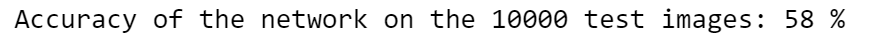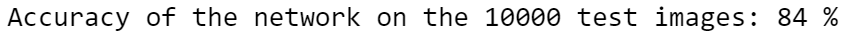Image classifier using CNN in Python and Pytorch. The classifier is trained on the CIFAR10 dataset.
The PEP 8 and Pylint styles are used to format this code.
Attempt 1:
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
# flatten all dimensions except batch
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
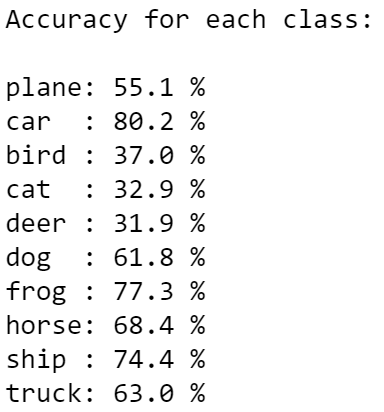
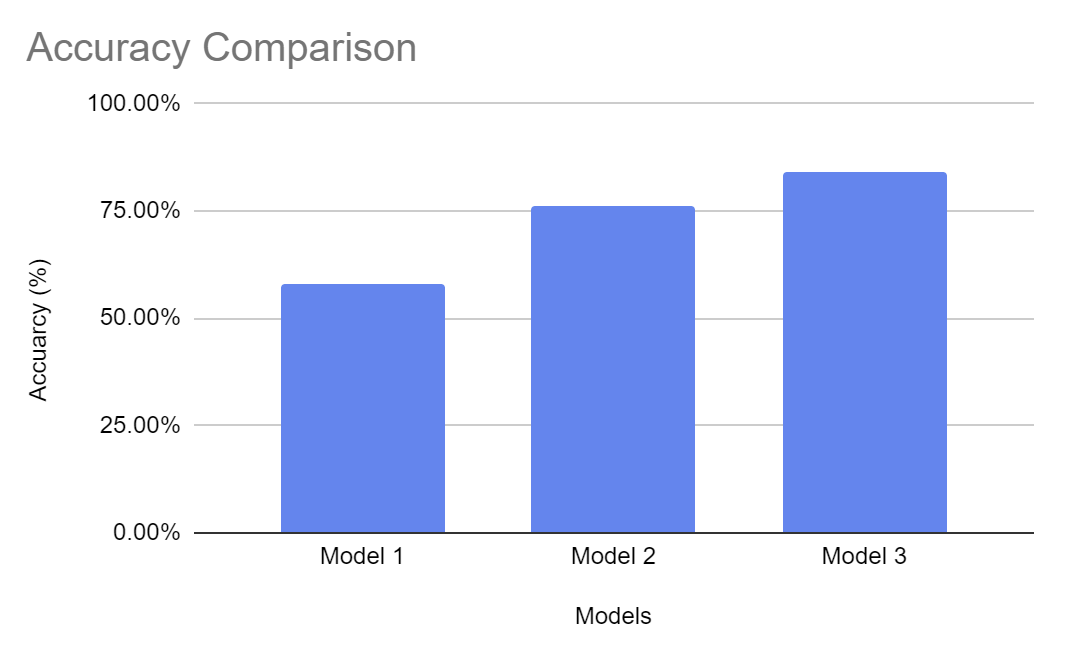
This model gives an accuracy of 58%. Evidently, there is room for improvement. In the next few attempts, the model and the hyperparameters are tweaked to increase the score.
Attempt 2:
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# convolutional layer
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3, padding=1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 3, padding=1)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, padding=1)
# max pooling layer
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
# fully connected layers
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(64 * 4 * 4, 512)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 64)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(64, 10)
# dropout
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=.5)
def forward(self, x):
# add sequence of convolutional and max pooling layers
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv3(x)))
# flattening
x = x.view(-1, 64 * 4 * 4)
# fully connected layers
x = self.dropout(F.relu(self.fc1(x)))
x = self.dropout(F.relu(self.fc2(x)))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
This attempt uses a sequential CNN with more layers and a larger batch size along with a defined flattening layer. The channels are set to 3 and 16, 16 and 32, and 32 and 64 for the first, second, and third Convolutional Layers, respectively. In the MaxPool layer, it is changed to downsample the input representation by taking the maximum value over the window defined by pool size for each dimension along the features axis. It also includes a 50% dropout layer to reduce overfitting. The number of epochs are also adjusted to optimize accuracy.
