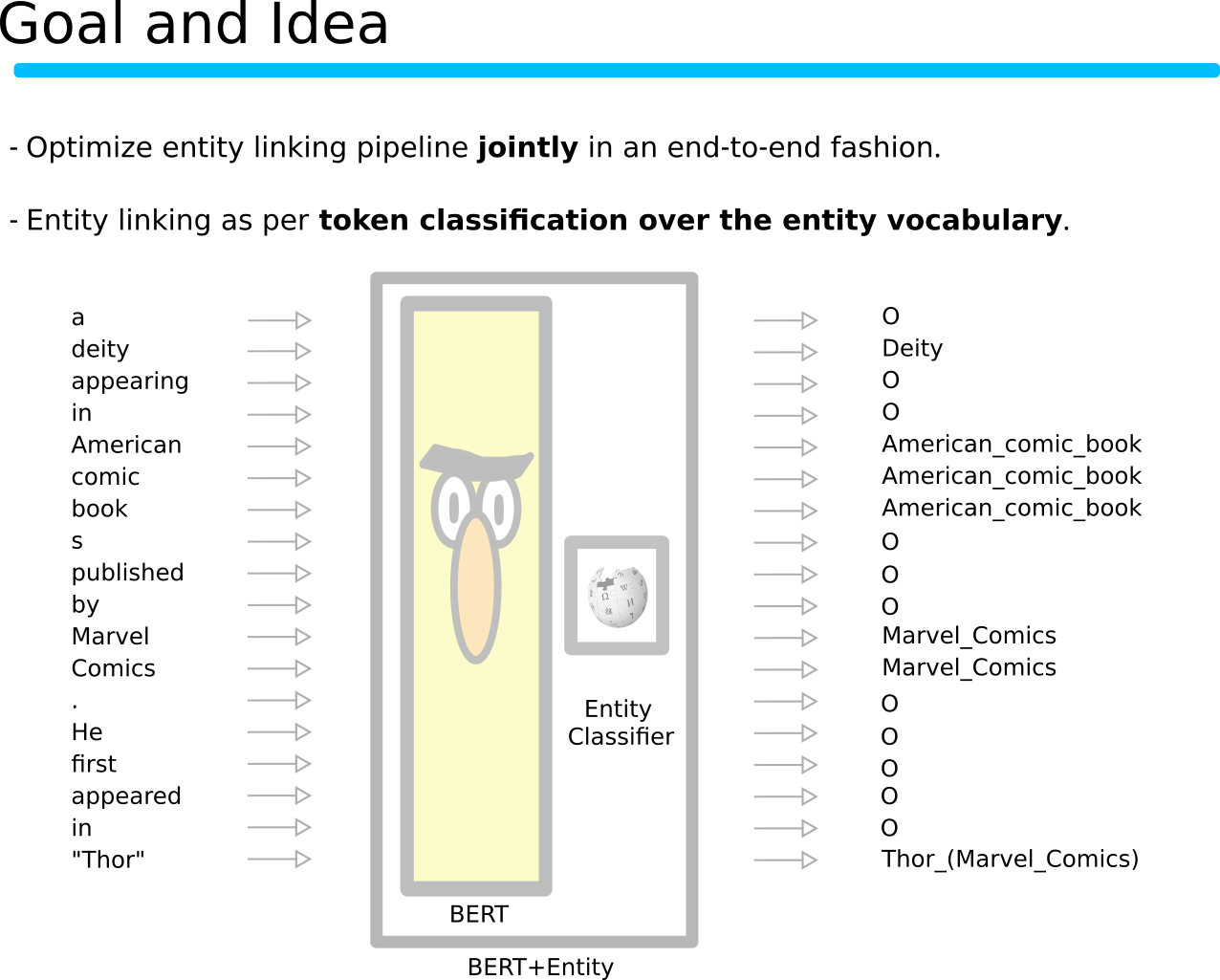
This repository contains the code for the CONLL 2019 paper "Investigating Entity Knowledge in BERT with Simple Neural End-To-End Entity Linking". The code is provided as a documentation for the paper and also for follow-up research.
