Swiss army knife for RabbitMQ. Tap/Pub/Sub messages, create/delete/bind queues and exchanges, inspect broker.
- Features
- Screenshots
- Installation
- Usage
- JSON message format
- Filtering output of info command
- Build from source
- Test data generator
- Contributing
- Author
- Copyright and license
- tap to messages being sent to exchanges using RabbitMQ exchange-to-exchange bindings without affecting actual message delivery (aka tapping)
- display broker related information using the RabbitMQ REST management API
- save messages and meta data for later analysis and replay
- publish messages to exchanges
- consume messages from a queue (subscribe)
- supports TLS
- no runtime dependencies (statically linked golang single file binary)
- simple to use command line tool
- runs on Linux, Windows, Mac and wherever you can compile go
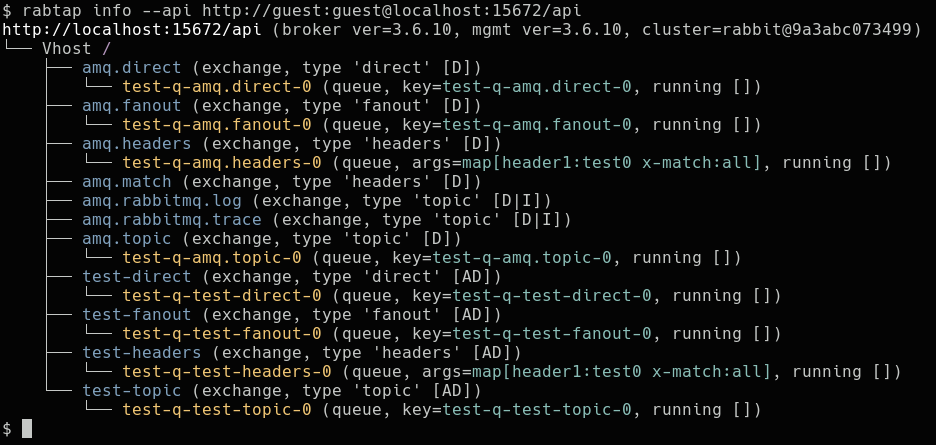
Output of rabtap info command:
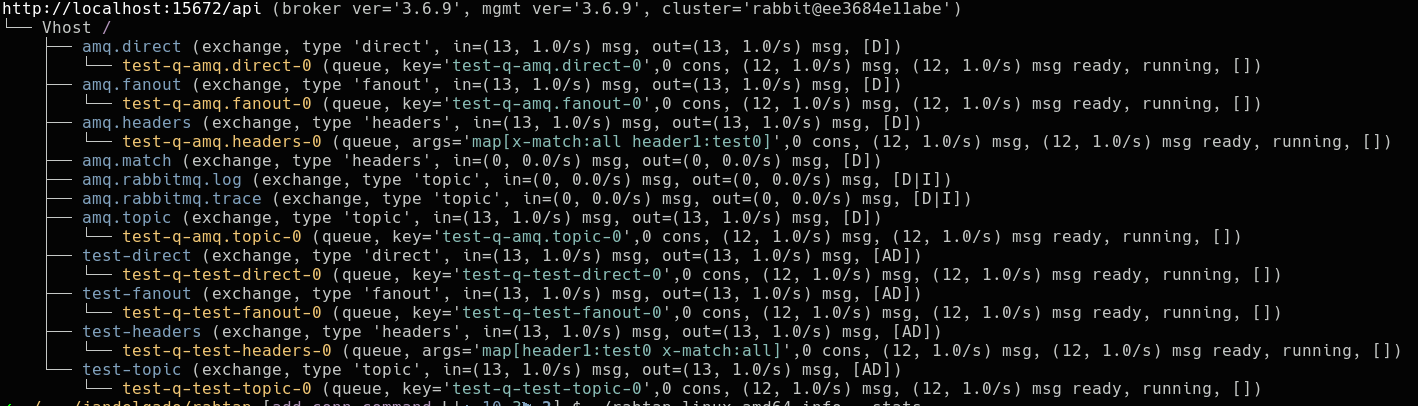
Output of rabtap info --stats command, showing additional statistics:
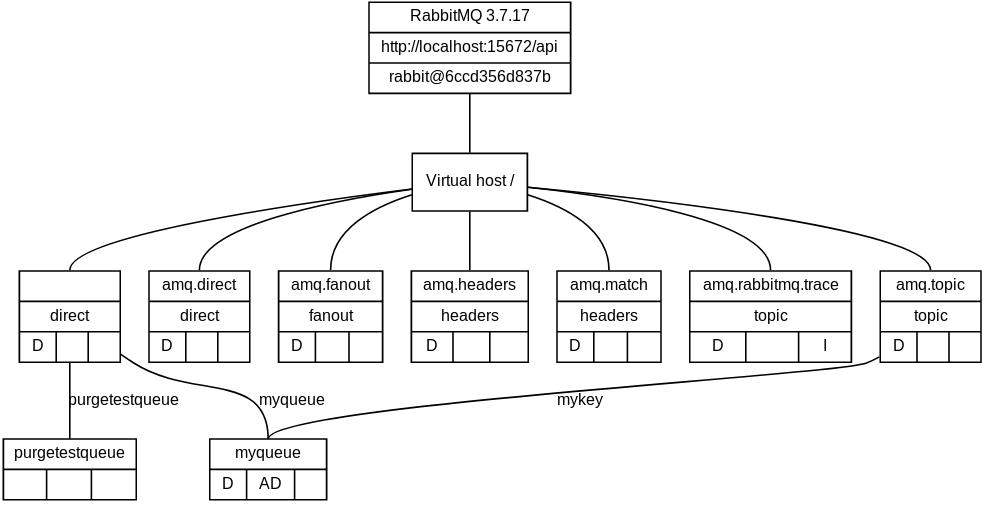
Using the --format=dot option, the info command can generate output in the
dot format, which can be visualized using graphviz, e.g. rabtap info --show-default --format dot | dot -T svg > mybroker.svg. The resulting SVG
file can be visualized with a web browser.
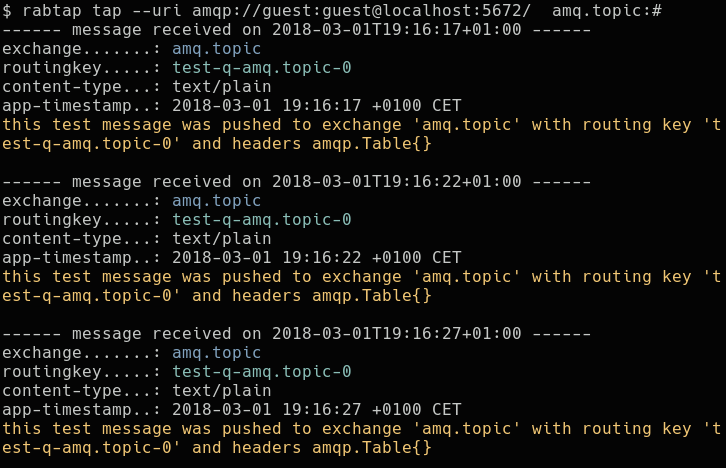
Output of rabtap in tap mode, showing message meta data and the message body:
Pre-compiled binaries can be downloaded for multiple platforms from the releases page.
Rabtap can be installed from the Arch Linux User Repository (AUR):
$ yay -S rabtap-binSee the build from source section if you prefer to compile from source.
rabtap - RabbitMQ wire tap. github.com/jandelgado/rabtap
Usage:
rabtap -h|--help
