This is the official code of ICLR'22 paper Representation-Agnostic Shape Fields written in PyTorch.
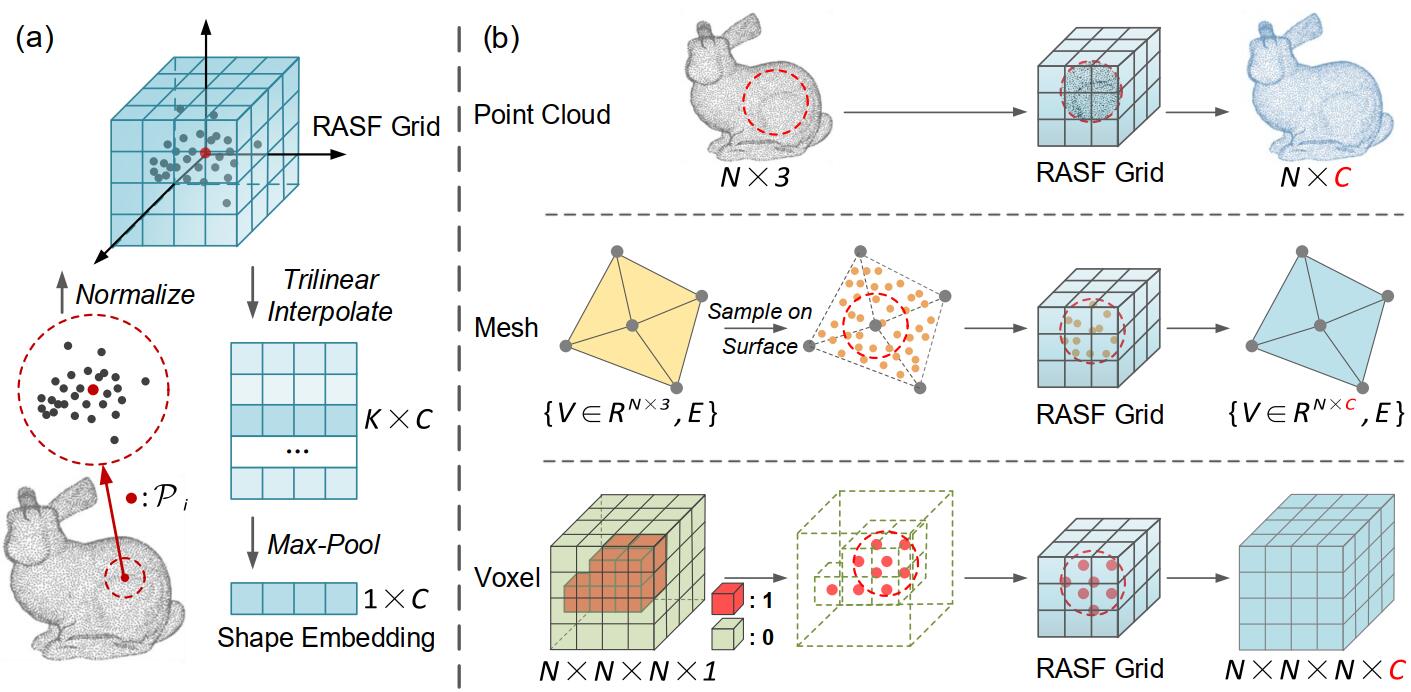
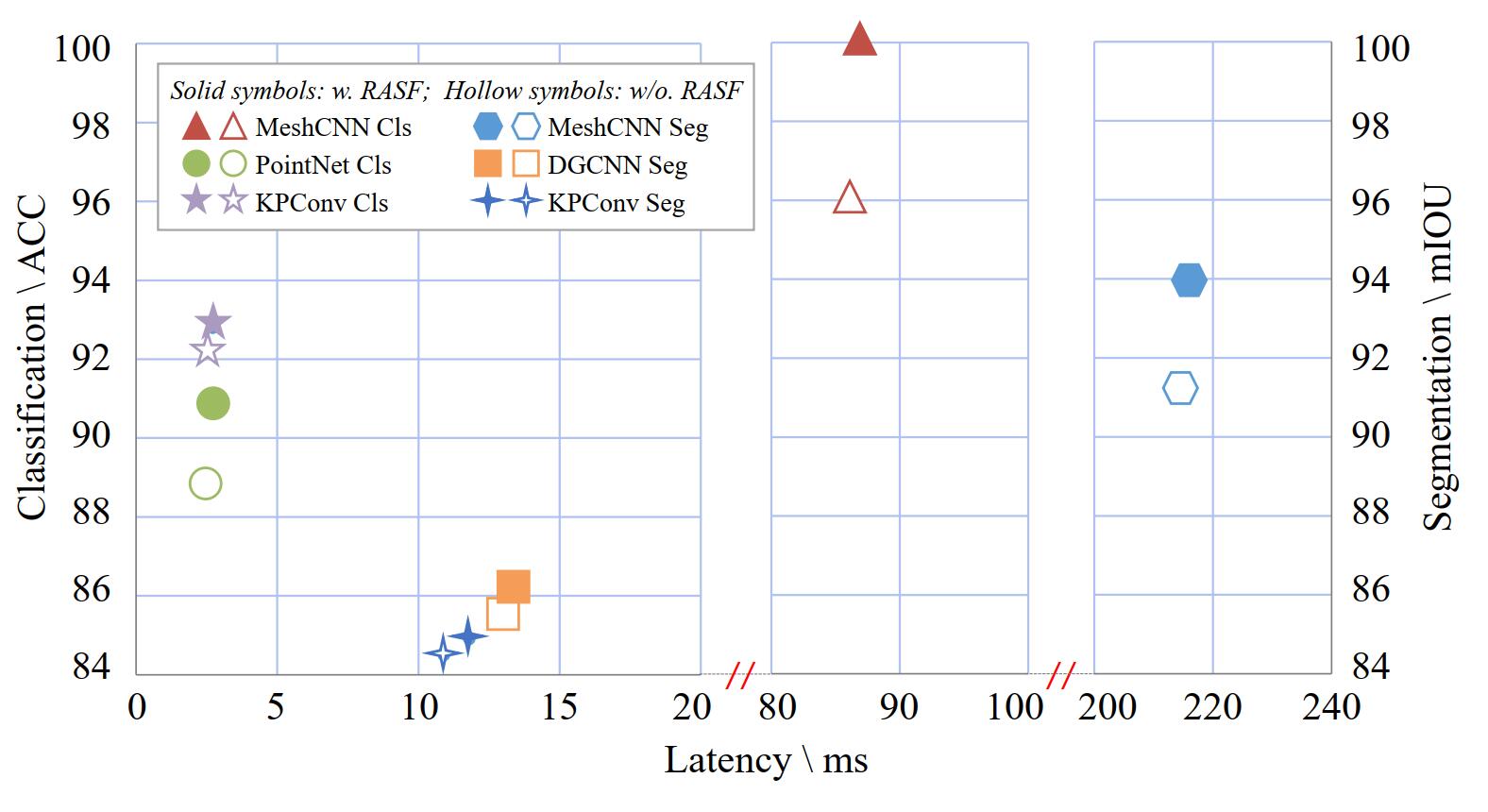 Representation-Agnostic Shape Fields (RASF) is a generalizable and computation-efficient shape embedding layer for 3D deep learning. Shape embeddings for various 3D shape representations (point clouds, meshes and voxels) are retrieved by coordinates indexing. We provide two effective schemes for RASF pre-training, that is shape reconstruction and normal estimation, to enable RASF to learn robust and general shape embeddings. Once trained, RASF could be plugged into any 3D neural network with negligible cost. RASF widely boosts the performance for various 3D representations, neural backbones and applications.
Representation-Agnostic Shape Fields (RASF) is a generalizable and computation-efficient shape embedding layer for 3D deep learning. Shape embeddings for various 3D shape representations (point clouds, meshes and voxels) are retrieved by coordinates indexing. We provide two effective schemes for RASF pre-training, that is shape reconstruction and normal estimation, to enable RASF to learn robust and general shape embeddings. Once trained, RASF could be plugged into any 3D neural network with negligible cost. RASF widely boosts the performance for various 3D representations, neural backbones and applications.
Note: Since a large parts of our downstream experiments are modified based on other codebases, directly releasing all the code would be a bit messy. We are stilling working on refactoring the code to make it more graceful. Currently we only release the experiemnts of PointNet and PointNet++ for classfication and segmentation for point clouds data.
- RASF.py: The basic module of RASF
- experiments/:
- pointclouds/: Downstream tasks on point clouds.
- meshes/ (WIP): Downstream tasks on meshes.
- voxels/ (WIP): Downstream tasks on voxels.