The content of this page covers the following topics:
- Quick start
- Preparation and Installation
- Preprocessing of Wikipedia and the AIDA-CONLL entity linking benchmark into a sequence tagging format
- Finetuning/Training a BERT-Entity model on Wikipedia
- Finetuning a BERT-Entity model on the AIDA-CONLL entity linking benchmark
- Using a BERT-Entity model in a downstream task
- Issues and possible improvements
Here are all the steps until the finetuning and evaluation on the AIDA-CoNLL benchmark in a prototyping setting (i.e. a smaller model pretrained on reduced Wikipedia data):
-
The project is installed as follows:
git clone https://github.com/samuelbroscheit/entity_knowledge_in_bert.git cd entity_knowledge_in_bert pip install -r requirements.txt git submodule update --init -
Add paths to environment
source setup_paths -
Create directory
mkdir -p data/benchmarks/The AIDA-CoNLL benchmark file should be located under
data/benchmarks/aida-yago2-dataset/AIDA-YAGO2-dataset.tsv. Get it from https://www.mpi-inf.mpg.de/departments/databases-and-information-systems/research/yago-naga/aida/downloads/ . If you get it from somewhere else, then please make sure that you have the correct file with 6 columns: Token, Mention, Yago Name, Wiki Name, Wiki Id, Freebase Id. -
Run preprocessing
python bert_entity/preprocess_all.py -c config/dummy__preprocess.yaml -
Run pretraining on Wikipedia
python bert_entity/train.py -c config/dummy__train_on_wiki.yaml -
Finetune on AIDA-CoNLL benchmark
python bert_entity/train.py -c config/dummy__train_on_aida_conll.yaml -
Evaluate the best model on the AIDA-CoNLL benchmark
python bert_entity/train.py -c config/dummy__train_on_aida_conll.yaml --eval_on_test_only True --resume_from_checkpoint data/checkpoints/dummy_aidaconll_00001/best_f1-0.pt
For downloading and processing the full data and for storing checkpoints you should have at least 500GB of free space in the respective filesystem. If you just want to prototype there are also prepared configurations that need less space (~100GB).
To install run the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/samuelbroscheit/entity_knowledge_in_bert.git
cd entity_knowledge_in_bert
pip install -r requirements.txt
git submodule update --init
Every time you run the code you have to setup up the paths for python with
source setup_paths
First create the directory
mkdir -p data/benchmarks/
and then retrieve the AIDA CoNLL-YAGO2 benchmark from https://www.mpi-inf.mpg.de/departments/databases-and-information-systems/research/yago-naga/aida/downloads/ (the benchmark is referred to as AIDA Conll throughout the code). The resulting file should be located under data/benchmarks/aida-yago2-dataset/AIDA-YAGO2-dataset.tsv. If you get it from somewhere else, please make sure that you have the correct file with 6 columns: Token, Mention, Yago Name, Wiki Name, Wiki Id, Freebase Id.
The preprocessing pipeline will take care of all downloads and processing of the data. You run the preprocessing with:
python bert_entity/preprocess_all.py -c PREPROC_CONFIG_FILE_NAME
PREPROC_CONFIG_FILE_NAME is a yaml file, but all options can also be given on the command line.
In the config folder you will find two configurations:
-
config/dummy__preprocess.yaml is a setting for prototyping and testing the preprocessing pipeline and for prototyping the BERT-Entity training.
-
config/conll2019__preprocess.yaml is the setting "Setting 2" that was used in the the CoNLL 2019 paper for the BERT-Entity model with ~500K entities.
The PREPROC_CONFIG_FILE_NAME supports the following configurations:
--debug Print debug messages
# General settings
--wiki_lang_version Wiki language version, e.g. enwiki
--data_version_name Data identifier/version; e.g. if you experiment with different
preprocessing options you should use different names here to create
new directories.
--num_most_freq_entities Number of most frequent entities that should be collected from the
entity set collected from the Wikipedia dump
--add_missing_conll_entities Whether entities for the AIDA CONLL benchmark that are missing from
the most frequent entities collected from the Wikipedia dump should
be added to the entity vocabulary
--uncased Should the input token dictionary be uncased
# DownloadWikiDump
--download_data_only_dummy Only download one wiki file
--download_2017_enwiki Download the enwiki 2017 dump to reproduce the experiments for the
CONLL 2019 paper
# CollectMentionEntityCounts
--collect_mention_entities_num_workers
Number of worker for parallel processing of the Wikipedia dump to
collect mention entities.
# WikiExtractor
--wikiextractor_num_workers Number of worker for parallel processing of the Wikipedia dump
# CreateWikiTrainingData
--create_training_data_num_workers
Number of worker for parallel processing to create the sequence
tagging training data
--create_training_data_num_entities_in_necessary_articles
Threshold on the #entities in necessary articles (i.e. articles that
contain entities in the most frequent entity vocabulary) that should
be considered for training data
# CreateIntegerizedWikiTrainingData
--create_integerized_training_num_workers
Number of worker for parallel processing to create the integerized
sequence tagging training data, also determines the number of created
shards.
--create_integerized_training_instance_text_length
Text length of the integerized training instances
--create_integerized_training_instance_text_overlap
Overlap between integerized training instances
--create_integerized_training_max_entity_per_shard_count
Max count per entity in each shard. For each
--create_integerized_training_valid_size
Sample size for validation data.
--create_integerized_training_test_size
Sample size for test data.
