@RestController
@RequestMapping("/grade")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class GradingController {
private final GradingService gradingService;
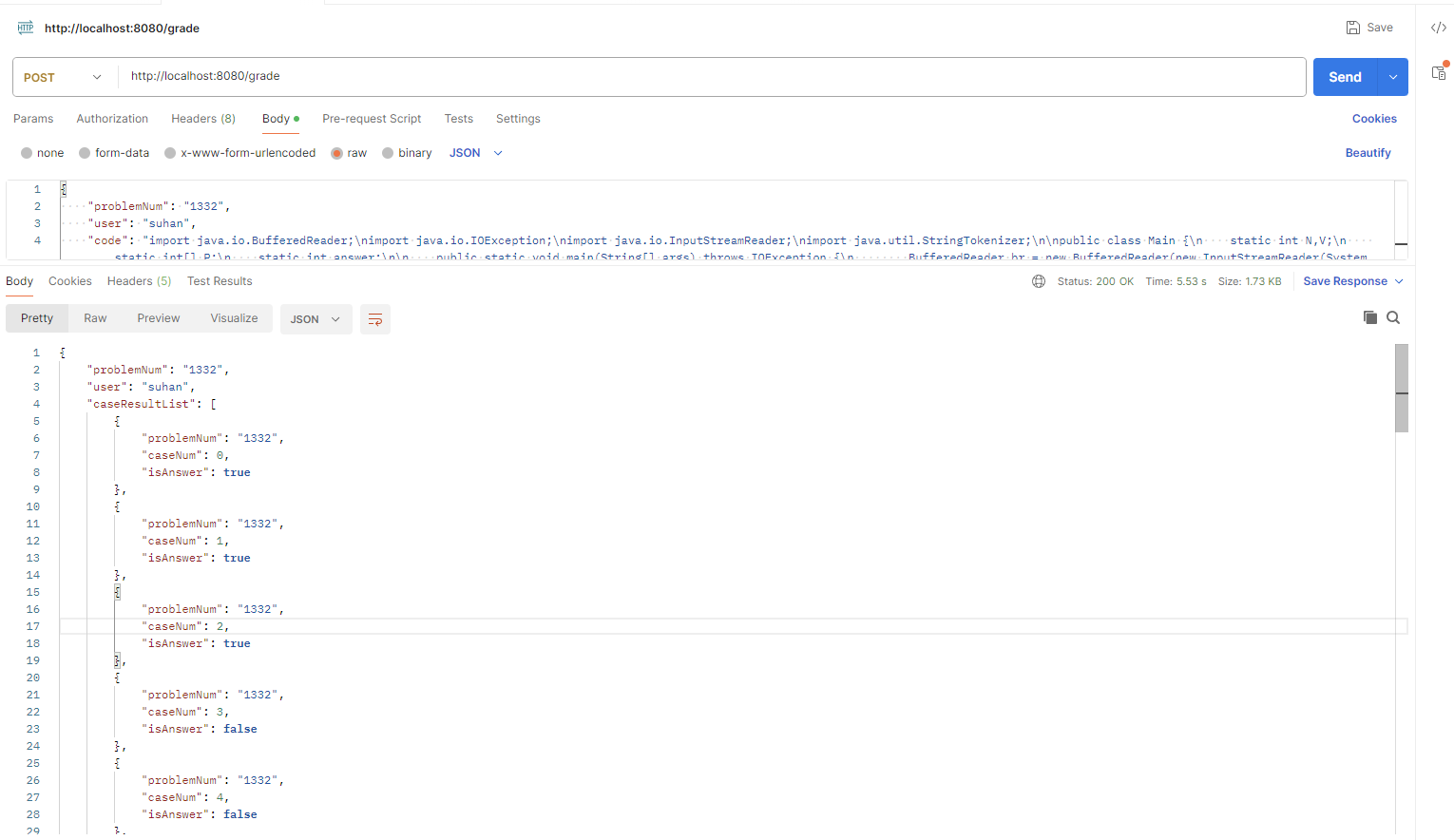
/**
* userAnswer :
* {
* "problemNum" : "2609",
* "user" : "hshhan0221",
* "code" : "import ... "
* }
* 위 데이터를 받아 채점한 후 결과 반환
* 결과 형식은 다음과 같음
* {
* "problemNum" : "2609",
* "user" : "hshhan0221",
* "caseResultList" : [
* {
* "problemNum" : "2609",
* "caseNum" : 0,
* "isAnswer" : true,
* },
* {
* "problemNum" : "2609",
* "caseNum" : 1,
* "isAnswer" : false,
* },
* ],
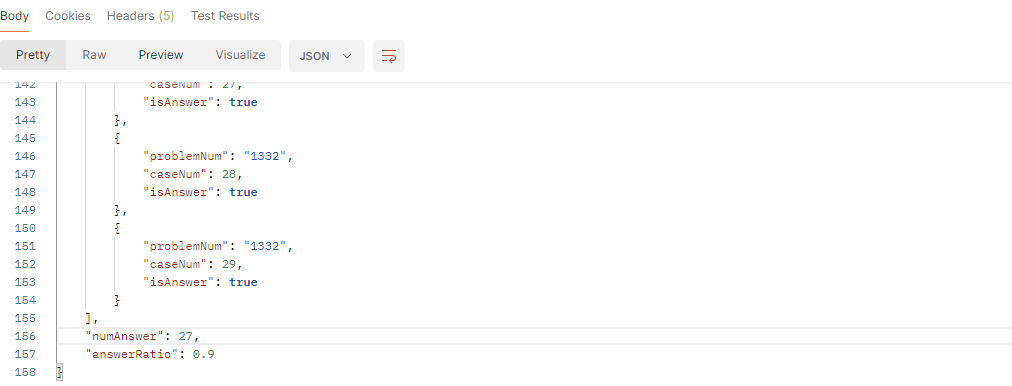
* "numAnswer" : 10,
* "answerRatio" 1.0
