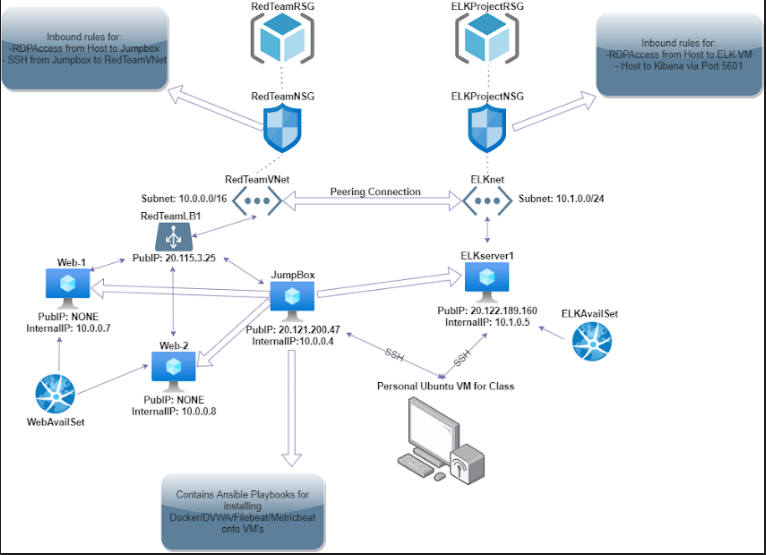
The files in this repository were used to configure the network depicted below.
These files have been tested and used to generate a live ELK deployment on Azure. They can be used to either recreate the entire deployment pictured above. Alternatively, select portions of the yml file may be used to install only certain pieces of it, such as Filebeat.
- Ansible RedTeam Playbook
- ELK InitializationPlaybook
- Filebeat Configuration
- Filebeat Playbook
- Metricbeat Configuration
- Metricbeat Playbook
This document contains the following details:
- Description of the Topology
- Access Policies
- ELK Configuration
- Beats in Use
- Machines Being Monitored
- How to Use the Ansible Build
The main purpose of this network is to expose a load-balanced and monitored instance of DVWA, the D*mn Vulnerable Web Application.
Load balancing ensures that the application will be highly available, in addition to restricting access to the network.
- What aspect of security do load balancers protect? What is the advantage of a jump box?
- Load balancers will help to restrict network traffic in a way that doesn't hinder regular use, but protects against DDoS attacks and more.
- Jump Box's act as an initializing box, or a middle man. This helps reduce certain risks like an abundance of public IP's. Additionally they also pose as a single entry point into the entire network, should it be compromised.
Integrating an ELK server allows users to easily monitor the vulnerable VMs for changes to the Network and system logs.
- What does Filebeat watch for?
- Filebeat monitors log files. It will collect log events and log files specified by admins, and then foward the information to Elasticsearch or Logstash. -What does Metricbeat record?
- Metricbeat outputs various metrics and statistics from the operating system and services running on a server.
The configuration details of each machine may be found below. Note: Use the Markdown Table Generator to add/remove values from the table.
| Name | Function | IP Address | Operating System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jump Box | Gateway | 10.0.0.4/20.120.112.221 | Linux |
| Web-1 | UbuntuVM | 10.0.0.7 | Linux |
| Web-2 | UbuntuVM | 10.0.0.8 | Linux |
| ELKserver | UbuntuVM | 10.1.0.5/20.65.73.178 | Linux |
The machines on the internal network are not exposed to the public Internet.
Only the Jump-Box machine can accept connections from the Internet. Access to this machine is only allowed from the following IP addresses: -My personal student UbuntuVM via my public IP through TCP 5601
Machines within the network can only be accessed by SSH'ing from the Jump-Box.
- Which machine did you allow to access your ELK VM? What was its IP address?
- Student UbuntuVM via SSH port 22 with the public IP of 20.120.112.221
A summary of the access policies in place can be found in the table below.
| Name | Publicly Accessible | Allowed IP Addresses |
|---|---|---|
| Jump Box | Yes | 10.0.0.4 10.0.0.2 |
| Web-1 | No | 10.0.0.7 via SSH 22 |
| Web-2 | No | 10.0.0.8 via SSH 22 |
| ElkServer | No | UbuntuVM with my public IP using TCP 5601 |
Ansible was used to automate configuration of the ELK machine. No configuration was performed manually, which is advantageous because...
- What is the main advantage of automating configuration with Ansible?
- Ansible allows for quick deployment of various applications to many computers via YAML
The playbook implements the following tasks:
- In 3-5 bullets, explain the steps of the ELK installation play. E.g., install Docker; download image; etc.
- Specify machines
- name: Install & Configure ELK with Docker hosts: elk remote_user: sysadmin become: true tasks:
- Increase Virtual Memory
- name: Utilize More Memory sysctl: name: vm.max_map_count value: 262144 state: present reload: yes
- Install Docker.io
- name: Install Docker.io apt: update_cache: yes name: docker.io state: present
- Install Python-pip
name: Install pip3 apt: force_apt_get: yes name: python3-pip state: present
- Install Docker Python Module
- name: Install Docker Python Module pip: name: docker state: present
- Download and Launch Elk Docker Container and make available ports
- name: Download and launch ELK container docker_container: name: ELK image: sebp/elk:761 state: started restart_policy: always published_ports: - 5601:5601 - 9200:9200 - 5044:5044
- Enable Docker services to run
- name: Enable my docker services systemd: name: docker enabled: yes
The following screenshot displays the result of running docker ps after successfully configuring the ELK instance.
This ELK server is configured to monitor the following machines:
- List the IP addresses of the machines you are monitoring
- Web-1 10.0.0.7
- Web-2 10.0.0.8
We have installed the following Beats on these machines:
- Specify which Beats you successfully installed
- Filebeat & Metricbeat
These Beats allow us to collect the following information from each machine:
- In 1-2 sentences, explain what kind of data each beat collects, and provide 1 example of what you expect to see. E.g.,
Winlogbeatcollects Windows logs, which we use to track user logon events, etc.- Filebeat is a lightweight shipper for forwarding and centralizing log data. Installed as an agent on your servers, Filebeat monitors the log files or locations that you specify, collects log events, and forwards them either to Elasticsearch or Logstash for indexing.
- Metricbeat is a lightweight shipper that you can install on your servers to periodically collect metrics from the operating system and from services running on the server. Metricbeat takes the metrics and statistics that it collects and ships them to the output that you specify, such as Elasticsearch or Logstash
In order to use the playbook, you will need to have an Ansible control node already configured. Assuming you have such a control node provisioned:
SSH into the control node and follow the steps below:
- Copy the yaml config file to the ansible folder.
- Update the configuration file to include remote users and the ports.
- Run the playbook, and navigate to Kibana:(port) to check that the installation worked as expected. In our case we went to Kibana:5601/app/home.
Answer the following questions to fill in the blanks:
-
Which file is the playbook? Where do you copy it?
- For Ansible create Ansible Playbook
- For Filebeat create Filebeat Playbook
- For Metricbeat create Metricbeat Playbook
- Copy the file here: /etc/ansible/
-
Which file do you update to make Ansible run the playbook on a specific machine? How do I specify which machine to install the ELK server on versus which to install Filebeat on?_
- You would update: /etc/ansible/hosts
-
Which URL do you navigate to in order to check that the ELK server is running?