1ClickECK was built to rapidly deploy with ease an K8s (AWS EKS/Azure AKS/GCP GKE) cluster, install ECK, and the ES Stack.
Total time from configuration to a fully launched ECK cluster generally should take less than 10 minutes. The automation; 1ClickECK, is idempotent.
Note - Automation deploys OpenEBS which exposes and uses locally attached storage. More info, go to the OpenEBS section
1ClickECK currently deploys
- EKS, AKS, GKE
- ECK (Optional)
- ElasticSearch
- Kibana
- License loading (Bring your own ES license)
Does not deploy
- APM Server
- Fleet
- Elastic Maps
- Enterprise Search
Quick Start
Details regarding clients required to run the automtaion are outlined in the following sections. However if a ubuntu 20.+ instance is available, a quick start client install script is available here
https://github.com/sunileman/1ClickECK/blob/main/scripts/1ClickECK-client-install.sh
This will install all the required libaries and CLIs for the automation.
General
- Ubuntu host to install all clients listed below (terraform, aws cli, etc). Automation has been tested on ONLY on Ubuntu host
- Install Terraform client
- Install kubectl client
- AWS
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/install-kubectl.html
- The version of kubectl must match the version of eks/aks you plan on deploying. The version number is set in terraform.tfvars, variable eks_version/aks_version
- GCP
- AWS
- Install git client
- To clone this repo and when possible, contribute back :)
- ElasticSearch Enterprise License
- Only required to use enterprise features such as ML, autoscale, etc
AWS
- AWS CLI installed fully configured on the lastest version 2 release.
GIT
- Not required. If interested in pulling the repo via ssh to keep up with updates applied to this automation
https://docs.github.com/en/authentication/connecting-to-github-with-ssh/generating-a-new-ssh-key-and-adding-it-to-the-ssh-agent
Azure
- AZ CLI CLI installed fully configured
- Azure service principal
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/developer/terraform/authenticate-to-azure?tabs=bash#create-a-service-principal
- Make note of the
appId,display_name,password, andtenantID - Set the following env variables
export ARM_CLIENT_ID="Your appID" export ARM_CLIENT_SECRET="Your app secret" export ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID="Your Azure SUBSCRIPTION" export ARM_TENANT_ID="Your tenantID" export TF_VAR_aks_service_principal_app_id="Your appID" export TF_VAR_aks_service_principal_client_secret="Your app secret" GCP- https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/how-to/cluster-access-for-kubectl#gcloud
- run gcloud init to initialize your client
- Note - project must be set in terraform.tfvars. Project value within tags variable is used to tag instances with project value. Not the same as gcp project which is set in terrform.tfvars.
Required Arguments
-c [aws|azure|gcp]
-b [all|k8s]
-d
-r disable openebs
de destroy ECK
i get cluster info
Examples
To run the automation in the background. Output will be writen to nohup.out.
nohup ./1ClickECK.sh -b all -c [aws|gcp|azure] &Once the automation completes, Kibana endpoints along with username and password should be displayed. To retrieve again, simply run
The automation will set your local kubectl manifest. Verify by running
kubectl get nodesTear Down all assets built by the automation
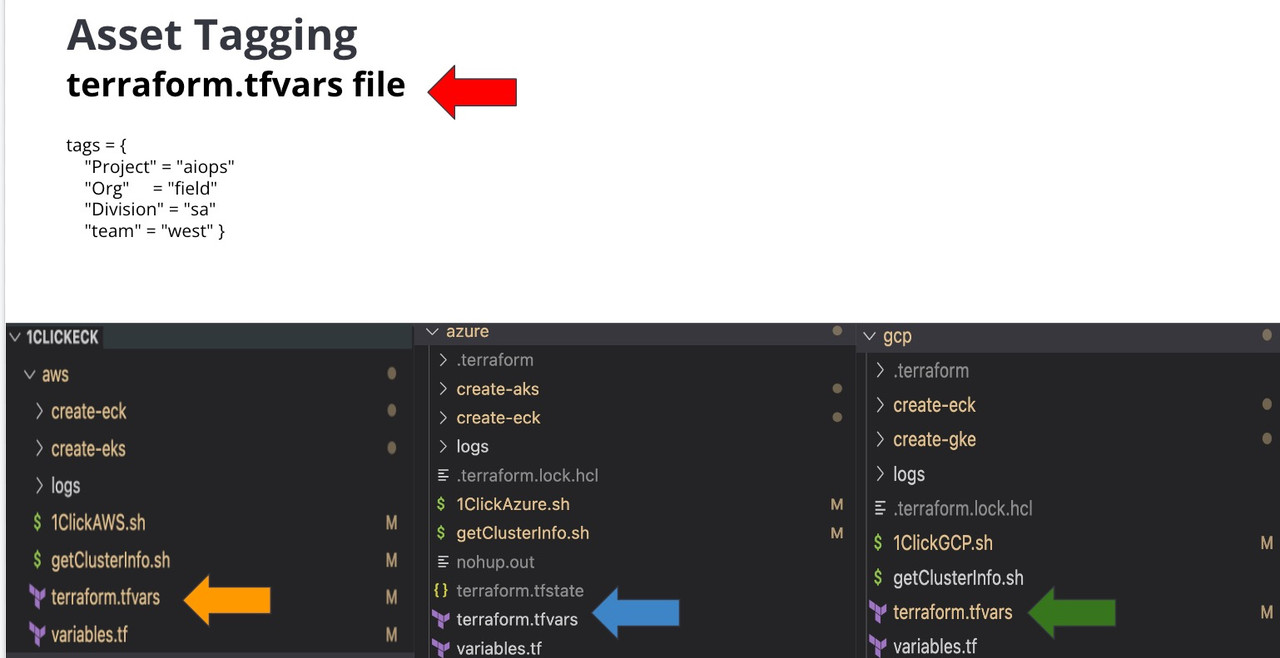
./1ClickEckOnEKS.sh -d -c [aws|gcp|azure]The automation requires a few variables to be set in the .[aws|azure]/terraform.tfvars file
Name of your deployment/project
tags.Project
Name of owner
tags.Owner
Name which will be appended to the EKS deployment. Max 6 characters
tags.username
Any variable found in ./[aws|azure]/variables.tf can be set as an envionrment variable.
