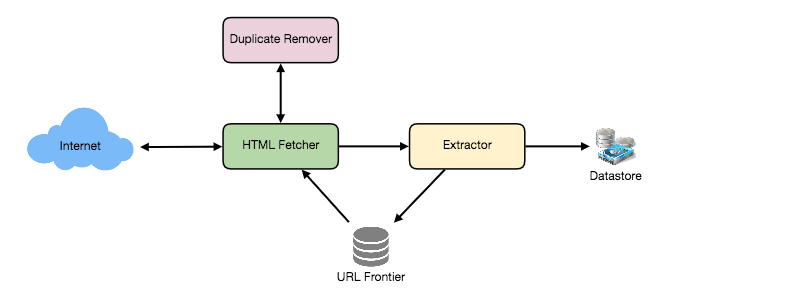
The Web Crawler downloads all website pages from a given domain into a local folder, ensuring each page is downloaded only once. It uses Breadth-First Search (BFS) for systematic traversal, preventing deep exploration, avoiding duplicates, supporting parallel processing, and managing memory efficiently. By traversing pages level by level and maintaining a queue of URLs, BFS ensures comprehensive coverage, prevents infinite loops, and optimizes resource usage.
This implementation introduces concurrency and a page limit for improved efficiency.
The system consists of different parts:
-
Crawler: Responsible for managing the crawling process, including fetching web pages, parsing HTML content, extracting links, and downloading pages. It uses BFS algorithm for crawling the website urls.
-
Queue: Maintains a queue of URLs to be crawled. URLs are added to the frontier in a BFS manner, ensuring systematic exploration of the website hierarchy.
-
Domain Caching: Each domain who is traversed, its travered urls are added to the cache, to prevent the crawler from crawling them again.
-
File Naming Logic: Generates filenames based on URLs to ensure uniqueness and compatibility with the filesystem.
-
Local Folder Creation: Creates a local folder for storing downloaded pages, organized by domain names.
-
URL Normalization: Ensures URLs leading to the same page have the same representation to avoid duplicate downloads.
-
URL Extraction: Parses HTML to extract URLs from anchor tags' href attributes.
-
Domain Matching: Determines if a URL belongs to the same domain as the entry point URL to prevent crawling external links.
Several factors may affect the performance and scalability of the web crawler:
-
Network Latency: Fetching pages over the network may be slow, especially for large or slow websites.
-
I/O Operations: Writing pages to the local filesystem may be slow, especially with high disk I/O.
-
Concurrency: Processing multiple URLs concurrently can improve performance but may lead to resource contention.
-
Cache Performance: The performance of the domain cache can impact overall crawling speed. Optimizing cache usage and ensuring efficient data access are crucial for maintaining system performance.
To improve scalability:
-
Distributed Architecture: Distribute the workload across multiple servers for scalability and resilience.
-
Load Balancing: Use a load balancer to evenly distribute requests among crawler instances.
-
Distributed File Storage: Consider using distributed file storage solutions like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage, which provide scalable and reliable storage for crawled pages.
-
Distributed Caching: Implement caching mechanisms to store previously crawled pages and reduce redundant downloads. Consider using an in-memory caching system like Redis or Memcached, or a distributed cache.
-
Data Replication: Replicate the domain cache and file storage across multiple servers to maintain consistency and improve fault tolerance. Implementing replication mechanisms ensures that each server has access to the latest data and can handle requests independently.
-
Monitoring and Alerting: Implement monitoring systems to detect and respond to performance issues or failures.
If more resources are added then the page limit can be adjusted accordingly.
Provide the entry point URL and local folder path where pages will be stored. Run the crawler script to start crawling and downloading pages.
npm install
npm start