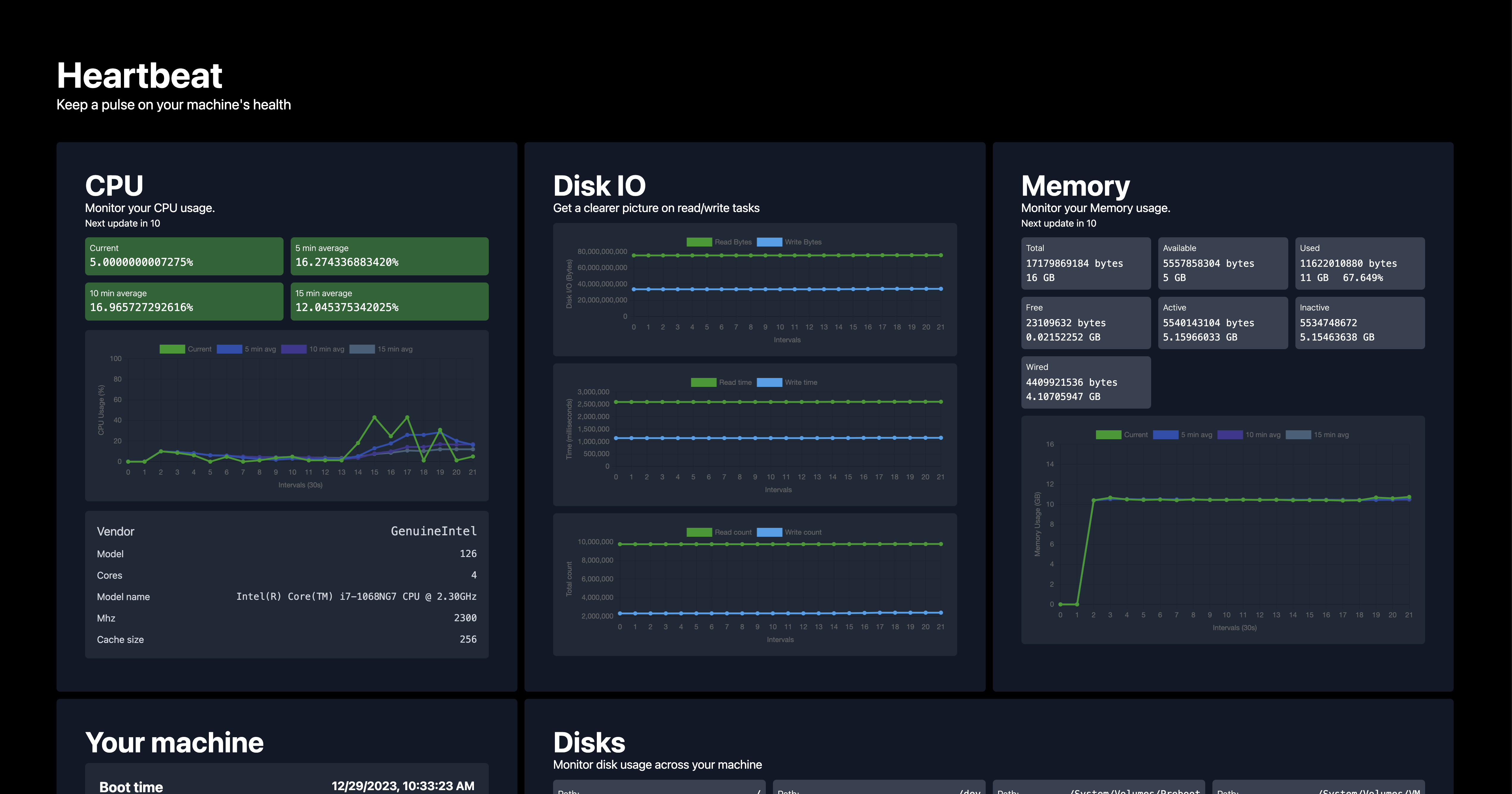
Heartbeat is system health monitoring tool. It's comprised of a backend server written in Go and a Next.js frontend. Together, the application provides real-time monitoring of various key system metrics, showcasing how Go can be used for efficient system data collection and how these metrics can be visualized in a web interface.
The primary goal of Heartbeat is to offer a clear and immediate view of key performance metrics for a server environment. It's designed for developers, system administrators, or anyone interested in getting hands-on experience with system or server monitoring tools. Key features include:
- Real-Time Data: Tracks and displays real-time CPU, memory, disk, and network usage.
- Historical Trends: Visualizes CPU and memory usage over different time intervals for trend analysis.
- Process Information: Provides details on specific running processes.
- Network Insights: Includes detailed list of network operations.
- User-Friendly Interface: The Next.js frontend simplifies data presentation, making it accessible even for those new to system monitoring.
Note: Heartbeat was built as a hobby project, and is not production ready. If you intend to use it in production, you'll need to make some further adjustments for security, like adding authentication.
Building Heartbeat has been an educational journey in utilizing Go for backend development, focusing on performance and concurrency, and integrating it with a modern JavaScript framework like Next.js for the frontend. This project serves as a practical example for anyone interested in learning about these technologies or server monitoring concepts.
- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/sandypockets/heartbeat.gitRun the following commands to start the backend server:
cd heartbeat/server
go run main.goYou should see a message in the terminal saying that the server is running on port 8080.
