A Python Based application (with Tkinter GUI) for BGP Flowspec Flow programming.
The manager uses a backend sFlow collector (sFlow-RT) and Exabgp to find IPv4 and IPv6 DDOS flows, or flows that match configured inspection policy) and then programs the BGP Flowspec routes on the Edge routers.
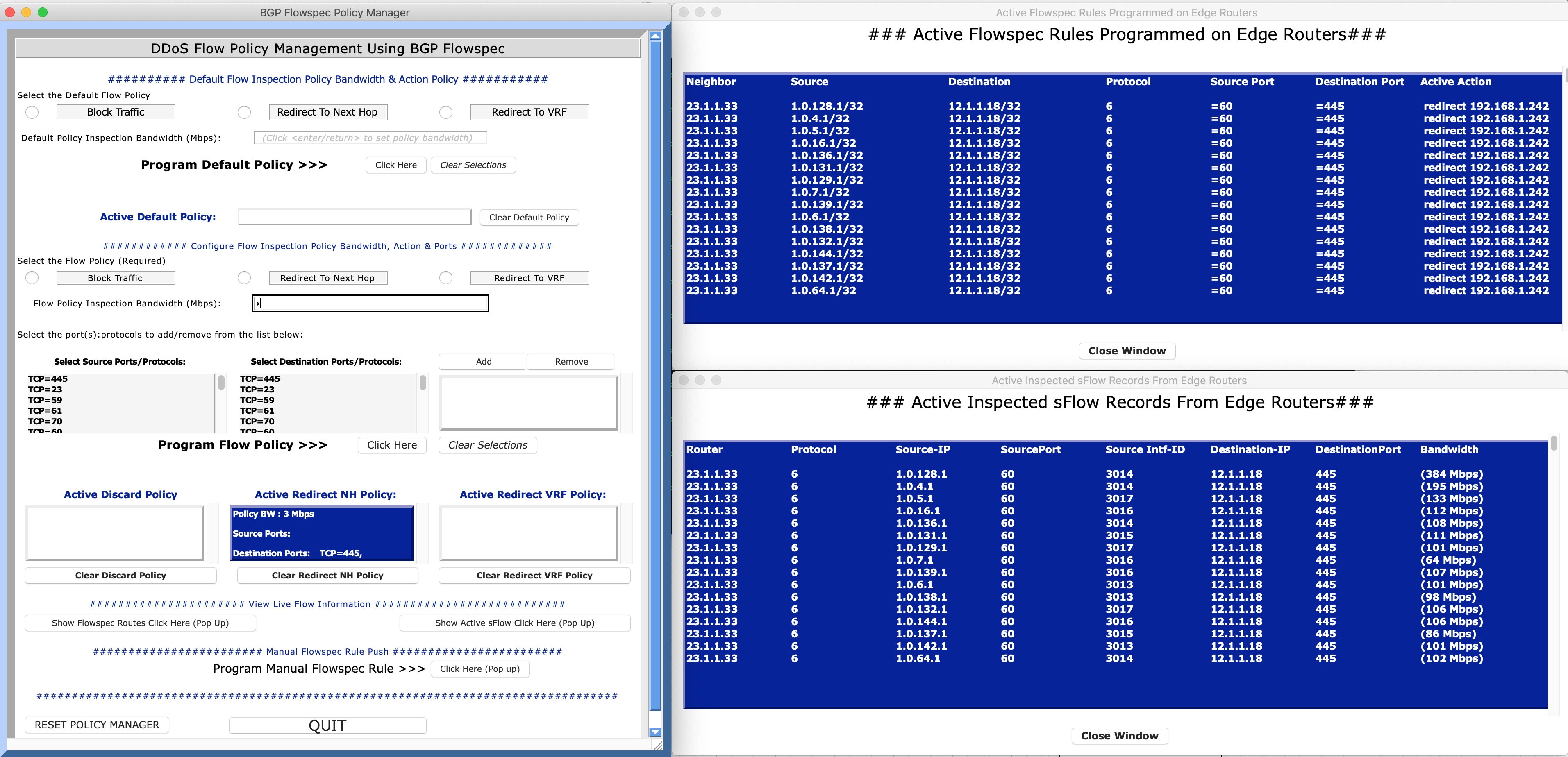
Below is a picture of the Flowspec UI:
Figure 1: FlowspecPolicyManager UI
The flows are discovered polling sFlow-RT via the API and then programmed on the edge routers using ExaBGPs API
The manager can be run on a VM or a BMS, but in addition it is all dockerized and can be run in a container (instructions below)
For details on EXABGP refer to this link: https://github.com/Exa-Networks/exabgp
Detals on sFlow-RT can be found here: https://sflow-rt.com/
To build your own local version all you need to do is install Docker and clone the git repository:
git clone git@github.com:russellkelly/BGPFlowspecPolicyManager.git
Switch to the clone directory BGPFlowspecPolicyManager
cd BGPFlowspecPolicyManager
Then in the cloned (BGPFlowspecPolicyManager) directory run:
make build
This command runs build: (Builds the image flowspec-manager:latest).