* }
*/
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<?> grading(@RequestBody UserAnswer userAnswer) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 유저 데이터를 통해 채점
List<CaseResult> caseResultList = gradingService.grading(userAnswer.getProblemNum(), userAnswer.getCode());
// 채점 결과 저장
UserAnswerResponse response = UserAnswerResponse.builder()
.user(userAnswer.getUser())
.problemNum(userAnswer.getProblemNum())
.caseResultList(caseResultList)
.build();
// 정답수, 정답률 등록
response.setInfo();
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(response);
}
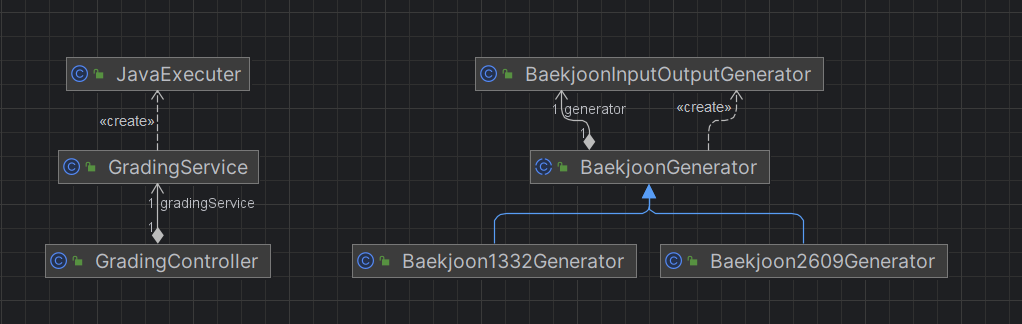
}유저 데이터를 받아 gradingService의 채점 메소드를 호출하여 결과를 반환한다.
