FILE COMPRESSION USING HUFFMAN ADAPTED ENCODING
-
C++ programs which can compress and extract the file using ADAPTED HUFFMAN CODING : A lossless data compression using variable length codes. It is the most efficient algorithm for data compression.
-
The program encode.cpp needs the name of file as an argument. It will the compress the file using Huffman encoding algorithm and generate a new compressed file with .huf extension.
-
The program decode.cpp needs the name of compressed file with extension .huf. Optionally you can also give a second argument specifying the name of the decoded output file.
-
The compression ratios depend on the type of the input file.
-
For small files(order of bytes) it is not recommended to compress, because of fractional compression ratio. The compressed file occupies more space than input file.
-
In general, larger the input file sizes, better is the compression ratios. The compression ratios depend on the probabilities of source's data.
-
Here's the approach our method use:
- Sort the frequencies and group it into groups of 8.
- Label each connection as 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 and create a tree structure just like in Huffman Coding.
- Retrieve the modified ID for each componant of the message.
- Create a Reference Table for the new alloted values to the characters.
Let us see the Algo.
ALGORITHM for ENCODER
-
Read the input file and store the contents as a string.
-
Initialize an empty map called 'freqmap' to store the frequencies of each character in the input file.
-
Iterate through the input string and count the frequency of each character.
-
For each character in the input string, create a node object with the frequency and character value, and push it into a priority queue called 'minHeap'.
-
While the size of the minHeap is greater than 1, do the following:
-
Pop the top two elements (n1 and n2) from the minHeap.
-
Create a new node with the sum of the frequencies of n1 and n2, and set the left and right children of the node to n1 and n2 respectively.
-
Push the new node into the minHeap.
-
The remaining node in the minHeap is the root of the huffman tree.
-
Initialize an empty map called 'table' to store the character-code mappings.
-
Call the 'getMappings' function to generate the character-code mappings and store them in the 'table' map.
-
Initialize a string called 'encodedData' to store the encoded data.
-
Iterate through the input string and for each character, append the corresponding code from the 'table' map to the 'encodedData' string.
-
Flatten the huffman tree to a string using the 'convertToString' function and store it in a string called 'huffmanTree'.
-
Calculate the number of padding bits needed to make the encoded data a multiple of 8 bits.
-
Write the number of padding bits, the length of the huffman tree, the huffman tree string, and the encoded data string to the output file.
ALGORITHM for DECODER -
Check if the input file is '.huf' format by calling the 'dothuf' function with the input file name as the argument. If it returns false, print "Invalid Input file" and return 0.
-
Read the input file and store its contents in the 'data' string. If the file cannot be found, print "File not found" and return 0.
-
Extract the padding and Huffman tree length from the 'data' string.
-
Extract the Huffman tree from the 'data' string.
-
Build the Huffman tree using the 'buildTree' function with the extracted Huffman tree string and its length as arguments.
-
Extract the encoded data from the 'data' string.
-
Initialize a string 'decodedData' and a pointer 'p' to the root of the Huffman tree.
-
Iterate through the encoded data, shifting left in the Huffman tree if the current character is '0' and shifting right if it is '1'. If the current node is a leaf node, append its character to 'decodedData' and reset 'p' to the root of the tree.
-
Remove the padding from the 'decodedData' string.
-
Write the 'decodedData' string to the output file.
-
Close the output file.
-
Print "Decompression Done!!"
-
End the algorithm.
TIME COMPLEXITY -
The priority queue (implemented as a min heap) has a time complexity of O(log n) for inserting and removing elements, so the overall time complexity of the huffman tree construction is O(n log n).
-
The time complexity of the remaining parts of the code, such as reading the input file, counting the frequencies of the characters, and generating the mappings, are all O(n) operations, so they do not significantly affect the overall time complexity.
-
Note: The above analysis assumes that the time complexity of the map data structure used in the code is O(1) for insert and lookup operations, which is generally the case for most modern implementations of the map data structure.
Refer encode.cpp to see what is done by each segment of code.
