After pre-training, fine-tune the model on noisy synthetic crowd counting data using the following command:
# Finetuning pre-trained model
$ python3 finetune_wrapper.py --experiment finetuning/unsupervised/noisy_synth_regress \
--data_dir "path/to/dataset" \
--train_data "DS_NOISY_SYNTH" \
--test_data "YOUR_DATASET" \
--N 2 \
--experiment_path "path/to/experiments" \
--model_path "path_to_saved_model" \
--params_dir "./config/"--experiment: the path to the finetuning procedures (currently only finetuning/unsupervised/noisy_synth_regress, but you could write your own)--data_dir: Path to the directory where your crowd counting dataset is located.--train_data: Specify the top-level directory name for the training data source (e.g., "DS_NOISY_SYNTH").--test_data: Specify the top-level directory name of your (real) crowd counting test dataset (e.g., "DS_JHU").--N: how to patch the image, (i.e, N = 3 would split an image into a 3x3 grid)--experiment_path: Path to the directory where pre-trained experiment results were saved.--model_path: directory name for the pre-trained model from the ranking data pre-training step (i.e. "best_model")--params_dir: Path to the directory containing model configuration parameters.
This two-step process involves pre-training on ranking data to leverage ranking image pairs and then fine-tuning on noisy synthetic crowd counting data. Ensure that you replace the placeholders with your specific dataset and directory paths, and adjust other parameters and experiment configurations as needed for your project requirements.
We will be updating this repository with a link to the synthetic and real data shortly.
We will be updating this repository with a link to the pre-trained checkpoints shortly.
If you use any part of this work in your projects or publications, please cite:
@misc{dalessandro2023syrac,
title={SYRAC: Synthesize, Rank, and Count},
author={Adriano D'Alessandro and Ali Mahdavi-Amiri and Ghassan Hamarneh},
year={2023},
eprint={2310.01662},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
Crowd counting has legitimate use cases such as urban planning, event management, and retail analysis. However, it also involves human surveillance, which can be misused by bad actors. We should always be deeply skeptical of any human surveillance use cases downstream of our research. Given ths, we release all of our source code under the Open RAIL-S LICENSE in an attempt to mitigate downstream misuse.