This project explores the implementation of Semi-Supervised Learning (Semi-SL) using the Mean Teacher approach on the Two Moons dataset. The goal is to demonstrate the effectiveness of semi-supervised learning techniques, especially in scenarios with limited labeled data.
- Generate Fixed Datasets:
- Created datasets with fixed splits for training, labeled, and unlabeled data for Semi-SL and Self-SL.
- Variants generated:
- TwoMoons_2Dto1D_uniform
- TwoMoons_2Dto1D_single_gaussian
- TwoMoons_2Dto1D_two_gaussians
- Augmentation Function:
- What transformation is considered augmentation to preserve class belonging?
- Visualize Datasets:
- Implemented visualization of the datasets using Plotly, including decision boundaries.
- Implement Vanilla Supervised Learning (SL) as a Baseline:
- Using all train data as labeled.
- Using only a small part (5 per each of 2 classes = 10) as labeled data.
- Metric calculations.
- Visualization of results.
- Implement Mean-Teacher Approach for Semi-SL:
- Utilized 10 labeled data points and 340 unlabeled data points.
-
Baseline Model (Supervised Learning on Full Training Data):
- Trained on 350 data points.
- ROC AUC: 1.000, Accuracy: 0.993.
- Visualization:
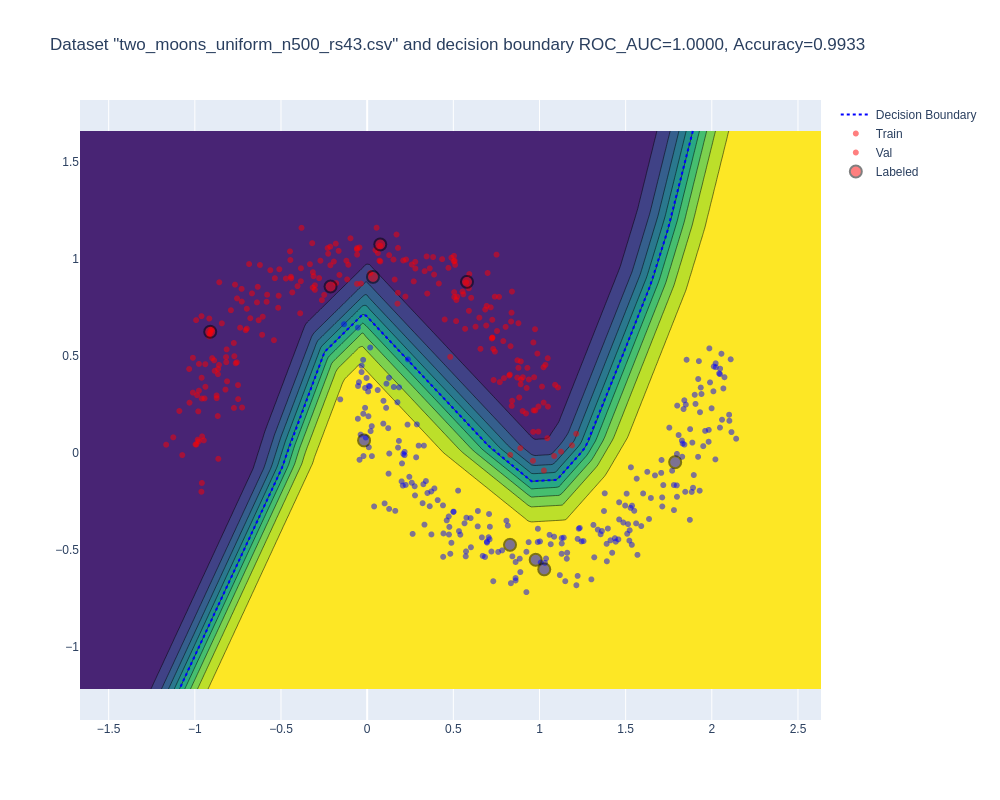
-
Reference Model (Supervised Learning on Small Labeled Subset):
- Trained on 10 data points.
- ROC AUC: 0.962, Accuracy: 0.887.
