Read these instructions carefully. Understand exactly what is expected before starting this Sprint Challenge.
This challenge allows you to practice the concepts and techniques learned over the past week and apply them in project. This Sprint explored JavaScript Fundamentals. During this Sprint, you studied array methods, this keyword, prototypes, and class syntax. In your challenge this week, you will demonstrate proficiency by completing a range of JavaScript problems.
This is an individual assessment. All work must be your own. Your challenge score is a measure of your ability to work independently using the material covered through this sprint. You need to demonstrate proficiency in the concepts and objectives introduced and practiced in preceding days.
You are not allowed to collaborate during the sprint challenge.
The index.js file contains all of your challenges. Please review it in full before answering the questions. If you complete the stretch goals please leave them in your file but commented out so that they do not affect the MVP tasks.
In meeting the minimum viable product (MVP) specifications listed below, you should have all tests passing. You can console.log to check your work and ensure you are submitting the correct results.
Set up codegrade early and commit your code regularly and meaningfully.
Demonstrate your understanding of this week's concepts by answering the following free-form questions.
Edit this document to include your answers after each question. Make sure to leave a blank line above and below your answer so it is clear and easy to read.
-
Explain the differences between
.map,.reduceand.filterand describe a use case for each. .map, .reduce, and .filter are all array methods in JavaScript that help you work with arrays in a more efficient way..map: This method creates a new array by applying a function to every element in an existing array. It is useful when you want to create a new array where each element is derived from the elements of another array. For example, you can use .map to create a new array of the squares of the numbers in an existing array of numbers.
.reduce: This method reduces an array to a single value by applying a function that you provide to each element in the array, from left to right. The function takes two arguments: an accumulator and the current value. It is commonly used to find the sum of all the numbers in an array or to flatten nested arrays.
.filter: This method creates a new array including elements where the filter function returns true and omitting the ones where it returns false. A common use case is to create a new array that contains only certain elements from an existing array, for example, filtering an array of numbers to only include numbers greater than a certain value.
-
Explain the difference between a callback and a higher order function. A callback function is a function that is passed as an argument to another function and is invoked inside that function. A higher-order function is a function that accepts another function as an argument and/or returns a function as a result.
In essence, a higher-order function is a function that works with callbacks, either by taking a function as an argument or by returning a function. A very common use of higher-order functions in JavaScript is event handlers and listeners, where a function is passed to handle events.
-
Explain what a closure is.
A closure is a feature in JavaScript where an inner function has access to the outer (enclosing) function’s variables — a scope chain. The closure has three scope chains: it has access to its own scope (variables defined between its curly brackets), it has access to the outer function’s variables, and it has access to the global variables.
This makes it possible to use closures to create a sort of private variables, helping to avoid variable name collisions and providing encapsulation.
- Describe the four principles of the 'this' keyword.
The four principles of the 'this' keyword in JavaScript are:
Global/Window Binding: When this is used in the global scope, it refers to the window object in the browser or the global object in Node.js.
Implicit Binding: When a function is called with an object to its left, this refers to the object to the left of the dot at the call time. This is the most common use case in object methods.
New Binding: When a function is called with the new keyword as a constructor, this refers to the new object that is created.
Explicit Binding: You can explicitly set what this refers to using call, apply, or bind methods.
- Why do we need super() in an extended class?
We need super() in an extended class to call the constructor of the superclass. This allows you to access and call functions on an object's parent class with JavaScript’s built-in super keyword.
Using super() in the constructor of the subclass makes sure that the constructor of the superclass is called first and that the properties of the superclass are properly initialized before any work in the subclass’s constructor is done. It's required to properly set up the prototype chain, ensuring that the inheritance is properly established.
You are expected to be able to answer questions in these areas. Your responses contribute to your Sprint Challenge grade.
Using VSCode and Command Line:
- Fork the repo
- Go into canvas and connect your repo to codegrade
- Clone your forked version of the repo
- DO NOT CREATE A BRANCH. You will be pushing your changes to the main/master today
- cd into your repo
- open the terminal in your vs code and type
npm install - next type
npm run testin your terminal - Complete your work making regular commits to main/master; your codegrade score will update each time you make a push.