gradingService의 채점 로직은 다음 링크에서 설명하겠다. 채점 로직
@Getter
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class UserAnswer {
String problemNum; // 문제 번호
String user; // 유저 아이디 or 이름
String code; // 유저 코드
}@Getter
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class UserAnswerResponse {
String problemNum; // 문제 번호
String user; // 유저 아이디 or 이름
List<CaseResult> caseResultList; // 테스트케이스 정답 결과 목록
int numAnswer; // 정답수
float answerRatio; // 정답률
// 정답수, 정답률 등록
public void setInfo(){
numAnswer = 0;
caseResultList.forEach(caseResult -> {
if(caseResult.getIsAnswer()) numAnswer++;
});
answerRatio = (float) numAnswer / caseResultList.size();
}
}@Getter
@Builder
public class CaseResult {
String problemNum; // 문제 번호
int caseNum; // 테스트 케이스 번호
Boolean isAnswer; // 정답 여부
}입력, 출력을 생성하는 함수형 인터페이스를 인자로 받아 데이터를 생성하고 파일로 저장하는 클래스
public class BaekjoonInputOutputGenerator {
public final static String baseDir = "src/main/java";
public final static String inputDir = "input";
public final static String outputDir = "output";
public final static String packagePath = BaekjoonInputOutputGenerator.class.getPackage().getName().replace('.', '/');
Path problemPath;
Path inputDirPath;
Path outputDirPath;
Path inputFilePath;
Path outputFilePath;
/*
아래와 같은 폴더 생성 후 데이터 생성
src/main/java/com/ssafy/codingtest/problem/baekjoon/{문제번호}/input
src/main/java/com/ssafy/codingtest/problem/baekjoon/{문제번호}/output
*/
public BaekjoonInputOutputGenerator(String problemNum) {
this.problemPath = getProblemFolderPath(problemNum);
this.inputDirPath = problemPath.resolve(inputDir);
this.outputDirPath = problemPath.resolve(outputDir);
}
/*
* inputFileName : 입력 데이터 파일 이름
* outputFileName : 출력 데이터 파일 이름
*
* 입력 데이터 생성 후 출력 데이터 생성
*/
public void makeData(String inputFileName, String outputFileName, Supplier<String> inputFunc, Function<List<String>, String> outputFunc) {
this.inputFilePath = inputDirPath.resolve(inputFileName);
this.outputFilePath = outputDirPath.resolve(outputFileName);
makeInput(inputFunc);
makeOutput(outputFunc);
}
public static Path getProblemFolderPath(String problemNum){
return Paths.get(baseDir, packagePath, getProblemFolderName(problemNum));
}
public static String getProblemFolderName(String problemNum){
return "p"+problemNum;
}
/*
* func : 입력 데이터 생성 함수
*
* 입력 데이터 생성 후 파일 저장
*/
public void makeInput(Supplier<String> func) {
String result = func.get();
// input.txt 파일에 저장
save(inputFilePath, result);
}
/*
* func : 출력 데이터 생성 함수
* - 입력 데이터 파일을 읽은 String 배열을 매개변수로 받음
*
* 출력 데이터 생성 후 파일 저장
*/
public void makeOutput(Function<List<String>,String> func) {
// input.txt 파일에서 데이터를 읽고 출력 데이터를 계산하여 output.txt에 저장
try {
List<String> lines = Files.readAllLines(inputFilePath, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
String result = func.apply(lines);
// output.txt 파일에 결과 저장
save(outputFilePath, result);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/*
* filePath : 파일 저장 경로
* result : 파일에 넣을 데이터
*
* 파일 생성 후 데이터 삽입
*/
private void save(Path filePath, String result) {
try {
// Ensure the directory exists
Files.createDirectories(filePath.getParent());
// Write data to the file
Files.writeString(filePath, result);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}테스트 케이스 개수 만큼 테스트 케이스 생성 후 저장하는 클래스
BaekjoonGenerator를 상속
setInputFunc에는 입력 조건에 맞는 입력을 랜덤하게 생성하는 로직을 구현후 반환
setOutputFunc에는 실제 알고리즘 내용을 등록
이때, 입력은 stdin이 아니라 List<String>으로 받기 때문에 이에 유의하여 작성한다.