Preprocessing consists of the following tasks (the respective code is in bert_entity/preprocessing):
-
CreateRedirects
-
Create a dictionary containing redirects for Wikipedia page names (*). The redirects are used for the Wikipedia mention extractions as well as for the AIDA-CONLL benchmark.
"AccessibleComputing": "Computer_accessibility"
-
-
CreateResolveToWikiNameDicts
-
Create a dictionary that map Freebase Ids and Wikipedia pages ids to Wikipedia page names (*). The disambiguations are used to detect entity annotations in the AIDA-CONLL benchmark that have become incompatible for newer Wikipedia versions.
"/m/01009ly3": "Dysdera_ancora""10": "Computer_accessibility"
-
-
CreateDisambiguationDict
-
Create a dictionary containing disambiguations for Wikipedia page names (*). The disambiguations are used to detect entity annotations in the AIDA-CONLL benchmark that have become incompatble for newer Wikipedia versions.
"Alien": ["Alien_(law)", "Alien_(software)", ... ]
-
-
DownloadWikiDump
- Download the current Wikipedia dump. Either download one file for a dummy / prototyping version. Set
download_data_only_dummyto True for just one file, ootherwise download all files. Setdownload_2017_enwikito True if not the latest dump should be retrieved but a 2017 dump like in the paper.
- Download the current Wikipedia dump. Either download one file for a dummy / prototyping version. Set
-
Wikiextractor
- Run Wikiextractor on the Wikipedia dump and extract all the mentions from it.
-
CollectMentionEntityCounts
- Collect mention entity counts from the Wikiextractor files.
-
PostProcessMentionEntityCounts
- Create entity indexes that will later be used in the creation of the Wikipedia training data. First, based on the configuration key
num_most_freq_entitiesthe top k most popular entities are selected. Based on those, other mappings are created to only contain counts and priors concerning the top k popular entities. Later the top k popular entities will also restrict the training data to only contain instances that contain popular entities. Also, ifadd_missing_conll_entitiesis set, the entity ids necessary for the AIDA-CONLL benchmark that are missing in the top k popular entities are added. This is to ensure that the evaluation measures are comparable to prior work.
- Create entity indexes that will later be used in the creation of the Wikipedia training data. First, based on the configuration key
-
CreateAIDACONLL
- Read the AIDA-CONLL benchmark dataset in and merge it with the NER annotations. Requires you to provide
data/benchmarks/aida-yago2-dataset/AIDA-YAGO2-dataset.tsv. Please make sure that you have the correct file with 6 columns: Token, Mention, Yago Name, Wiki Name, Wiki Id, Freebase Id.
- Read the AIDA-CONLL benchmark dataset in and merge it with the NER annotations. Requires you to provide
-
CreateKeywordProcessor
- Create a tri-based matcher to detect possible mentions of our known entities. We use this later to add autmatic annotations to the text. However, as we do not know the true entity for those mentions, they will have multiple labels, i.e. all entities from the p(e|m) prior.
-
CreateWikiTrainingData
- Create sequence labelling data. Tokenization is done with BertTokenizer. Tokens are either have a label when they have an associated Wikipedia link, or when they are in spans detected by the keyword matcher. Subsequently, we count the mentions in this data and create a discounted prior p(e|m) and the set of necessary Wikpedia articles, i.e. all the articles that contain links to the top k popular entities.
-
CreateIntegerizedWikiTrainingData
-
Create overlapping chunks of the Wikipedia articles. Outputs are stored as Python lists with integer ids. Configured by
create_integerized_training_instance_text_lengthandcreate_integerized_training_instance_text_overlap.Each worker creates his own shard, i.e., the number of shards is determined by
create_integerized_training_num_workers.Only saves a training instance (a chunk of a Wikipedia article) if at least one entity in that chunk has not been seen more than
create_integerized_training_max_entity_per_shard_counttimes. This downsamples highly frequent entities. Has to be set in relation tocreate_integerized_training_num_workersandnum_most_freq_entities. For the CONLL 2019 paper experiments the setting wascreate_integerized_training_max_entity_per_shard_count = 10 create_integerized_training_num_workers = 50 num_most_freq_entities = 500000
-
-
CreateIntegerizedCONLLTrainingData
- Create overlapping chunks of the benchmark articles. Outputs are stored as Python lists with integer ids. Configured by
create_integerized_training_instance_text_lengthandcreate_integerized_training_instance_text_overlap.
- Create overlapping chunks of the benchmark articles. Outputs are stored as Python lists with integer ids. Configured by
Here we use an already extracted mapping provided by DBPedia that was created from a 2016 dump. Please note that in the experiments for the paper a Wikipedia dump from 2017 was used. The DbPedia dictionaries might not be adequate for the latest wiki dumps.