rabtap info [--api=APIURI] [--consumers] [--stats] [--filter=EXPR] [--omit-empty]
[--show-default] [--mode=MODE] [--format=FORMAT] [-knv]
[--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap tap EXCHANGES [--uri=URI] [--saveto=DIR] [--format=FORMAT] [-jknsv]
[--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap (tap --uri=URI EXCHANGES)... [--saveto=DIR] [--format=FORMAT] [-jknsv]
[--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap sub QUEUE [--uri URI] [--saveto=DIR] [--format=FORMAT] [--no-auto-ack] [-jksvn]
[--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap pub [--uri=URI] [SOURCE] [--exchange=EXCHANGE] [--routingkey=KEY] [--format=FORMAT]
[--delay=DELAY | --speed=FACTOR] [-jkv]
[--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap exchange create EXCHANGE [--uri=URI] [--type=TYPE] [-adkv]
[--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap exchange rm EXCHANGE [--uri=URI] [-kv] [--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap queue create QUEUE [--uri=URI] [-adkv] [--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap queue bind QUEUE to EXCHANGE --bindingkey=KEY [--uri=URI] [-kv]
[--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap queue unbind QUEUE from EXCHANGE --bindingkey=KEY [--uri=URI] [-kv]
[--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap queue rm QUEUE [--uri=URI] [-kv] [--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap queue purge QUEUE [--uri=URI] [-kv] [--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap conn close CONNECTION [--api=APIURI] [--reason=REASON] [-kv] [--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE] [--tls-key-file=KEYFILE] [--tls-ca-file=CAFILE]
rabtap --version
Arguments and options:
EXCHANGES comma-separated list of exchanges and binding keys,
e.g. amq.topic:# or exchange1:key1,exchange2:key2.
