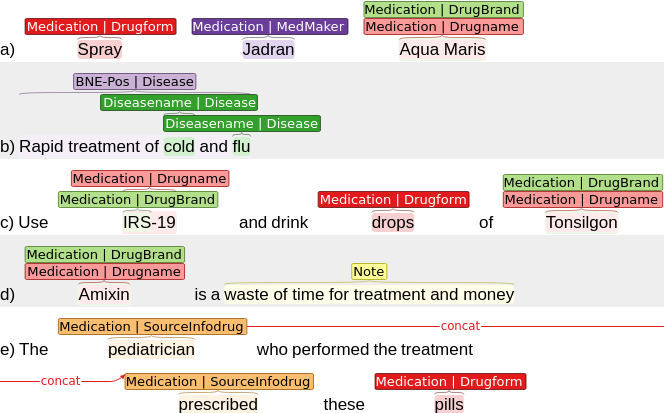
This repository provides the RDRS dataset.
| Task | Sub-tasks | Size Categories | Languages | Language Creators | Annotations Creators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text Classification | - pharmacological Named Entity Recognition (NER); - Relation Extraction (RE); - Coreference Extraction; - Text Normalization |
3821 docs; 83910 entities; 55717 relations |
Russian, monolingual |
Russian | experts |
Russian Drug Reviews corpus (RDRS) is a Russian-language annotated corpus consisting of medicine reviews posed by Internet users from the Otzovik web site, with complex named entity recognition (NER) labeling of pharmaceutically relevant entities, and their relations.
This is the third version of the corpus (or RDRS-3800), which includes 3,821 reviews. About the previous versions (RDRS-1600 and RDRS-2800), you can read at link).
The main specifications of our corpus are shown in Statistics section.
Information about the data structure, detailed description of the fields and an example for a document from the dataset are presented in Data Format and Data Fields sections.
The materials about annotation procedure described in Dataset Creation section.
Application of the dataset for different tasks is discussed in Supported Tasks section.
We've prepared a bash script to help you get started with the dataset.
To download the dataset you need to go to the repository directory ("./RDRS/") and run at cmd:
mkdir ./data
. get_data.shAlternatively, you can follow the steps:
- Download the data archive at link:
mkdir ./data
wget "https://sagteam.ru/RDRS/RDRS_v3_folds.tar.gz" -P ./data/- Extract the data by using the command:
tar -xzvf ./data/RDRS_v3_folds.tar.gz -C ./data/- (Optional) Remove the archive:
rm -f ./data/RDRS_v3_folds.tar.gzAfter that you can find the data at "./RDRS/data/" directory.
The data is presented in json format as a list of documents, where each document is a dictionary with keys: "text_id", "text", "entities", "relations", "coreference". For a detailed description of these keys and nested dictionary items, see below in the Data Fields section.
An example of a document from the dataset is shown in file: "sample_doc.json".
First level tags:
- text_id - review id;
- text - review text;
- entities - a list containing data about annotated mentions;
- relations - a list containing data about relations between mentions;
- coreference - a dictionary containing coreference annotation data.
Each element of the entities list has a dictionary structure, where the key is the entity number, and the value is a dictionary describing this entity. A detailed description of the types is presented in the markup description on the website https://sagteam.ru/en/med-corpus/annotation/. To describe entities, dictionaries with the following fields are used (the [field] field means that it may be absent):
- entity_id - mention id.
- xmiID - alternate mention id assigned by the Webanno annotation system when exporting in xmi format.
- spans - a list in which information is stored about passages in which the entity is mentioned, each element of the list is a dictionary with fields begin and end (end not inclusive), which indicate the indexes of the span boundary.
- text - the text of the mention, composed of all spans specified in the spans field.
- MedEntityType - main type of the mention, one of: Medication, Disease, ADR, Note.
- [DisType] - Disease mention subtype. Field can be absent if MedEntityType is not Disease.
- [MedType] - Medication mention subtype. Field can be absent if MedEntityType is not Medication.
- [medform_standart] - standardized name for the form of the drug. The field is present if MedType==Drugform.
- [MedFrom] - whether the drug is distributed in Russia (Domestic) or only abroad (Foreign). The field is only present if MedType == Drugname.
- [ATC] - anatomical-therapeutic-chemical classification code (if MedType==Drugname or MedType==Drugclass).
- [MKB10] - ICD-10 classification code (if DisType==Diseasename).
- [MedDRA] - Preferred term from MedDRA (if MedEntityType==ADR or MedEntityType==Disease and DisType==Indication). If an entity allows several normalization options, the corresponding concepts are separated by "|".
- Context - a list indicating which contexts the mention belongs to in the review.
- tag - list of tags. Tag is a combination of MedEntityType and subtype.