Once you have alle the preprocessing done, you can run the training on Wikipidia to learn a BERT-Entity model. When you have learned a BERT-Entity model on Wikipedia you can resume it to finetune it on the AIDA-CONLL benchmark.
Run the training with:
python bert_entity/train.py -c TRAIN_CONFIG_FILE_NAME
TRAIN_CONFIG_FILE_NAME is a yaml file, but all options can also be given on the command line.
Run evaluation with:
python bert_entity/train.py -c TRAIN_CONFIG_FILE_NAME --eval_on_test_only True --resume_from_checkpoint LOGDIR/best_f1-0.pt
LOGDIR is the path that was set in TRAIN_CONFIG_FILE_NAME with key logdir .
In the config folder you will find the following configurations:
-
config/dummy__train_on_wiki.yaml is a setting for prototyping the BERT-Entity training on Wikipieda.
-
config/dummy__train_on_aida_conll.yaml is a setting to finetune the best found model from
dummy__train_on_wiki.yamlon the the aida-yago2 dataset. -
config/conll2019__train_on_wiki.yaml is a setting for reproducing the BERT-Entity training on Wikipieda from the CoNLL 2019 paper.
-
config/conll2019__train_on_aida_conll.yaml is a setting to finetune the best found model from
conll2019__train_on_wiki.yamlon the the aida-yago2 dataset to reproduce the CoNLL 2019 paper.
The TRAIN_CONFIG_FILE_NAME supports the following configurations:
--debug DEBUG
--logdir LOGDIR; the output dir where checkpints and logfiles are stored
--data_workers number of data workers to prepare training instances
--data_version_name use the same identifier that was used for the same key in
preprocessing
--device GPU device used for training
--eval_device GPU device used for evaluation
--out_device GPU device used to collect the most probable entities in the batch
--dataset 'EDLDataset' for training on Wikipedia or 'CONLLEDLDataset'
for training on AIDA-CONLL
--model Either 'Net' for training on Wikipedia or 'ConllNet' for
training on AIDA-CONLL
--eval_on_test_only only run evaluation on test (requires --resume_from_checkpoint)
--batch_size batch size in training
--eval_batch_size batch size in evluation
--accumulate_batch_gradients accumulate gradients over this many batches
--n_epochs max number of epochs
--finetuning start finetuning after this many epochs
--checkpoint_eval_steps evaluate every this many epochs
--checkpoint_save_steps save a checkpoint every this many epochs
--dont_save_checkpoints dont_save_checkpoints
--sparse Use a sparse embedding layer
--encoder_lr encoder learning rate
--decoder_lr decoder learning rate
--encoder_weight_decay encoder weight decay
--decoder_weight_decay decoder weight decay
--bert_dropout BERT_DROPOUT
--label_size nr of entities considered in the label vector for each instance
--topk_neg_examples TOPK_NEG_EXAMPLES
--entity_embedding_size entity_embedding_size
--project project entity embedding
--resume_from_checkpoint path of checkpoint to resume from
--resume_reset_epoch reset the epochs from the checkpoint for resuming (f.ex.
training on AIDA-CONLL)
--resume_optimizer_from_checkpoint resume optimizer from checkpoint
--eval_before_training evluate once before training
--data_path_conll path to the conll file that was create in data_version_name
--exclude_parameter_names_regex regex to exclude params from training, i.e. freeze them
See files in downstream_tasks. Documentation is a TODO.
- The code is currently poorly documented and not always nice to read.
- Currently all checkpoints are kept which requires a lot of disk space, should be configurable to only keep the K most current checkpoints.
- Training is slow because of accumulating the most probable entities per batch. This could be sped up with adaptive softmax like change, i.e. first decide if token is an entity.
- Resuming currently only works on the epoch level. To enable resuming in between epochs, the shuffled indexes for an epoch have to be stored in the LOGDIR or checkpoint.
- When AIDA CoNLL entities are missing from the top k popular entities and are added to the vocabulary, should make sure that confounders with high BPE token overlap are added as well.
- Configuration to create integerized Wiki training data is hard to grasp, i.e. which training instances are included depends on
create_integerized_training_max_entity_per_shard_count,create_integerized_training_num_workersandnum_most_freq_entities. Their influence is difficult to describe, should be more straightforward. - It would be much better to produce an annotated document and evaluate it with https://github.com/wikilinks/neleval . neleval is widely used and has all the necessary metrics implemented.
- Investigate shrinking the model size and improve prediction speed.
if you find this code useful for your research please cite
@inproceedings{broscheit-2019-investigating,
title = "Investigating Entity Knowledge in {BERT} with Simple Neural End-To-End Entity Linking",
author = "Broscheit, Samuel",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 23rd Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning (CoNLL)",
month = nov,
year = "2019",
address = "Hong Kong, China",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/K19-1063",
doi = "10.18653/v1/K19-1063",
pages = "677--685",
}