Run the following commands to start the frontend server:
cd heartbeat/client
yarn
yarn devYou should see a message in the terminal saying that the server is running on port 3000.
The heartbeat server (running on port 8080) provides the following endpoints. The frontend uses the Next.js API routes (running on port 3000) in the same structure to consume the server's API.
- GET
/api/cpu - GET
/api/memory - GET
/api/disk - GET
/api/network - GET
/api/diskio - GET
/api/uptime - GET
/api/process
Returns a JSON response containing a float64 representing the CPU usage of the machine that the server is running on.
Example response:
{
"avg_10min": 14.025692096349218,
"avg_15min": 11.311592912035149,
"avg_5min": 25.32370013920623,
"current_usage": 19.35470336494544
}Returns a JSON object with details about the memory usage of the machine.
Example response:
{
"memory_usage": {
"total": 16000000000, // Total memory in bytes.
"available": 6000000000, // Memory available for use in bytes.
"used": 10000000000, // Memory currently in use in bytes.
"usedPercent": 62.5, // Percentage of total memory currently in use.
"free": 50000000, // Free memory in bytes.
"active": 5500000000, // Memory actively in use or recently used.
"inactive": 4500000000, // Memory not actively in use.
"wired": 4000000000 // Memory marked to stay in RAM, not to be moved to disk.
}
}Returns a JSON object with an array of disk usage information. Each item in the array represents a separate partition.
Example response:
{
"disk_usage": [
{
"path": "/", // Mount path of the partition.
"fstype": "apfs", // File system type of the partition.
"total": 500000000000, // Total size of the partition in bytes.
"free": 100000000000, // Free space available on the partition in bytes.
"used": 400000000000, // Space used on the partition in bytes.
"usedPercent": 80.0, // Percentage of the partition that is used.
"inodesTotal": 1000000, // Total number of inodes.
"inodesUsed": 500000, // Number of inodes used.
"inodesFree": 500000, // Number of inodes free.
"inodesUsedPercent": 50.0 // Percentage of inodes that are used.
}
]
}Returns a JSON object with Disk I/O (Input/Output) statistics for each disk on the machine. Each item in the array represents a separate disk.
Example response:
{
"disk0": {
"readCount": 1024567, // Total number of reads completed.
"writeCount": 324567, // Total number of writes completed.
"readBytes": 9876543210, // Total number of bytes read.
"writeBytes": 1234567890, // Total number of bytes written.
"readTime": 456123, // Total time spent on read operations (ms).
"writeTime": 789123, // Total time spent on write operations (ms).
"iopsInProgress": 5, // Number of I/O operations in progress.
"ioTime": 891234, // Total time spent on I/O operations (ms).
"weightedIO": 12345, // Weighted time spent on I/O operations (ms).
"name": "diskX1", // Name of the disk.
"serialNumber": "ABCD1234XYZ", // Serial number of the disk.
"label": "MainStorage" // Label of the disk.
}
}Returns a JSON object containing the uptime of the machine in seconds.
Example response:
{
"uptime": 36000
}Returns a JSON response object containing network information for each network interface within the environment that the server is running on.
Example response:
{
"io_usage": [
{
"name": "lo0", // Name of the network interface.
"bytesSent": 1000000, // Total bytes sent through this interface.
"bytesRecv": 1000000, // Total bytes received through this interface.
"packetsSent": 1000, // Number of network packets sent.
"packetsRecv": 1000, // Number of network packets received.
"errin": 0, // Count of incoming errors.
"errout": 0, // Count of outgoing errors.
"dropin": 0, // Count of incoming packets dropped.
"dropout": 0, // Count of outgoing packets dropped.
"fifoin": 0, // FIFO buffer errors on incoming data.
"fifoout": 0 // FIFO buffer errors on outgoing data.
}
],
"interfaces": [
{
"index": 2, // Unique identifier for the network interface.
"mtu": 1500, // Maximum Transmission Unit in bytes.
"name": "eth0", // Designated name of the network interface.
"hardwareaddr": "00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E", // Hardware (MAC) address of the interface.
"flags": ["up", "broadcast", "multicast"], // Flags indicating the interface's state and capabilities.
"addrs": [{"addr": "192.168.1.100"}] // IP addresses associated with the interface.
}
],
"connections": [
{
"fd": 3, // File Descriptor for the network socket.
"family": 2, // Address family (2 for AF_INET - IPv4).
"type": 1, // Type of socket (1 for SOCK_STREAM - TCP).
"localaddr": {
"ip": "192.168.1.100", // Local IP address.
"port": 8080 // Local port number.
},
"remoteaddr": {
"ip": "192.168.1.101", // Remote IP address.
"port": 443 // Remote port number.
},
"status": "ESTABLISHED", // Status of the connection.
"uids": [1001], // User IDs associated with the connection.
"pid": 1234 // Process ID owning the socket.
}
]
}If you want to learn more about a connection[i].pid, then you can make a request to the /api/process endpoint, passing in the process ID as a pid query parameter.
Accepts a pid query parameter. Returns a JSON response object containing information about a given process running on the environment that the server is running on.
Example response:
{
"cmdline": "/Path/To/Cmdline/Process/Executable",
"name": "Process Name",
"pid": 1234
}