public abstract class BaekjoonGenerator {
// 입.출력 데이터 생성기
protected BaekjoonInputOutputGenerator generator;
// 기본 데이터
protected String inputFileName; // 입력 데이터 파일 이름
protected String outputFileName; // 출력 데이터 파일 이름
protected Supplier<String> inputFunc; // 입력 데이터 생성 함수
protected Function<List<String>, String> outputFunc; // 출력 데이터 생성 함수
// 테스트 케이스 개수
protected int size = 10;
public BaekjoonGenerator(String problemNum) {
generator = new BaekjoonInputOutputGenerator(problemNum);
inputFileName = "input_" + problemNum + "_";
outputFileName = "output_" + problemNum + "_";
inputFunc = setInputFunc();
outputFunc = setOutputFunc();
}
public abstract Supplier<String> setInputFunc(); // 입력 데이터 생성 함수
public abstract Function<List<String>, String> setOutputFunc(); // 출력 데이터 생성 함수
public void generate() {
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
generator.makeData(inputFileName+i,outputFileName+i, inputFunc, outputFunc);
}
}
}체점 데이터(테스트 케이스)를 생성하려면 BaekjoonGenerator를 상속받아 setInputFunc, setOutputFunc를 override해서 실행하면 된다.
public class Baekjoon1332Generator extends BaekjoonGenerator {
// 알고리즘에 필요한 데이터
Random random = new Random();
int MAX_N = 50;
int MAX_V = 1000;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Baekjoon1332Generator baekjoon1332Generator = new Baekjoon1332Generator();
baekjoon1332Generator.size = 30;
baekjoon1332Generator.generate();
}
public Baekjoon1332Generator(){
super("1332");
}
// 입력 데이터 생성 함수
@Override
public Supplier<String> setInputFunc() {
return () -> {
// 문제의 개수 N과 최댓값과 최솟값의 차이 V 생성
int N = random.nextInt(MAX_N) + 1; // 1 이상 50 이하의 자연수
int V = random.nextInt(MAX_V) + 1; // 1 이상 1000 이하의 자연수
// 유진이가 느끼는 흥미도 P 배열 생성
int[] P = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
P[i] = random.nextInt(1001); // 0 이상 1000 이하의 자연수
}
// 입력 데이터 출력
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(N).append(" ").append(V).append("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
sb.append(P[i]).append(" ");
}
sb.append(" ");
return sb.toString();
};
}
// 출력 데이터 생성 함수
@Override
public Function<List<String>, String> setOutputFunc() {
return (lines) -> {
String[] numbers = lines.get(0).split(" ");
int N = Integer.parseInt(numbers[0]);
int V = Integer.parseInt(numbers[1]);
int[] P = new int[N];
numbers = lines.get(1).split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
P[i] = Integer.parseInt(numbers[i]);
}
int answer = N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < N; j++) {
if(Math.abs(P[i] - P[j]) >= V){
// 최소, 최대 차이가 V 이상인 경우
int cnt = 1 + (i + 1)/2 + (j - i + 1)/2;
answer = Math.min(answer, cnt);
}
}
}
return String.valueOf(answer);
};
}
}결과는 다음과 같이 저장된다.
- input
- output
아래 class의 saveAndCompile을 통해 파일 저장 및 컴파일을 하고 run 함수를 통해 파일 데이터를 입력으로 하여 실행 결과를 받아올 수 있다.