EXCHANGE name of an exchange, e.g. amq.direct.
SOURCE file or directory to publish in pub mode. If omitted, stdin will be read.
QUEUE name of a queue.
CONNECTION name of a connection.
DIR directory to read messages from.
-a, --autodelete create auto delete exchange/queue.
--api=APIURI connect to given API server. If APIURI is omitted,
the environment variable RABTAP_APIURI will be used.
-b, --bindingkey=KEY binding key to use in bind queue command.
--by-connection output of info command starts with connections.
--consumers include consumers and connections in output of info command.
--delay=DELAY Time to wait between sending messages during publish.
If not set then messages will be delayed as recorded.
The value must be suffixed with a time unit, e.g. ms, s etc.
-d, --durable create durable exchange/queue.
--exchange=EXCHANGE Optional exchange to publish to. If omitted, exchange will
be taken from message being published (see JSON message format).
--filter=EXPR Predicate for info command to filter queues [default: true]
--format=FORMAT * for tap, pub, sub command: format to write/read messages to console
and optionally to file (when --saveto DIR is given).
Valid options are: "raw", "json", "json-nopp". Default: raw
* for info command: controls generated output format. Valid
options are: "text", "dot". Default: text
-h, --help print this help.
-j, --json Deprecated. Use "--format json" instead.
-k, --insecure allow insecure TLS connections (no certificate check).
--tls-cert-file=CERTFILE A Cert file to use for client authentication.
--tls-key-file=KEYFILE A Key file to use for client authentication.
--tls-ca-file=CAFILE A CA Cert file to use for client authentication.
--mode=MODE mode for info command. One of "byConnection", "byExchange".
[default: byExchange].
-n, --no-color don't colorize output (also environment variable NO_COLOR).
--no-auto-ack disable auto-ack in subscribe mode. This will lead to
unacked messages on the broker which will be requeued
when the channel is closed.
--omit-empty don't show echanges without bindings in info command.
--reason=REASON reason why the connection was closed [default: closed by rabtap].
-r, --routingkey=KEY routing key to use in publish mode. If omitted, routing key
will be taken from message being published (see JSON
message format).
--saveto=DIR also save messages and metadata to DIR.
--show-default include default exchange in output info command.
-s, --silent suppress message output to stdout.
--speed=FACTOR Speed factor to use during publish [default: 1.0].
--stats include statistics in output of info command.
-t, --type=TYPE exchange type [default: fanout].
--uri=URI connect to given AQMP broker. If omitted, the
environment variable RABTAP_AMQPURI will be used.
-v, --verbose enable verbose mode.
--version show version information and exit.
