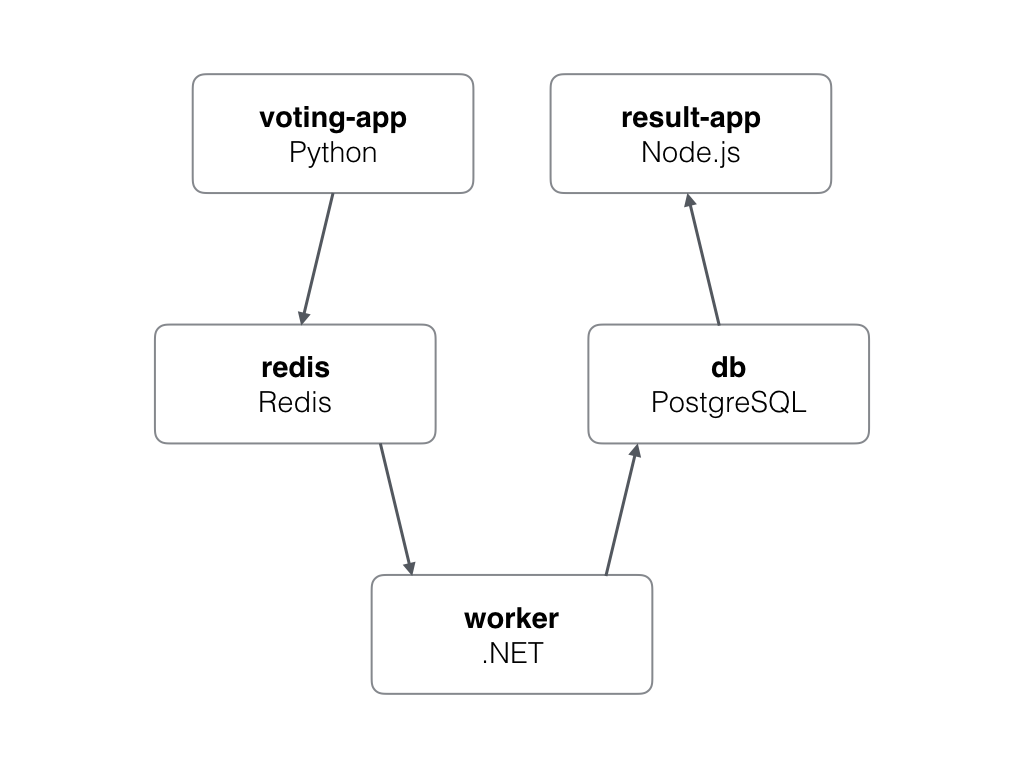
A simple distributed application running across multiple Docker containers.
Download Docker Desktop for Mac or Windows. Docker Compose will be automatically installed. On Linux, make sure you have the latest version of Compose.
The Linux stack uses Python, Node.js, .NET Core (or optionally Java), with Redis for messaging and Postgres for storage.
If you're using Docker Desktop on Windows, you can run the Linux version by switching to Linux containers, or run the Windows containers version.
Run in this directory:
docker-compose up
The app will be running at http://localhost:5000, and the results will be at http://localhost:5001.
Alternately, if you want to run it on a Docker Swarm, first make sure you have a swarm. If you don't, run:
docker swarm init
Once you have your swarm, in this directory run:
docker stack deploy --compose-file docker-stack.yml vote
An alternative version of the app uses Windows containers based on Nano Server. This stack runs on .NET Core, using NATS for messaging and TiDB for storage.
You can build from source using:
docker-compose -f docker-compose-windows.yml build
Then run the app using:
docker-compose -f docker-compose-windows.yml up -d
Or in a Windows swarm, run
docker stack deploy -c docker-stack-windows.yml vote
The app will be running at http://localhost:5000, and the results will be at http://localhost:5001.
The folder k8s-specifications contains the yaml specifications of the Voting App's services.
First create the vote namespace
$ kubectl create namespace vote
Run the following command to create the deployments and services objects:
$ kubectl create -f k8s-specifications/
deployment "db" created
service "db" created
deployment "redis" created
service "redis" created
deployment "result" created
service "result" created
deployment "vote" created
service "vote" created
deployment "worker" created
The vote interface is then available on port 31000 on each host of the cluster, the result one is available on port 31001.
💡 Recommended if you're using Google Cloud Platform and want to try it on a realistic cluster.
-
Install tools specified in the previous section (Docker, kubectl, skaffold)
-
Create a Google Kubernetes Engine cluster and make sure
kubectlis pointing to the cluster.gcloud services enable container.googleapis.comgcloud container clusters create demo --enable-autoupgrade \ --enable-autoscaling --min-nodes=3 --max-nodes=10 --num-nodes=5 --zone=us-central1-akubectl get nodes -
Enable Google Container Registry (GCR) on your GCP project and configure the
dockerCLI to authenticate to GCR:gcloud services enable containerregistry.googleapis.comgcloud auth configure-docker -q
-
Create Vote namespace in Kubernetes
kubectl create namespace vote
-
In the root of this repository, run
skaffold run --default-repo=gcr.io/[PROJECT_ID], where [PROJECT_ID] is your GCP project ID.This command:
- builds the container images
- pushes them to GCR
- applies the
./k8s-specificationsdeploying the application to Kubernetes.
Optional: Build docker images in Goole Container Builder If you don't have docker running locally and want to still build the images, you can use the -p gcb option to build it on Google Cloud
skaffold run --default-repo=gcr.io/gcr.io/[PROJECT_ID] -p gcb
Troubleshooting: If you get "No space left on device" error on Google Cloud Shell, you can build the images on Google Cloud Build: Enable the Cloud Build API, then run
skaffold run -p gcb --default-repo=gcr.io/[PROJECT_ID]instead.If you have errors with the application, you can use the
-tailoption in skaffold to tail all the logs -
Find the IP address of your application, then visit the application on your browser to confirm installation.
kubectl get services -n voteTroubleshooting: A Kubernetes bug (will be fixed in 1.12) combined with a Skaffold bug causes load balancer to not to work even after getting an IP address. If you are seeing this, run
kubectl get service frontend-external -o=yaml | kubectl apply -f-to trigger load balancer reconfiguration.
- A front-end web app in Python or ASP.NET Core which lets you vote between two options
- A Redis or NATS queue which collects new votes
- A .NET Core, Java or .NET Core 2.1 worker which consumes votes and stores them in…
- A Postgres or TiDB database backed by a Docker volume
- A Node.js or ASP.NET Core SignalR webapp which shows the results of the voting in real time
The voting application only accepts one vote per client. It does not register votes if a vote has already been submitted from a client.
This isn't an example of a properly architected perfectly designed distributed app... it's just a simple example of the various types of pieces and languages you might see (queues, persistent data, etc), and how to deal with them in Docker at a basic level.