- RASF_pretraining/: Pretrain RASF on pretext tasks.
- utils/: Utils for training.
- config.py: Configurations for paths and settings.
- weights/: Directory to place the pretrained RASF weights.
- data/: Directory to place the downloaded datasets.
Only basic PyTorch packages are needed.
pip install -r requirements.txt
We show the usage of RASF on point clouds data. Demos on meshes and voxels would be presented with the rest experiments.
# inference for a batch of point clouds
rasf = RASF()
rasf.load_state_dict(torch.load('./experiments/weights/recon_weights.pt'))
pcd = torch.rand(16,1000,3) # shape: [batch, num_p, 3]
RASF_embedding = rasf.batch_samples(pcd) # shape: [batch, rasf_channel, num_p]
pcd_with_RASF = torch.cat([pcd.transpose(2,1), RASF_embedding], 1) # shape: [batch, (rasf_channel+3), num_p]
Download ModelNet40 and ShapeNetPart from this link. Put them in ./experiments/data as below:
./experiments/data
|--- modelnet40_normal_resampled
|--- shapenetcore_partanno_segmentation_benchmark_v0_normal
Download the pretrained weights from Onedrive and put them in ./experiments/weights. Or you can run the pretraining code yourself and put the weights in the above directory. In this case, modify the weights path in ./experiments/config.py.
To evaluate RASF performance on point clouds, run ./experiments/pointclouds/modelnet40_cls.py and ./experiments/pointclouds/shapenetpart_seg.py.
Modify ./experiments/config.py to determine whether to use RASF embeddings and the choice of backbones.
This codebase borrows a lot from Pointnet_Pointnet2_pytorch. Thanks for their help!
If you find this project useful in your research, please cite the following papers:
@inproceedings{huang2022representation,
title={Representation-Agnostic Shape Fields},
author={Huang, Xiaoyang and Yang, Jiancheng and Wang, Yanjun and Chen, Ziyu and Li, Linguo and Li, Teng and Ni, Bingbing and Zhang, Wenjun},
booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2022}
}