export TF_VAR_<variable name>="your value"
export TF_VAR_variable_<list variable type>='["value", "value"]'Envionrment variables and setting variables in terraform.tfvars can be used together.
Consider terraform variable order of Precedence: https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/language/values/variables#variable-definition-precedence
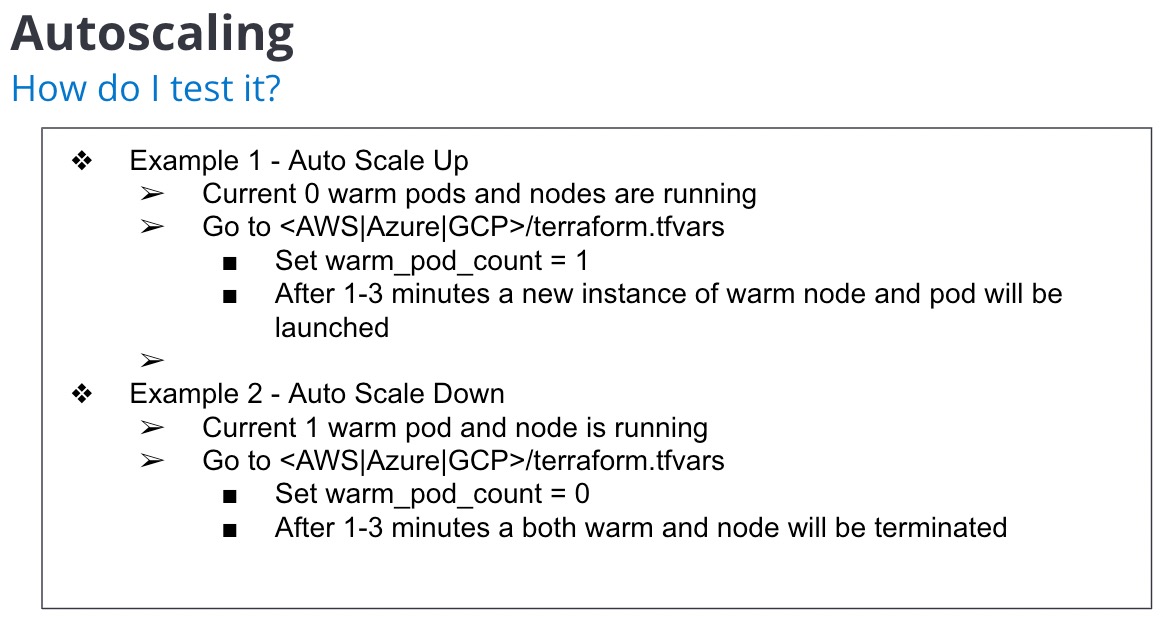
Note - Instance and pod count
Instance count = Number of K8s nodes per type (hot/warm/etc))
Pod count = Number of pods per type (hot/warm/etc) which will be deployed on the instance type.
For example you can deploy 4 hot pods on 1 hot K8s instance type.

./[aws|azure]/variables file host all possible variables supported by this deployment.
If a varialble is not present in ./[aws|azure]/terraform.tfvars, the default value will be taken from ./[aws|azure]/variables.tf
If default value is not acceptable, set the varialble value in ./[aws|azure]/terraform.tfvars
For example, the default number of es hot instances is 3. That default value is set in ./[aws|azure]/variables.tf. To
change this value to 10; in ./[aws|azure]/terraform.tfvars file, set hot_instance_count = 10.
Another example. The default instance type for warm is im4gn.4xlarge. To change this value to
im4gn.8xlarge; in ./[aws|azure]/terraform.tfvars file, set warm_instance_type = im4gn.8xlarge.