Each element of the relations list has a dictionary structure with the following fields:: first_entity, second_entity, relation_type, relation_class
- first_entity - a dictionary that describes one of the mentions in a relation
- second_entity - a dictionary that describes one of the mentions in a relation
- relation_type - relation type, one of:'ADR_Medication:MedTypeDrugname', 'Disease:DisTypeDiseasename_Disease:DisTypeIndication', 'Medication:MedTypeDrugname_Disease:DisTypeDiseasename', 'Medication:MedTypeDrugname_Medication:MedTypeSourceInfodrug'
- relation_class - relationship class, takes the value 1 if the entities have a common label in the Context field (there is a relationship between the entities), or 0 if the entities are not united by the same context (no relationship).
In the coreference coreference chains a specified by dictionary with 2 fields:
- mentions contains list of mention spans described by its boundaries in the text startPos and endPos;
- clusters сcontains a list of chains (clusters). each chain in this list of mention indexes from mentions that are coreferent.
The corpus contains:
- 3821 documents
- 11812 mentions of drugnames linked to 604 ATC codes;
- 4934 mentions of diseasenames linked to 428 ICD-10 codes;
- 5050 mentions of ADR linked to 615 unique MedDRA terms;
- and 7456 indications linked to 627 unique MedDRA terms; More detailed statistics can be found on our website
Mention labeling for the review texts has been performed by a group of four annotators using a guide developed jointly by machine learning experts and pharmacists. Two annotators were qualified pharmacists, and the two others were students with pharmaceutical education. The process of creation of this dataset describet in the article (please cite it if you are using this dataset):
@article{sboev2022analysis,
title={Analysis of the full-size russian corpus of internet drug reviews with complex ner labeling using deep learning neural networks and language models},
author={Sboev, Alexander and Sboeva, Sanna and Moloshnikov, Ivan and Gryaznov, Artem and Rybka, Roman and Naumov, Alexander and Selivanov, Anton and Rylkov, Gleb and Ilyin, Vyacheslav},
journal={Applied Sciences},
volume={12},
number={1},
pages={491},
year={2022},
publisher={MDPI}
}
When solving the NER problem using the RDRS corpus, it is necessary to extract mentions of ADR, Diseasename, Indication, Drugname, SourceInfoDrug from the review text. Metric - F1-exact for each category, macro averaging. Top scores:
| Dataset | ADR | Disease | Indication | Drug | Source | F1-macro | Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDRS 3800 | 60.1 | 87.2 | 67.5 | 96.6 | 72.5 | 76.7 | [Selivanov A.A., Gryaznov A.V. Rybka R.B., Sboev A.G., Sboeva S.G., Klyueva Yu.A. Relation Extraction from Texts Containing Pharmacologically Significant Information on base of Multilingual Language Models] |
| RDRS 2800 | 63.8 | 96.0 | 89.7 | 63.3 | 73.2 | 77.2 | [Sboev A.G., Rybka R.B., Naumov A.V., Selivanov A.A., Gryaznov A.V., Moloshnikov I.A. An accuracy comparison of the Joint and Sequential Approaches for End-to-End Related Named Entities Extraction in the Texts of Russian-Language Reviews Based on Neural Networks IOPscience, - (2022)] |
Articles devoted to this task:
- Sboev A.G., Moloshnikov I.A., Selivanov A.A., Rylkov G.V., Rybka R.B. The two-stage algorithm for extraction of the significant pharmaceutical named entities and their relations in the Russian-language reviews on medications on base of the XLM-RoBERTa language model Springer's Studies in Computational Intelligence, - (2022)
- Sboev A.G., Rybka R.B., Naumov A.V., Selivanov A.A., Gryaznov A.V., Moloshnikov I.A. An accuracy comparison of the Joint and Sequential Approaches for End-to-End Related Named Entities Extraction in the Texts of Russian-Language Reviews Based on Neural Networks IOPscience, - (2022)
- Sboev A.G., Sboeva S.G., Moloshnikov I.A., Gryaznov. A.V., Rybka R.B., Naumov A.V., Selivanov A.A., Rylkov G.V., Ilyin V.A. Analysis of the Full-Size Russian Corpus of Internet Drug Reviews with Complex NER Labeling Using Deep Learning Neural Networks and Language Models Applied Sciences (Switzerland), Т. 12. – №. 1. – С. 491. (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010491
- Selivanov A.A., Gryaznov A.V. Rybka R.B., Sboev A.G., Sboeva S.G., Klyueva Yu.A. Relation Extraction from Texts Containing Pharmacologically Significant Information on base of Multilingual Language Models Sissa Medialab Srl, том 429 (2022)
When solving the RE problem on the RDRS corpus, it is necessary to determine the existence of a relationship between two entities. Four types of relationships are considered: ADR–Drugname, Drugname–SourceInfodrug, Drugname–Diseasename, Diseasename–Indication. Top scores:
| Dataset | Entities origin | ADR–Drugname | Drugname–Diseasename | Drugname–SourceInfodrug | Diseasename–Indication | F1-macro | Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDRS 3800 | Gold | - | - | - | - | 87.2 | [Selivanov A.A., Gryaznov A.V. Rybka R.B., Sboev A.G., Sboeva S.G., Klyueva Yu.A. Relation Extraction from Texts Containing Pharmacologically Significant Information on base of Multilingual Language Models Sissa Medialab Srl, том 429 (год публикации - 2022)] |
| RDRS 3800 | Predicted | - | - | - | - | 60.1 | [Selivanov A.A., Gryaznov A.V. Rybka R.B., Sboev A.G., Sboeva S.G., Klyueva Yu.A. Relation Extraction from Texts Containing Pharmacologically Significant Information on base of Multilingual Language Models Sissa Medialab Srl, том 429 (год публикации - 2022)] |
| RDRS 2800 | Gold | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| RDRS 2800 | Predicted | 51.2 | 69.4 | 49.2 | 38.6 | 52.1 | [Сбоев А.Г., Рыбка Р. Б., Наумов А.В., Селиванов А.А, Грязнов А.В., Молошников И.А. An accuracy comparison of the Joint and Sequential Approaches for End-to-End Related Named Entities Extraction in the Texts of Russian-Language Reviews Based on Neural Networks IOPscience, - (год публикации - 2022)] |
Articles devoted to this task:
- Sboev A.G., Moloshnikov I.A., Selivanov A.A.? Rylkov G.V., Rybka R.B. The two-stage algorithm for extraction of the significant pharmaceutical named entities and their relations in the Russian-language reviews on medications on base of the XLM-RoBERTa language model Springer's Studies in Computational Intelligence, - ( 2022)
- Sboev A.G., Selivanov A.A., Rybka R.B., Moloshnikov I.A., Rylkov G.V. Evaluation of Machine Learning Methods for Relation Extraction Between Drug Adverse Effects and Medications in Russian Texts of Internet User Reviews Proceedings of Science, - (2022)
- Sboev A.G., Rybka R.B., Naumov A.V., Selivanov A.A., Gryaznov A.V., Moloshnikov I.A. An accuracy comparison of the Joint and Sequential Approaches for End-to-End Related Named Entities Extraction in the Texts of Russian-Language Reviews Based on Neural Networks IOPscience, - (2022)
- Sboev A.G., Selivanov A.A., Moloshnikov I.A., Rybka R.B., Gryaznov A.V., Sboeva S.G., Rylkov G.V. Extraction of the Relations among Significant Pharmacological Entities in Russian-Language Reviews of Internet Users on Medications Big Data and Cognitive Computing; MDPI AG (Switzerland), 6(1), 10 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6010010
- Selivanov A.A., Gryaznov A.V. Rybka R.B., Sboev A.G., Sboeva S.G., Klyueva Yu.A. Relation Extraction from Texts Containing Pharmacologically Significant Information on base of Multilingual Language Models Sissa Medialab Srl, том 429 (2022)
We consider the Medical Concept Normalization problem, in which it is necessary to link mentions extracted from the review text to medical concept (a Preferred term level concept from the dictionary MedDRA).
Metric - F1
Top results:
| Dataset | Mentions Origin | F1-micro | F1-macro | Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDRS 3800 | Gold | 76.5 | 30.5 | [Sboev A.G., Rybka R.B., Gryaznov A.V., Moloshnikov I.A., Sboeva S.G., Rylkov G., Selivanov A.A. Adverse Drug Reaction Concept Normalization in Russian-Language Reviews of Internet Users. Big Data and Cognitive Computing Big Data and Cognitive Computing;MDPI AG (Switzerland), 6(4), 145 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6040145] |
| RDRS 3800 | Gold | 76.2 | 32.6 | [Sboev A.G., Rybka R.B., Gryaznov A.V., Moloshnikov I.A., Sboeva S.G., Rylkov G., Selivanov A.A. Adverse Drug Reaction Concept Normalization in Russian-Language Reviews of Internet Users. Big Data and Cognitive Computing Big Data and Cognitive Computing;MDPI AG (Switzerland), 6(4), 145 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6040145] |
Articles devoted to this task:
- Sboev A.G., Rybka R.B., Gryaznov A.V., Moloshnikov I.A., Sboeva S.G., Rylkov G., Selivanov A.A. Adverse Drug Reaction Concept Normalization in Russian-Language Reviews of Internet Users. Big Data and Cognitive Computing Big Data and Cognitive Computing;MDPI AG (Switzerland), 6(4), 145 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6040145
The problem of binary classification in which the text of the review determines whether the described medicine was useful.
Metric - F1
Top results:
| Dataset | F1-macro | Paper |
|---|---|---|
| RDRS 2800 | 0.92 | [Sboev A.G., Naumov A.V., Moloshnikov I.A., Rybka R.B. Sentiment Analysis of Russian Reviews to Estimate the Usefulness of Drugs Using the Domain-Specific XLM-RoBERTa Model Springer's Studies in Computational Intelligence, - (2022)] |
Articles devoted to this task:
- Sboev A.G., Naumov A.V., Moloshnikov I.A., Rybka R.B. Sentiment Analysis of Russian Reviews to Estimate the Usefulness of Drugs Using the Domain-Specific XLM-RoBERTa Model Springer's Studies in Computational Intelligence, - ( 2022)