These changes led us to an increase of 76% accuracy. To increase the accuracy more, the next attempt tweaks the hyperparameters more.
Attempt 3:
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv_layer = nn.Sequential(
# Conv Layer block 1
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
# Conv Layer block 2
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Dropout2d(p=0.05),
# Conv Layer block 3
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
)
self.fc_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.1),
nn.Linear(4096, 1024),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(1024, 512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.1),
nn.Linear(512, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
"""Perform forward."""
# conv layers
x = self.conv_layer(x)
# flatten
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
# fc layer
x = self.fc_layer(x)
return x
The revised model above has an increased amount of layers, and added Convolutional blocks that have a kernel size of 3. Channel sizes are also adjusted.
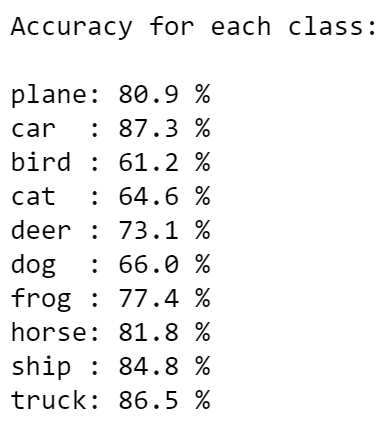
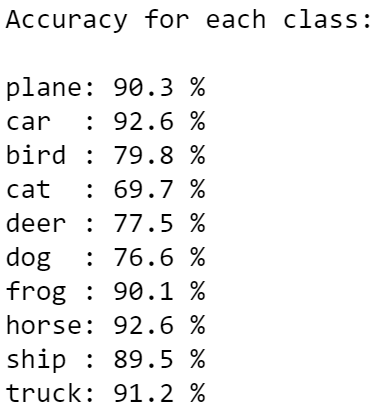
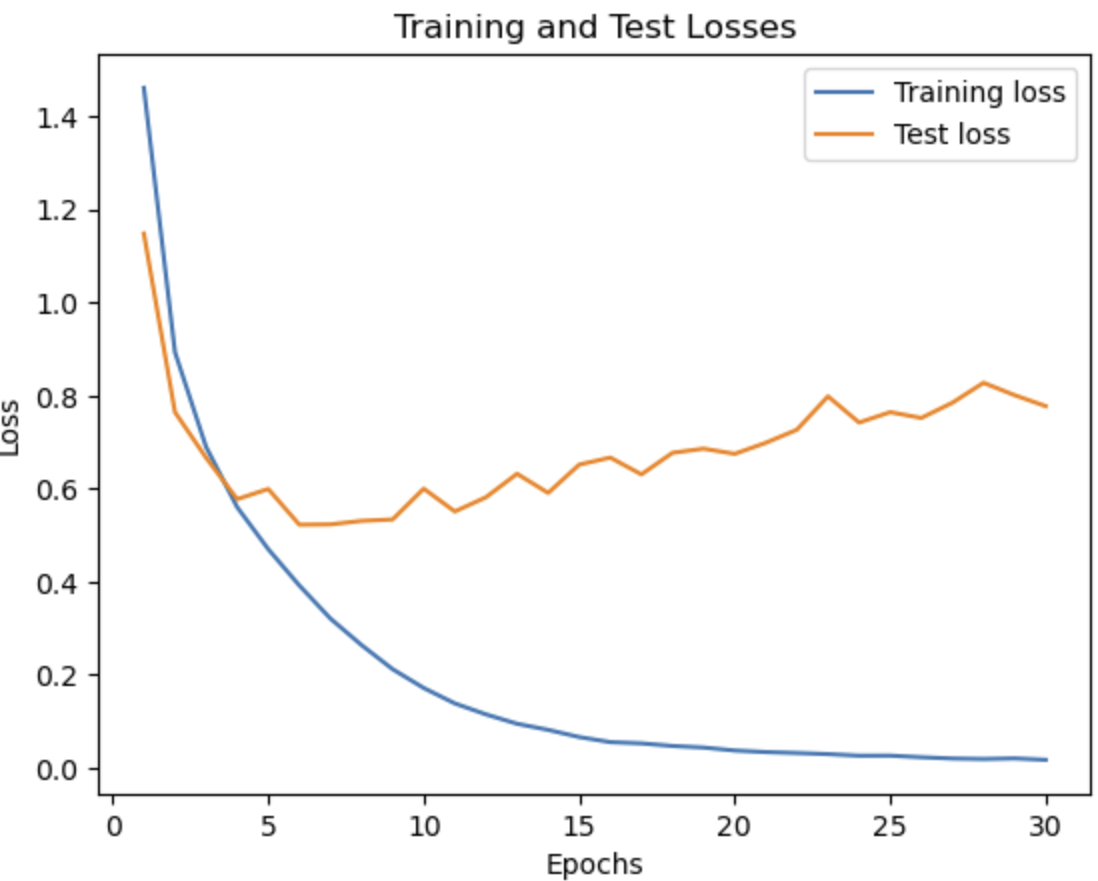
Now the accuracy has improved to 84%. The batches in the previous models were too small in proportion to our large dataset.
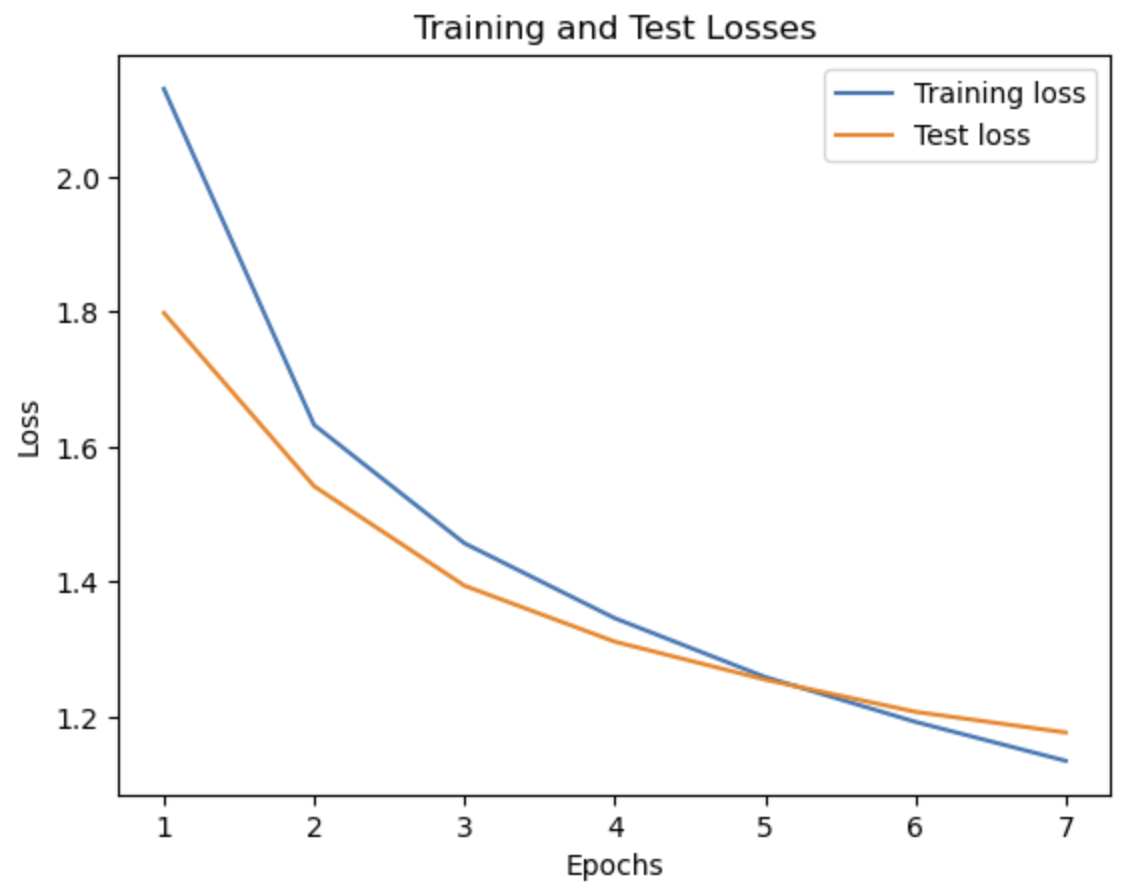
More plots of each model's performance are provided in the images folder.