The above Makefile command builds an image with the latest ExaBgp:master, and sFlow-RT installed. It also installs all the required dependencies in the docker image
There are a few dependencies needed on the local PC for the Tkinter GUI to run. These are covered below.
This Application will run with Python 2.7 or Python 3 (though Python 3 has been less extensively tested).
Install the following packages if running Python 2.7 or 3.x:
- Python Requests module
- Python Pyyaml module
- Python Schedule Module
The commands to install on Windows (after installing Python 2.7.15 or 3.4) are below:
python -m pip install requests
python -m pip install pyyaml
python -m pip install schedule
python -m pip install win-inet-pton (needed on Windows only)
Similar commands can be run in Mac OSX or Linux using brew or apt-get.
Note: If you want to run this demo outside of a container (above) install
EXABGP (version 4.0.10) : https://github.com/Exa-Networks/exabgp.git
sFlow-RT : https://sflow-rt.com/download.php
Once the git repository has been cloned locally and the images installed as above proceed with the following steps:
Amend the variables in the file below to match your topology :
TopologyVariables.yaml file. (THIS IS THE ONLY FILE THAT NEEDS TO BE AMENDED)
Change the following in TopologyVariables.yaml:
The AS to match your topology
Exabgp_as:
as: *****
The Edge Flowspec Router details to match the topology
EdgeRouters:
- RouterID: ***.***.***.***
AS: *****
VRF: ***:***
IPNH: ***.***.***.***
To render the exabgp.conf file and the configurations for the edge routers (EdgeRouterConfigs.cfg).
python RenderConfigFiles.py
The configuration snippets for the Edge routers can be implemented on the routers.
The script will attempt to determine the local PCs public IP address. Check the
exabgp.conf
To start the container (running sFlow-RT and Exabgp locally) run:
make flowspec
To check if sFlow-RT is running browse to http://localhost:8008. This view of the sFlow collector can be used to check that the edge routers are in fact sending sFlow records to the collector.
A rudimentary telnet to localhost on port 5000 will connect to the Exabgp API
You can ssh to the local container by running .
ssh flowspec@localhost -p 2022 (password is flowspec)
The topology file can be edited to change the frequency the app iterates and that sflow-RT is polled for new/changed flows.
The timer between application run/poll to determine offending flows, the multiplier (of the App run time ) between Sflow Polling. Max non-zero sFlow entries the application will iterate through, sorted from highest flow to lowest. Default for this is (5, 15 seconds and 4000 for the app runtime, sFlow multiplier, and the sFlow cache iteration respectively)
AppRunTimer: 5
SflowMultiplier: 3
maxsflowentries: 4000
Finally, you can add remove specific TCP UDP ports to match on. Additionally ICMP messages can be added as required. When the topology file is amended the main app will pick up the changes and reflect in the GUI. Ensure the YAML formatting is correct!
PortList:
- TCP=445
- TCP=23
- UDP=53
- ICMP Echo-Reply=0
- ICMP Echo-Request=8
python FlowspecPolicyManager.py
Thats it!
Within the application there is also a reset button that clears the BGP peers, removes the flow data etc.
There is an option to restart the Exabgp and sflow-RT processes from within the container by running the script below. Follow the steps below.
ssh flowspec@localhost -p 2022 (password is flowspec)
./RestartContainerServices.sh
This can also be executed directly from the host machine
docker exec flowspec-container bash /home/flowspec/RestartContainerServices.sh
The BGPFlowSpecManager script will need to be started afterwards.
If there is some issue with the Application container it is very easy to recreate.
In the BgpFlowspecPolicyManager directory run the following:
make clean
Recreate the container:
make flowspec