Word of caution on instance types for node groups (hot, warm, etc). When selecting an instance type, verify the AMI type: AL2_x86_64, AL2_x86_64_GPU, AL2_ARM_64. Instance type must fall withn specific AMI Type.
**Instance types
This deployment only supports DAS, not EBS
Ingest to pods are set by the following variables
[master|hot|warm|cold|frozen|ml]_accept_ingest=false
GCP - To skip node pool creation
[master|hot|warm|cold|frozen|ml]_create_node_pool=false
Deployment without a license will use a basic license configuration.
If a ES license is available to you, place it under ./[aws|azure|gcp]/create-eck/license and name the license file es-license.json.
The deployment will pick up license file
If a license file needs to be applied or changed after deployment, simply run ./[aws|azure|gpc]/create-eck/eck-add-license.sh
Once EKS is deployed, ES pods will be deployed leveraging resources defined in the K8s manifest.
Each node type (master, hot, warm, ml, etc) spec is defined within ./[aws|azure]/variables.tf.
Change the pod spec to your desired configuration.
For example
ml_pod_count=value
ml_pod_cpu=value
ml_pod_memory=value
ml_pod_storage=value
ml_pod_ES_JAVA_OPTS=valueLatest release of ES, if jvm arguments aren't spplied for heap size, half the available memory within the pod will be used for heap. Take this into consideration if the defaults aren't acceptables
By default ECK will mount openebs storage class to ES pods. To use a different storage class is simple
Run kubeclt get sc to retrieve available storage classes.
GKE Example
[master|hot|warm|cold|frozen|ml]_pod_storage_class = "premium-rwo"
AWS Example
[master|hot|warm|cold|frozen|ml]_pod_storage_class = "gp3"
Azure Example
[master|hot|warm|cold|frozen|ml]_pod_storage_class = "managed-csi-premium"
Run the automation with r option to disable openebs
The automation; 1ClickECK, is idempotent. Therefore if updates to ECK or ES have been applied, simple rerun 1ClickECK with the same -b -c arguments
Automation will set local kube config (kubectl) after automation run. If local kube config needs to be reset, simple rerun the automation (even if there is no change) to set local kube config.
To reset your local kubeclt, run
/1ClickECK/[gpc|aws|azure]/create-[eks|aks|gke]/setkubectl.shOpenEBS is a automatic disk provisioner for K8s. There may be scanerios the defaults from OpenEBS are not useful. To handle these scanerios, run the automation with -r option to disable openEBS
./1ClickECK -c gcp -b k8s -r
If openEBS exist on K8s cluster and to remove run this
./1ClickECK/<aws|gcp|azure>/create-gke/addons/openebs/1ClickRemoveOpenEBS.sh
If additional storage classes are available and need to be leverage, set the following variables with the storage class name
[master|hot|warm|cold|frozen|ml]_pod_storage_class = <Storage Class Name>
AWS GPE
The automation installs EBS CSI along with required IAM permissions. Additionally the automation will create a stroage calls gp3. It can be used by setting
[master|hot|warm|cold|frozen|ml]_pod_storage_class = gp3
Azure AKS bash into pod
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/node-access
GCP GKE bash into pod
https://cloud.google.com/migrate/containers/docs/troubleshooting/executing-shell-commands
OOMKilledPod JVM is requesting more memory than pod limits
exec plugin: invalid apiversion "client.authentication.k8s.io/v1alpha1"The version of K8s does not match kubectl client. Please refer to: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/install-kubectl.html
All automation logs are stored in ./logs
Error: Kubernetes cluster unreachable: invalid configuration: no configuration has been provided, try setting KUBERNETES_MASTER environment variabletry: export KUBE_CONFIG_PATH=~/.kube/config
If one of the pods is stuck in init stage run
kubectl describe pod <podname>
That should give you an idea on what went wrong. If the mount fails due to srv/local not available, rerun openEBS.
How to enter pod within GKE nodes
gcloud compute ssh <NODE_NAME> --zone <ZONE>
-Logs showing markup Use lnav to view logs: https://lnav.org/
Azure Error
Error: building AzureRM Client: Authenticating using the Azure CLI is only supported as a User (not a Service Principal).
Set your azure creds prior to launching the automation
-Connection refused when trying to reach ES API port 9200
Verify at least 1 pod has role which does inclue master. The load balancer deployed selects nodes based on
elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/node-master: "false"
Error
│ Error: Failed to query available provider packages
│
│ Could not retrieve the list of available versions for provider
│ anschoewe/curl: could not connect to registry.terraform.io: Failed to
│ request discovery document: Get
│ "https://registry.terraform.io/.well-known/terraform.json": read tcp
│ xxxx:54284->xxxx:443: read: connection reset by peer
Rerun automation. Terraform api (target side) was reset.
Error
Try: aws creds are invalid. Verify by running
aws sts get-caller-identity