Examples:
rabtap tap --uri amqp://guest:guest@localhost/ amq.fanout:
rabtap tap --uri amqp://guest:guest@localhost/ amq.topic:#,amq.fanout:
rabtap pub --uri amqp://guest:guest@localhost/ amq.topic message.json -j
rabtap info --api http://guest:guest@localhost:15672/api
# use RABTAP_AMQPURI environment variable to specify broker instead of --uri
export RABTAP_AMQPURI=amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672/
rabtap queue create JDQ
rabtap queue bind JDQ to amq.topic --bindingkey=key
echo "Hello" | rabtap pub amq.topic --routingkey "key"
rabtap sub JDQ
rabtap queue rm JDQ
# use RABTAP_APIURI environment variable to specify mgmt api uri instead of --api
export RABTAP_APIURI=http://guest:guest@localhost:15672/api
rabtap info
rabtap info --filter "binding.Source == 'amq.topic'" --omit-empty
rabtap conn close "172.17.0.1:40874 -> 172.17.0.2:5672"
# use RABTAP_CERTFILE | RABTAP_KEYFILE | RABTAP_CAFILE environments variables
# instead of specify --tls-cert-file=CERTFILE --tls-key-file=KEYFILE --tls-ca-file=CAFILE
Rabtap understands the following commands:
tap- taps to an exchange and transparently receives messages sent to the exchange, without affecting actual message delivery (using exchange-to-exchange binding). Simulatanoussub- subscribes to a queue and consumes messages sent to the queue (acts like a RabbitMQ consumer)pub- publish messages to an exchange, optionally with the timing as recorded.info- show broker related info (exchanges, queues, bindings, stats). The features of an exchange are displayed in square brackets withD(durable),AD(auto delete) andI(internal). The features of a queue are displayed in square brackets withD(durable),AD(auto delete) andEX(exclusive). If--statisticsoption is enabled, basic statistics are included in the output. The--filteroption allows to filter output. See filtering section for details. Use the--by-connectionto sort output by connection (implies--consumers)queue- create/bind/unbind/remove/purge queueexchange- create/remove exchangeconnection- close connections
See the examples section for further information.
The specification of the RabbitMQ broker URI follows the AMQP URI specification as implemented by the go RabbitMQ client library.
Examples:
amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672/amqps://guest:guest@my-broker.dev:5671/amqps://guest:guest@my-broker.dev:5671/vhost
Note that according to RFC3986 it might be
necessary to escape certain characters like e.g. ? (%3F) or # (%23) as otherwise
parsing of the URI may fail with an error.
The --format=FORMAT option controls the format of the tap and sub
commands when writing messages to the console and optionally to the filesystem
(i.e. when --saveto is set).
The FORMAT parameter has the following effect on the output:
FORMAT |
Format on console | Format of saved messages (--saveto DIR) |
|---|---|---|
raw (default) |
Pretty-printed metadata + raw Message body | Metadata as JSON-File + Body as-is |
json |
Pretty-printed JSON wiht base64 encoded body | Pretty-printed JSON with base64 encoded body |
json-nopp |
Single line JSON wiht base64 encoded body | Pretty-printed JSON with base64 encoded body |
Notes:
- the
--jsonoption is now deprecated. Use--format=jsoninstead noppstands forno pretty-print
Use environment variables to specify standard values for broker and api endpoint.
In cases where the URI argument is optional, e.g. rabtap tap [-uri URI] exchange ..., the URI of the RabbitMQ broker can be set with the
environment variable RABTAP_AMQPURI. Example:
$ export RABTAP_AMQPURI=amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672/
$ rabtap tap amq.fanout:
...The default RabbitMQ management API URI can be set using the RABTAP_APIURI
environment variable. Example:
$ export RABTAP_APIURI=http://guest:guest@localhost:15672/api
$ rabtap info
...The default TLS config certificates path can be set using the RABTAP_TLS_CERTFILE and RABTAP_TLS_KEYFILE and RABTAP_TLS_CAFILE
environments variables. Example:
$ export RABTAP_TLS_CERTFILE=/etc/rabbitmq/ssl/cert.pem
$ export RABTAP_TLS_KEYFILE=/etc/rabbitmq/ssl/key.pem
$ export RABTAP_TLS_CAFILE =/etc/rabbitmq/ssl/ca.pem
$ echo "Hello" | rabtap pub amq.topic --routingkey "key"
...Set environment variable NO_COLOR to disable color output.
The following examples assume a RabbitMQ broker running on localhost:5672 and
the management API available on port 15672. Easiest way to start such an
instance is by running docker run -ti --rm -p 5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 rabbitmq:3-management or similar command to start a RabbitMQ container.
The info command uses the REST API of RabbitMQ to gather and display
topolgy related information from the broker.
The --mode MODE option controls how the output is structured. Valid options
for MODE are byExchange (default) or byConnection.
The --format=FORMAT option controls the format of generated output. Valid
options are text for console text format (default) or dot to output the
tree structure in dot format for visualization with graphviz.
Examples (assume that RABTAP_APIURI environment variable is set):
rabtap info --consumers- shows virtual hosts exchanges, queues and consumers of given broker in a tree view (see screenshot).rabtap info --mode=byConnection- shows virtual hosts, connections, consumers and queues of given broker in an tree view.rabtap info --format=dot | dot -T svg > broker.svg- renders broker info intodotformat and uses graphviz to render a SVG file for final visualization.