public class JavaExecuter {
String baseDir = "temp"; // 실행 파일이 생성될 폴더의 폴더
String folderName; // 실행 파일이 생성될 폴더
String fileName = "Main.java"; // 실팽 파일 이름
// 폴더 경로 설정
Path folderPath;
Path filePath;
public void saveAndCompile(String code){
save(code);
compile();
}
// 코드 String을 파일로 저장
public void save(String code){
// UUID 기반 폴더 이름 생성
folderName = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 폴더 경로 설정
folderPath = Paths.get(baseDir, folderName);
filePath = folderPath.resolve(fileName);
// 폴더 생성 및 Java 소스 코드 파일로 저장
try {
Files.createDirectories(folderPath);
Files.writeString(filePath, code, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Java source code has been written to " + filePath.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("An error occurred while writing the Java source code: " + e.getMessage());
}
};
// 파일을 읽어 컴파일후 클래스 파일 저장
public void compile(){
try {
Process compileProcess = new ProcessBuilder("javac","-encoding","UTF-8", filePath.toString()).inheritIO().start();
compileProcess.waitFor();
if (compileProcess.exitValue() == 0) {
System.out.println("Java source code compiled successfully.");
} else {
System.err.println("Compilation failed.");
}
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
System.err.println("An error occurred during compilation: " + e.getMessage());
}
};
// 클래스 파일을 읽고 입력 데이터를 넣어 실행후 출력 결과 반환
public String run(Path inputFilePath) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Process runProcess = new ProcessBuilder("java", "-cp", folderPath.toString(), "Main").start();
// 프로세스에 입력 스트림 연결
PrintWriter processInput = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(runProcess.getOutputStream()));
// 파일에서 입력을 읽어 프로세스에 전달
BufferedReader inputFileReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(Files.newInputStream(inputFilePath)));
String line;
while ((line = inputFileReader.readLine()) != null) {
processInput.println(line);
}
processInput.flush();
// 프로세스의 stdout 출력
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
BufferedReader processOutput = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(runProcess.getInputStream()));
String outputLine;
while ((outputLine = processOutput.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(outputLine).append("\n");
}
runProcess.waitFor();
return sb.toString().trim();
}
// 실행 폴더 및 파일 삭제
public void remove() {
try {
Files.walk(folderPath)
.sorted((a, b) -> -a.compareTo(b)) // 하위 폴더부터 삭제하기 위해 역순 정렬
.map(Path::toFile)
.forEach(File::delete);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}각 테스트 케이스마다 실행 결과를 저장하고 실제 정답과 비교하여 몇변 문제의 몇번 테스트케이스가 맞았는지 여부를 저장한다.
@Service
public class GradingService {
public List<CaseResult> grading(String problemNum, String code) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 컴파일, 실행을 위한 클래스
JavaExecuter executer = new JavaExecuter();
executer.saveAndCompile(code); // 코드 파일 저장 및 컴파일
// 테스트케이스 폴더 경로
Path folderPath = BaekjoonInputOutputGenerator.getProblemFolderPath(problemNum);
// 입력 테스트케이스 폴더 경로
Path inputDirPath = folderPath.resolve(BaekjoonInputOutputGenerator.inputDir);
// 출력 테스트케이스 폴더 경로
Path outputDirPath = folderPath.resolve(BaekjoonInputOutputGenerator.outputDir);
// Files.walk()를 사용하여 폴더 내 모든 파일 경로를 가져옴 - 모든 테스트케이스 가져옴
List<Path> inputPaths = Files.walk(inputDirPath).filter(Files::isRegularFile).toList();
List<Path> outputPaths = Files.walk(outputDirPath).filter(Files::isRegularFile).toList();
// 해당 문제의 몇번 테스트 케이스가 맞았는지 저장하는 변수
List<CaseResult> isAnswerList = new ArrayList<>();
// 실행 후 결과 저장
for (int i = 0; i < inputPaths.size(); i++) {
Path inputPath = inputPaths.get(i);
Path outputPath = outputPaths.get(i);
String result = executer.run(inputPath);
String answer = Files.readString(outputPath);
boolean isAnswer = result.equals(answer);
isAnswerList.add(CaseResult.builder()
.problemNum(problemNum)
.caseNum(i)
.isAnswer(isAnswer)
.build());
}
// 코드 파일 및 폴더 삭제
executer.remove();
return isAnswerList;
}
}@Getter
@Builder
public class CaseResult {
String problemNum;
int caseNum;
Boolean isAnswer;
}