Open a second terminal inside of your project by clicking on the split terminal icon
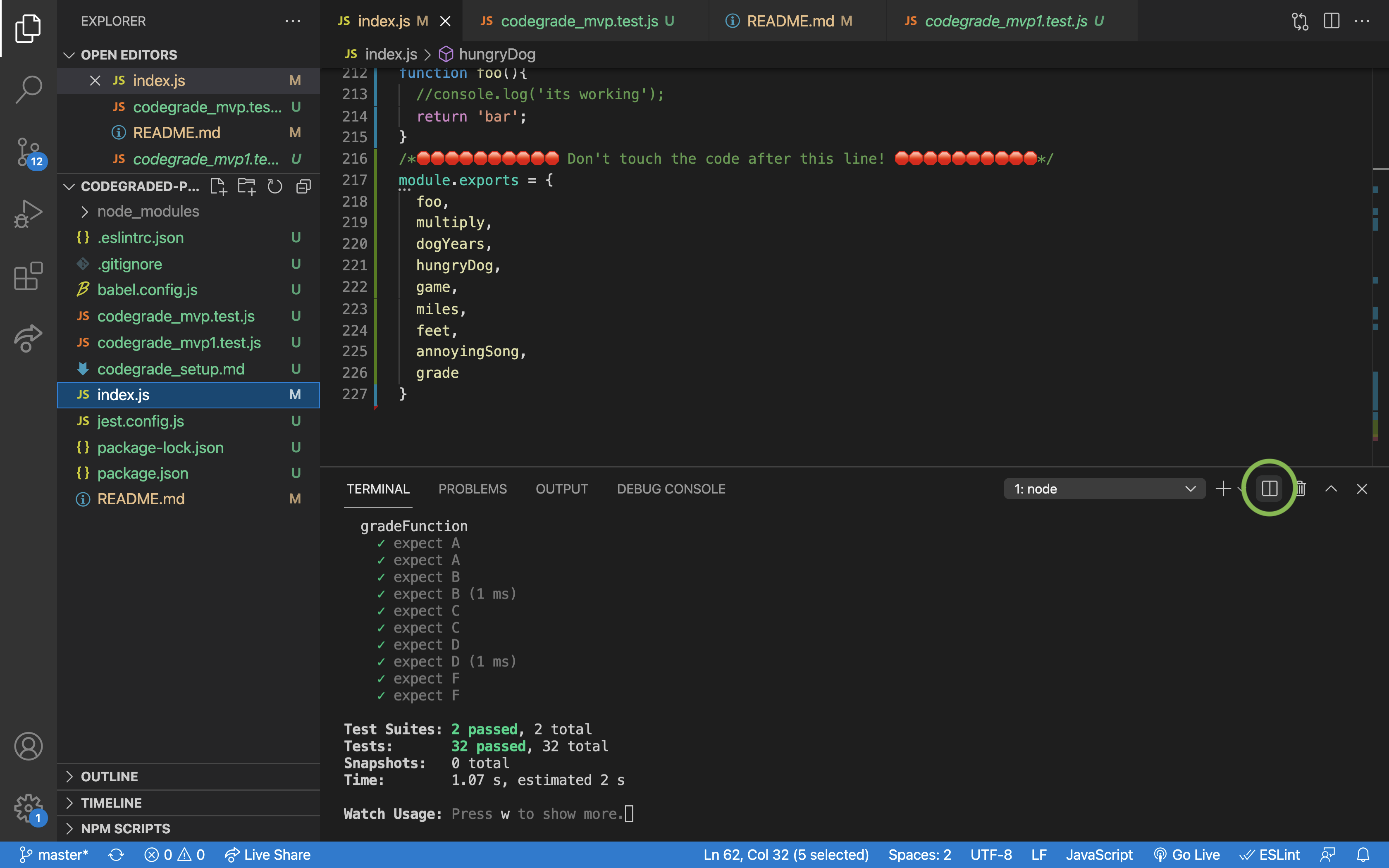
Inside of your second terminal type npm start
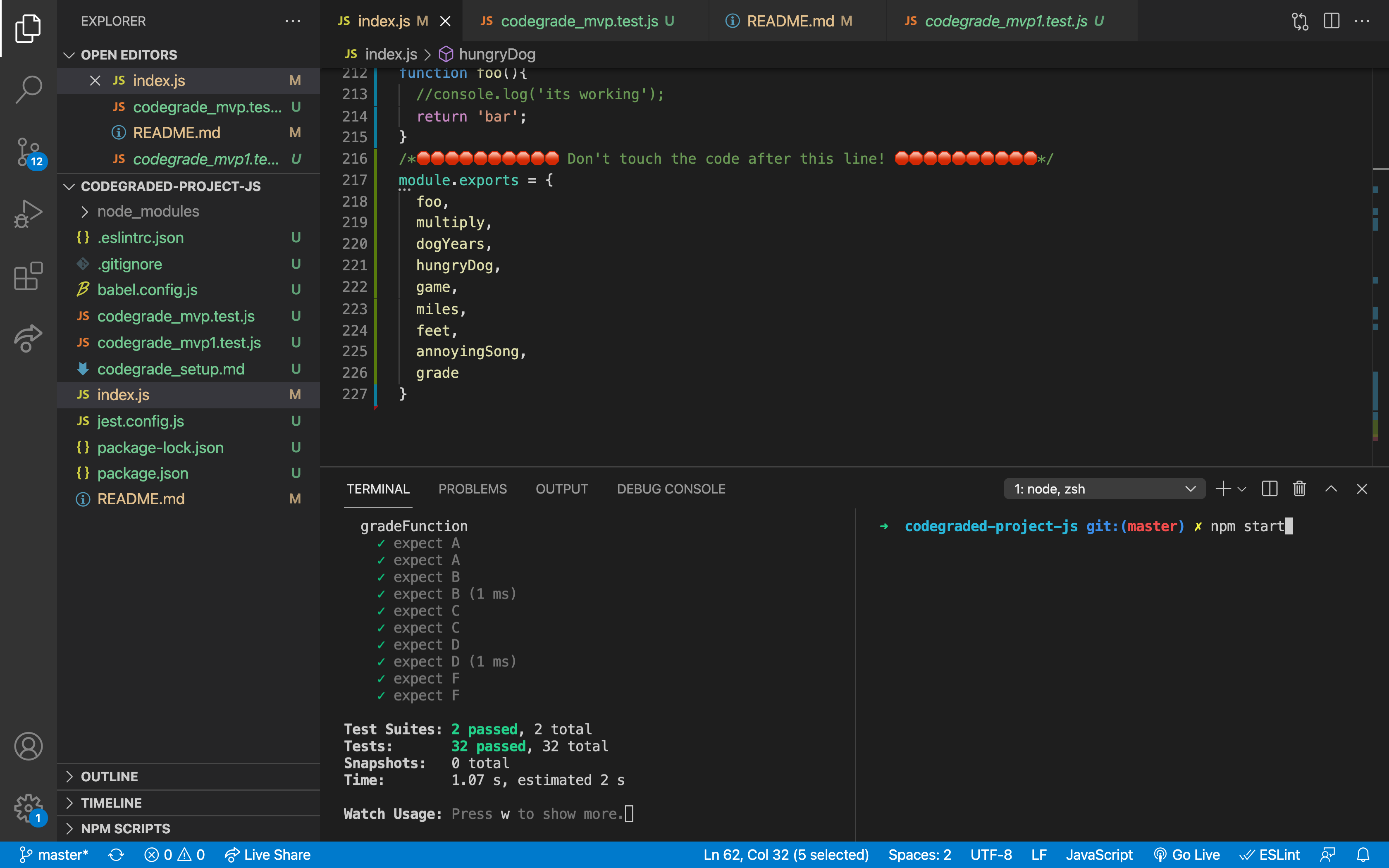
You will be running your tests in one terminal and debugging in the other. As you work on your code you should make use of console.log to check your progress and debug.
You must complete all tasks inside of index.js and answer the questions above.
In your solutions, it is essential that you follow best practices and produce clean and professional results. Schedule time to review, refine, and assess your work and perform basic professional polishing including spell-checking and grammar-checking on your work. It is better to submit a challenge that meets MVP than one that attempts too much and does not.
Please submit your project via codegrade by following these instructions (see part 2, submitting an assignment with codegrade).