The tap command allows to tap exchanges and transparently receives messages
sent to the exchanges. Rabtap automatically reconnects on connections
failures. The syntax of the tap command is rabtap tap [--uri URI] EXCHANGES
where the EXCHANGES argument specifies the exchanges and binding keys to use.
The EXCHANGES argument is of the form EXCHANGE:[KEY][,EXCHANGE:[KEY]]*. If
the exchange name contains a colon, use \\: to escape it, e.g.
myexchange\\:with\\:colons:KEY.
The acutal format of the binding key depends on the exchange type (e.g. direct, topic, headers) and is described in the RabbitMQ documentation.
Examples for binding keys used in tap command:
#on an exchange of typetopicwill make the tap receive all messages on the exchange.- a valid queue name for an exchange of type
directbinds exactly to messages destined for this queue - an empty binding key for exchanges of type
fanoutor typeheaderswill receive all messages published to these exchanges
Note: on exchanges of type headers the binding key is currently ignored and
all messages are received by the tap.
The following examples assume that the RABTAP_AMQPURI environment variable is
set, otherwise you have to pass the additional --uri URI parameter to the
commands below.
$ rabtap tap my-topic-exchange:#$ rabtap tap my-fanout-exchange:$ rabtap tap my-headers-exchange:$ rabtap tap my-direct-exchange:binding-key
The following example connects to multiple exchanges:
$ rabtap tap my-fanout-exchange:,my-topic-exchange:#,my-other-exchange:binding-key
The RabbitMQ Firehose Tracer allows to "see" every message that is published or delivered. To use it, the firehose tracer has to be enabled first:
$ rabbitmqctl rabbitmqctl trace_on Then every message published or delivered will be CC'd to the topic exhange amq.rabbitmq.trace.
At this exchange, the messages can now be tapped with rabtap:
$ rabtap --uri amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672/ tap amq.rabbitmq.trace:#Rabtap allows you also to connect simultaneously to multiple brokers and exchanges:
$ rabtap tap --uri amqp://broker1 amq.topic:# tap --uri amqp://broker2 amq.fanout:
The example connects to broker1 and taps to the amq.topic exchange and to
the amq.fanout exchange on broker2.
All tapped messages can be also be saved for later analysis or replay. Rabtap supports saving of messages in two formats: raw body and metadata in separate files or JSON message format with embedded metadata and message the body base64 encode. Examples:
$ rabtap tap amq.topic:# --saveto /tmp- saves messages as pair of files consisting of raw message body and JSON meta data file to/tmpdirectory.$ rabtap tap amq.topic:# --saveto /tmp --format json- saves messages as JSON files to/tmpdirectory.
Files are created with file name rabtap-+<Unix-Nano-Timestamp>+ . +
<extension>.
The sub command reads messages from a queue. Note that unlike tap, sub
will consume messages that are in effect removed from the specified queue.
Example:
$ rabtap sub somequeue --format json
Will consume messages from queue somequeue and print out messages in JSON
format (this is equivalent to using the now deprecated --json option). The
Example assumes that RABTAP_AMQPURI environment variable is set, as the
--uri AMQPURI parameter is omitted.
The pub command is used to publish messages to an exchange with a routing
key. The messages to be published are either read from a file, or from a
directory which contains previously recorded messages (e.g. using the
--saveto option of the tap command). Messages can be published either in
raw format, in which they are send as-is, or in JSON-format, as described
here, which includes message metadata and the body in a
single JSON document.
The general form of the pub command is
rabtap pub [--uri=URI] [SOURCE] [--exchange=EXCHANGE] [--routingkey=KEY] [--format=FORMAT]
[--delay=DELAY | --speed=FACTOR] [-jkv]
$ echo hello | rabtap pub amq.fanout- publish "hello" to exchange amqp.fanout$ rabtap pub messages.json --format=json- messages are read from filemessages.jsonin raptab JSON format. Target exchange and routing keys are read from the messages meta data. Themessages.jsonfile can contain multiple JSON documents as it is treated as a JSON stream. Rabtap will honor theXRabtapReceivedtimestamps of the messages and by default delay the messages as they were recorded. This behaviour can be overridden by the--delayand--speedoptions.$ rabtap pub amq.direct -r myKey --format=json messages.json --delay=0s- as before, but publish messages always to exchangeamq.directwith routing keymyKeyand without any delays.$ rabtap pub amq.direct -r myKey --format=raw somedir --delay=0s- as before, but assuming thatsomediris a directory, the messages are read from message files previously recorded to this directory and replayed in the order they were recorded.
