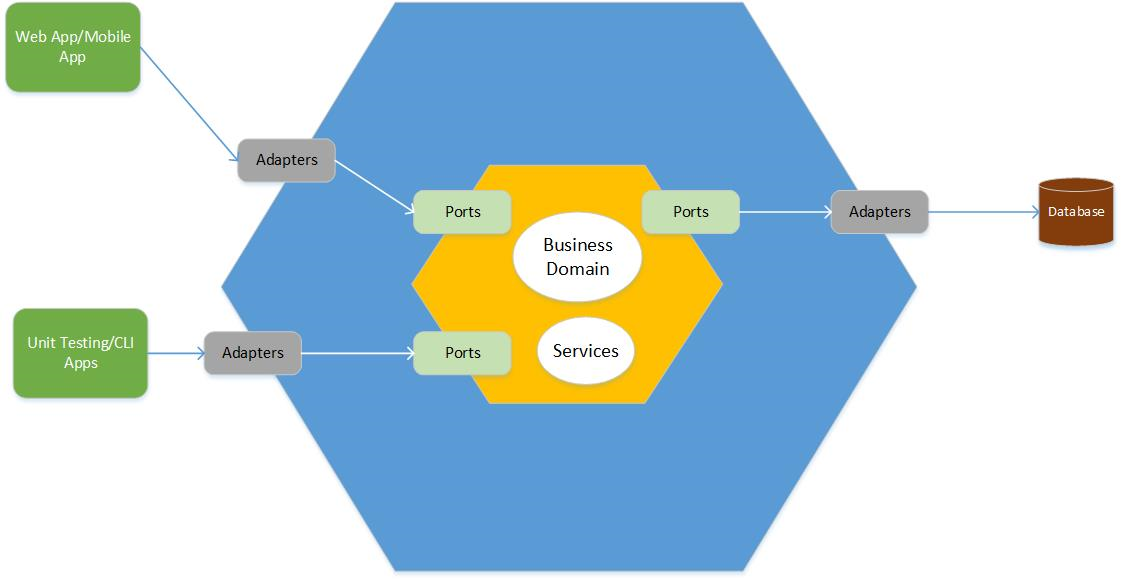
Sample of hexagonal architecture to handle login logic and user CRUD
This application support 2 kind of database MySQL and MongoDB to prove our ports is completely agnostic from the implementation.
By default it will connect into our mongo DB database with default host & port localhost:27017 and collection local
To connect into different database we need to set database information in environment variable
- MongoDB
set url=mongodb://localhost:27017/local
set timeout=30
set db=local
set driver=mongo
- MySQL
set url=root:Password.1@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/tes
set timeout=10
set db=tes
set driver=mysql
After setting the database information we only need to run the main.go file
go run main.go
Here is our API List and its payload:
- [GET] /user/{user_id}
/user/userid01 - [POST] /user
/user
{
Name: "Name",
Username: "username",
Password: "Password.User",
ID: "userid01",
Email: "usermail01@gmail.com",
Address: "User Address 01",
IsActive: false
}- [PUT] /user/{user_id}
/user/userid01
{
Name: "Name",
Username: "username",
Password: "Password.User",
ID: "userid01",
Email: "usermail01@gmail.com",
Address: "User Address 01",
IsActive: false
}-
[DELETE] /user/{user_id}
/user/userid01 -
[POST] /auth
{
Username: "username",
Password: "Password.User"
}The concept of Hexagonal Architecture is to make sure that we divide our software in such a way that each piece of the software maintains its separation of concerns so that our application is modular.
App & Domain Logic needs to be completely separated from the infrastructure like database or web service.
In the figure below, we have Domain Logic in the middle and Ports & Adapters layer on the outside which connect the Domain Logic to outside things like a user interface, Repository, REST API, External API or Message Queue.
So whenever our Domain Logic needs some infrastructure then we need to make our Domain Logic to depend on Ports.
Ports are simply interfaces that represent what that infrastructure needs to do.
For example if we need to get user data from a database, a port can be an interface that has a method that returns a list of users.
These ports are completely agnostic from the implementation.
Adapters do the concrete action and talk to the infrastructure
In the figure we can see that these Adapters are outside of the Domain Logic so that we keep our Domain Logic completely ignorant about infrastructure
You can refer to below images to gain more clarity, I got this image from medium post
:
By using this architecture we can make sure that the Business Logic itself is independent of any kind of framework.
So if we rely on framework to one of our Ports & Adapters, if the framework become depreciated or if want to use a different framework we could just take our Business Logic and move it over to that other framework.
We also can make sure that our Domain Logic are testable without any of the Port & Adapters, so if we don't have a database or an API we can still test the Business Logic and make sure that it actually works properly
So we have our service which is a user management and login and it will connect to serializer which will either serialize the data into json or message pack before serving it through REST API
And then on the other side we have our repository which will either choose to use MongoDB or MySQL based on how we start the application from command line.
So basically our API will be able to accept JSON or message pack format and also our repository is able to use both MongoDB and MySQL and it won't really affect our service
By implementing Hexagonal Architecture we also implement Dependency Inversion and Dependency Injection. Here is some explanations about project structure:
- api
contains handler for API - models
contains data models - repositories
contains Port interface for repository adapter- mongodb
contains mongo Adapter that implement UserRepository interface. This package will store mongo client and connect to mongoDB database to handle database query or command - mysql
contains MySQL Adapter that implement UserRepository interface. This package will store MySQL client and connect to MySQL server to handle database query or data manipulation
- mongodb
- serializer
contains Port interface for decode and encode serializer. It will be used in our API to decode and encode data.- json
contains json Adapter that implement serializer interface to encode and decode data - msgpack
contains message pack Adapter that implement serializer interface to encode and decode data
- json
- services
contains Port interface for our domain service and logic - logic
contains service Adapter that implement service interface to handle service logic like constructing repository parameter and calling repository interface to do data manipulation or query