- Feature extraction: Observe how the class accuracies consistently have lower accuracies for images of cats, dogs, and birds. This is likely because of these images have more colours, which suggests an issue in feature extraction.
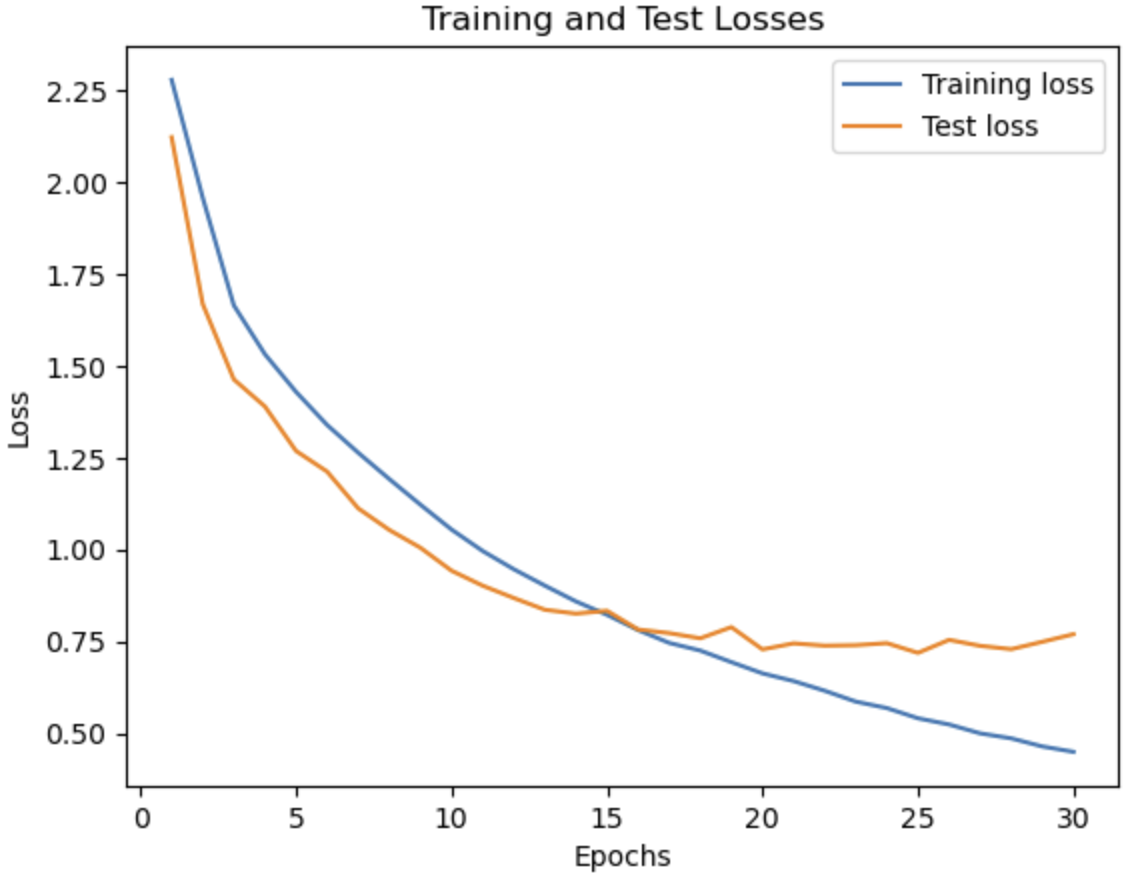
- Too many epochs: When the number of epochs is increased, the model overfits and the accuracy drops.
- Tuning hyperparameters: This is very time-consuming as training itself takes a very long time.