Rabtap instances can be connected through a pipe and messages will be read on
one side and published to the other. Note that for publish to work in streaming
mode, the JSON mode (--format json) must be used on both sides, so that
messages are encapsulated in JSON messages.
The example taps messages on broker1 and publishes the messages to the
amq.direct exchange on broker2
$ rabtap tap --uri amqp://broker1 my-topic-exchange:# --format json | \
rabtap pub --uri amqp://broker2 amq.direct -r routingKey --format jsonThe conn command allows to close a connection. The name of the connection to
be closed is expected as parameter. Use the info command with the
--consumers option to find the connection associated with a queue. Example:
$ rabtap info --consumers
http://localhost:15672/api (broker ver='3.6.9', mgmt ver='3.6.9', cluster='rabbit@ae1ad1477419')
└── Vhost /
├── amq.direct (exchange, type 'direct', [D])
:
└── test-topic (exchange, type 'topic', [AD])
├── test-q-test-topic-0 (queue, key='test-q-test-topic-0', running, [])
│ └── __rabtap-consumer-4823a3c0 (consumer user='guest', chan='172.17.0.1:59228 -> 172.17.0.2:5672 (1)')
│ └── '172.17.0.1:59228 -> 172.17.0.2:5672' (connection client='https://github.com/streadway/amqp', host='172.17.0.2:5672', peer='172.17.0.1:59228')
├── test-q-test-topic-1 (queue, key='test-q-test-topic-1', running, [])
:
$ rabtap conn close '172.17.0.1:59228 -> 172.17.0.2:5672'The queue command can be used to easily create, remove, bind or unbind queues:
$ rabtap queue create myqueue
$ rabtap info --show-default
http://localhost:15672/api (broker ver='3.7.8', mgmt ver='3.7.8', cluster='rabbit@b2fe3b3b6826')
└── Vhost /
├── (default) (exchange, type 'direct', [D])
│ └── myqueue (queue, key='myqueue', idle since 2018-12-07 20:46:15, [])
:
└── amq.topic (exchange, type 'topic', [D])
$ rabtap queue bind myqueue to amq.topic --bindingkey hello
$ rabtap info --show-default
http://localhost:15672/api (broker ver='3.7.8', mgmt ver='3.7.8', cluster='rabbit@b2fe3b3b6826')
└── Vhost /
├── (default) (exchange, type 'direct', [D])
│ └── myqueue (queue, key='myqueue', idle since 2018-12-07 20:46:15, [])
:
└── amq.topic (exchange, type 'topic', [D])
└── myqueue (queue, key='hello', idle since 2018-12-07 20:46:15, [])
$ rabtap queue unbind myqueue from amq.topic --bindingkey hello
$ rabtap info --show-default
http://localhost:15672/api (broker ver='3.7.8', mgmt ver='3.7.8', cluster='rabbit@b2fe3b3b6826')
└── Vhost /
├── (default) (exchange, type 'direct', [D])
│ └── myqueue (queue, key='myqueue', idle since 2018-12-07 20:46:15, [])
:
└── amq.topic (exchange, type 'topic', [D])
$ rabtap queue rm myqueue
$ raptap info
http://localhost:15672/api (broker ver='3.7.8', mgmt ver='3.7.8', cluster='rabbit@b2fe3b3b6826')
└── Vhost /
:
└── amq.topic (exchange, type 'topic', [D])Additionally use the purge command to remove all elements from a queue, e.g.
$ rabtap queue purge myqueue
When using the --format json option, messages are print/read as a stream of JSON
messages in the following format:
...
{
"ContentType": "text/plain",
"ContentEncoding": "",
"DeliveryMode": 0,
"Priority": 0,
"CorrelationID": "",
"ReplyTo": "",
"Expiration": "",
"MessageID": "",
"Timestamp": "2017-11-10T00:13:38+01:00",
"Type": "",
"UserID": "",
"AppID": "rabtap.testgen",
"DeliveryTag": 27,
"Redelivered": false,
"Exchange": "amq.topic",
"RoutingKey": "test-q-amq.topic-0",
"XRabtapReceivedTimestamp": "2019-06-13T19:33:51.920711583+02:00",
"Body": "dGhpcyB0ZXN0IG1lc3NhZ2U .... IGFuZCBoZWFkZXJzIGFtcXAuVGFibGV7fQ=="
}
...Note that in JSON mode, the Body is base64 encoded.