- Visualization:
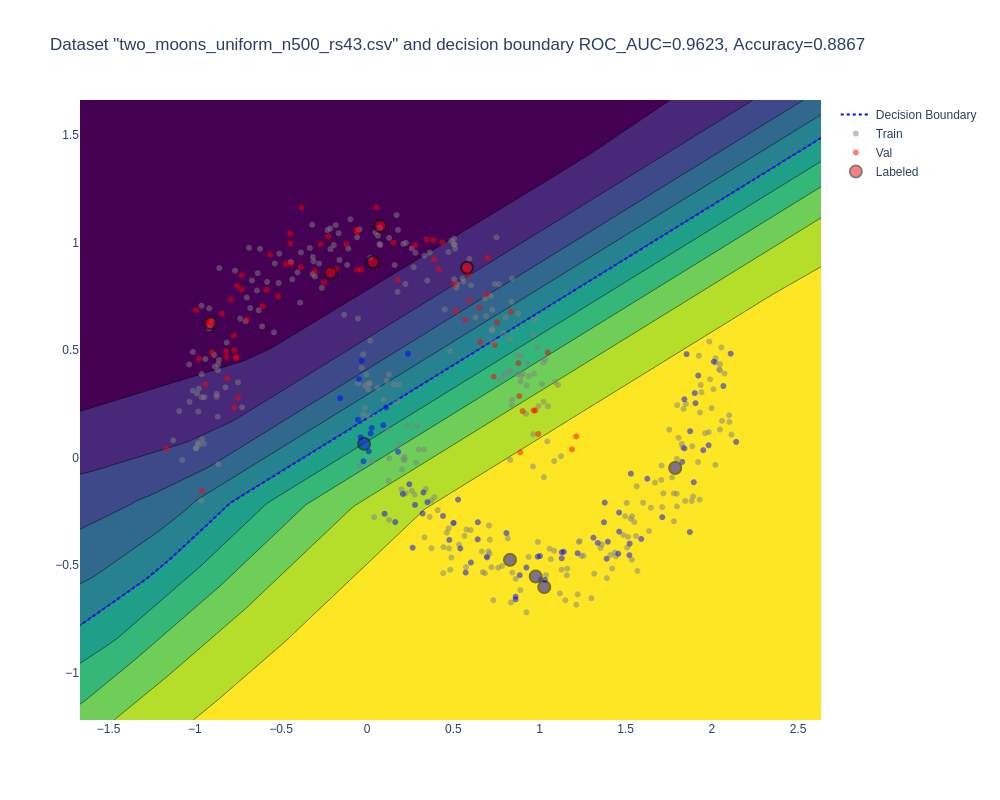
-
Mean Teacher Model (Semi-Supervised Learning):
- Trained on 10 labeled data points and 340 unlabeled data points.
- ROC AUC: 0.977, Accuracy: 0.920.
- Visualization:
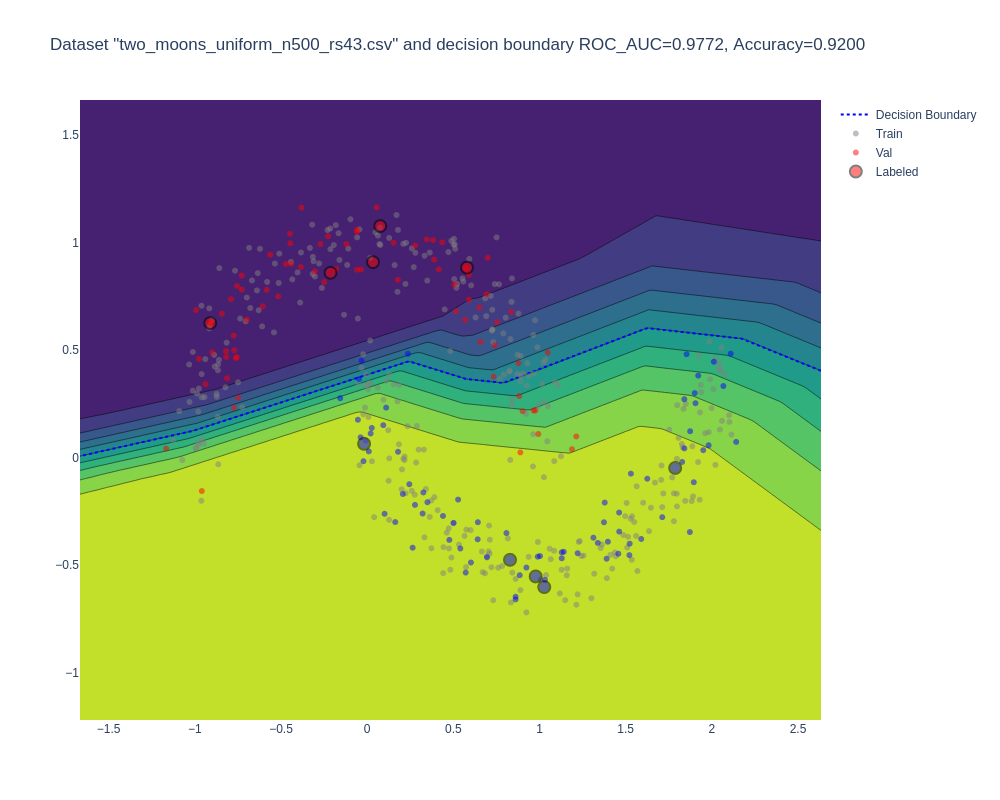
These results demonstrate the potential of Semi-Supervised Learning approaches, particularly the Mean Teacher model, in leveraging unlabeled data to achieve higher performance compared to purely supervised learning with limited labeled data.
All code and this README file were produced using OpenAI's GPT-4V.