When your brokers topology is complex, the output of the info command can
become very bloated. The --filter helps you to narrow output to the desired
information.
A filtering expression is a function that evaluates to true or false (i.e.
a predicate). Rabtap allows the specification of predicates to be applied
when printing queues using the info command. The output will only proceed
if the predicate evaluates to true.
Rabtap uses the govalute to evaluate the predicate. This allows or complex expressions.
See official govaluate documentation for further information.
Note: currently the filter is ignored when used in conjunction with
--by-connection.
During evaluation the context (i.e. the current exchange, queue and binding) is available in the expression as variables:
- the current exchange is bound to the variable exchange
- the current queue is bound to the variable queue
- the curren binding is bound to the variable binding
The examples assume that RABTAP_APIURI environment variable points to the
broker to be used, e.g. http://guest:guest@localhost:15672/api).
rabtap info --filter "exchange.Name == 'amq.direct'" --omit-empty- print only queues bound to exchangeamq.directand skip all empty exchanges.rabtap info --filter "queue.Name =~ '.*test.*'" --omit-empty- print all queues withtestin their name.rabtap info --filter "queue.Name =~ '.*test.*' && exchange.Type == 'topic'" --omit-empty- like before, but consider only exchanges of typetopic.rabtap info --filter "queue.Consumers > 0" --omit --stats --consumers- print all queues with at least one consumer
The types reflect more or less the JSON API objects of the REST API of RabbitMQ transformed to golang types.
Definition of the Exchange type
type Exchange struct {
Name string
Vhost string
Type string
Durable bool
AutoDelete bool
Internal bool
MessageStats struct {
PublishOut
PublishOutDetails struct {
Rate float64
}
PublishIn int
PublishInDetails struct {
Rate float64
}
}
}Definition of the Queue type
type Queue struct {
MessagesDetails struct {
Rate float64
}
Messages
MessagesUnacknowledgedDetails struct {
Rate float64
}
MessagesUnacknowledged int
MessagesReadyDetails struct {
Rate float64
}
MessagesReady int
ReductionsDetails struct {
Rate float64
}
Reductions int
Node string
Exclusive bool
AutoDelete bool
Durable bool
Vhost string
Name string
MessageBytesPagedOut int
MessagesPagedOut int
BackingQueueStatus struct {
Mode string
Q1 int
Q2 int
Q3 int
Q4 int
Len int
NextSeqID int
AvgIngressRate float64
AvgEgressRate float64
AvgAckIngressRate float64
AvgAckEgressRate float64
}
MessageBytesPersistent int
MessageBytesRAM int
MessageBytesUnacknowledged int
MessageBytesReady int
MessageBytes int
MessagesPersistent int
MessagesUnacknowledgedRAM int
MessagesReadyRAM int
MessagesRAM int
GarbageCollection struct {
MinorGcs int
FullsweepAfter int
MinHeapSize int
MinBinVheapSize int
MaxHeapSize int
}
State string
Consumers int
IdleSince string
Memory int
}Definition of the Binding type
type Binding struct {
Source string
Vhost string
Destination string
DestinationType string
RoutingKey string
PropertiesKey string
}$ GO111MODULE=on go get github.com/jandelgado/rabtap/cmd/rabtap
To build rabtap from source, you need go (version >= 1.12) and golangci-lint installed.
$ git clone https://github.com/jandelgado/rabtap && cd rabtap
$ make test -or- make short-test
$ make
In order to run all tests (make test) an instance of RabbitMQ is expected to
run on localhost. Easiest way to start one is running make run-broker, which
will start a RabbitMQ docker container (i.e. docker run -ti --rm -p 5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 rabbitmq:3-management).
A simple test data generator tool for manual tests is
included in the cmd/testgen directory.
- fork this repository
- create your feature branch
- add code
- add tests and make sure test coverage does not fall (
make test) - make sure pre-commit hook does not fail (
./pre-commit) - add documentation
- commit changes
- submit a PR
Jan Delgado (jdelgado at gmx dot net)
Copyright (c) 2017-2020 Jan Delgado. rabtap is licensed under the GPLv3 license.