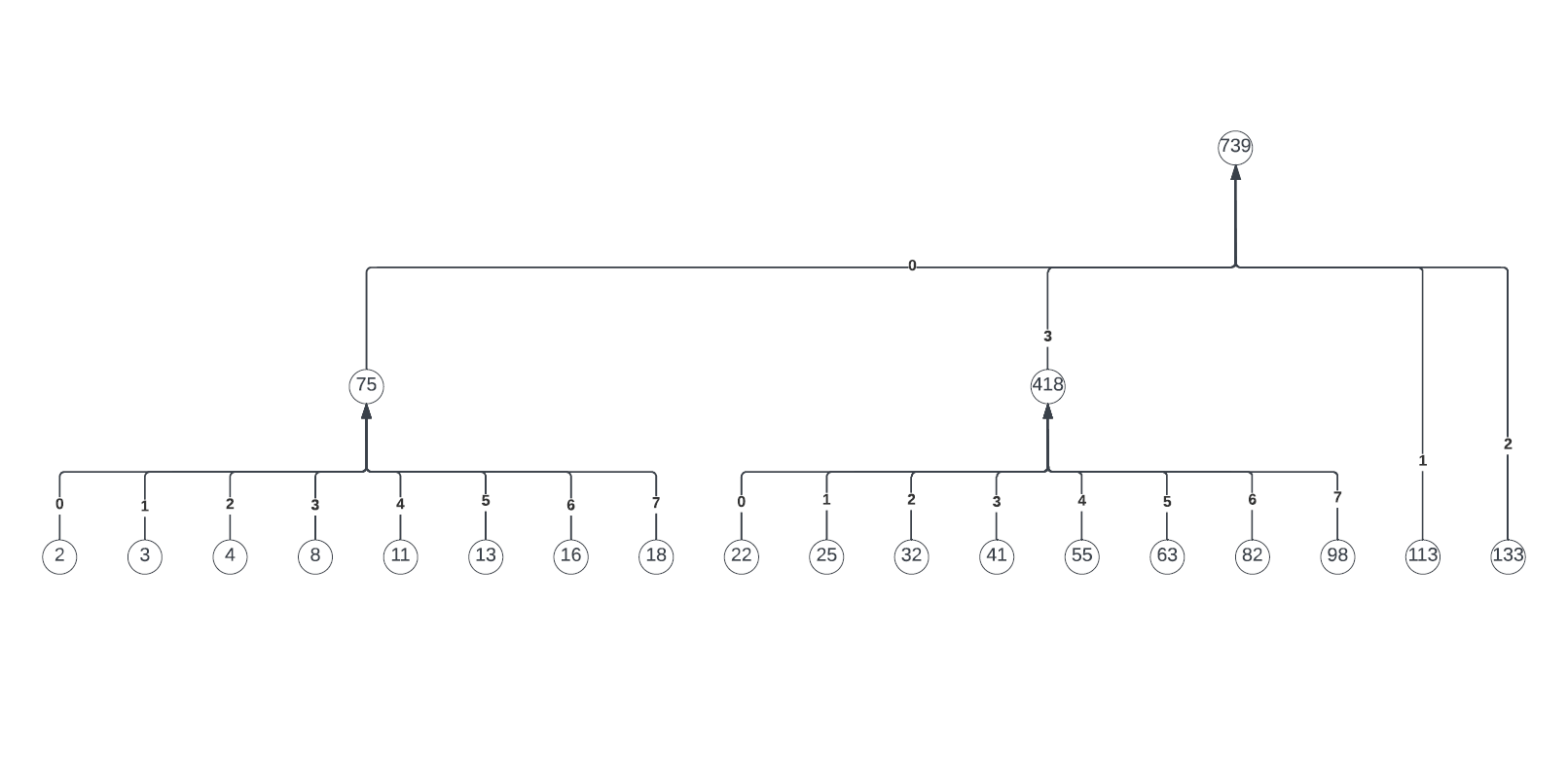
The reason why this approach is currently the most effecient is because it reduces the overall tree length by almost 4 times in average cases and worst case is near to average case of Huffman cide.
The characterID alloted to each character in a message is dependant on the length of the tree formed and for the same number message, the tree height of conventional Huffman encoding is higher than our proposed idea.
The same can be seen in the tree below
CONVENTIONAL HUFFMAN TREE
0-7 HUFFMAN TREE
As visible in the tree, the hieght is 8-bits, whereas in the 0-7 Huffman Code, it is 3-bits. This reduces overall size by almost half.
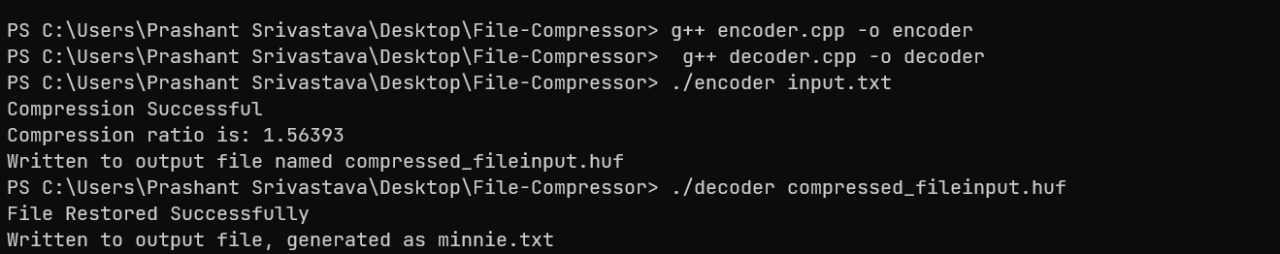
IMPLEMENTING THE CODE IN TERMINAL
This is what the input and output will look like in the terminal and all the files will be read or created locally on the system in the background.
-------------------ENCODE-------------------
Given code defines a string variable called data and two classes: node and comp.
The node class represents a node in the Huffman tree, which is used to encode the input data. Each node has four data members: left, right, val, and freq. The left and right members are pointers to other node objects and are used to link the nodes in the tree. The val member stores the character value of the node, and the freq member stores the frequency of occurrence of the character in the input data. The node class has a constructor that initializes these data members when a new node object is created.
*Defining comp class*
The comp class defines a comparison operator that compares the frequencies of two node objects. This operator is used to sort the node objects in a priority queue, with the nodes having the lowest frequency appearing first in the queue.
getMappings function
The getMappings function is used to find the Huffman codes for each character in the input data. It takes a pointer to a node object (the root of the Huffman tree) and a reference to a map object (which stores the mappings of characters to their corresponding Huffman codes) as arguments, and a string called s that stores the current code being built. The function works by recursively traversing the tree and appending a '0' to s when it moves left and a '1' when it moves right. When it reaches a leaf node (a node with no children), it stores the current value of s in the map object as the Huffman code for the character stored in the leaf node.
convertToString function
The convertToString function is used to flatten the Huffman tree into a string representation. It takes a pointer to a node object (the root of the Huffman tree) as an argument and returns a string that represents the tree. If the current node is a leaf node, the function appends a '-' character and the character value of the node to the string and returns it. Otherwise, it recursively calls itself on the left and right child nodes and concatenates the returned strings with '0' and '1' characters, respectively.
Main Function
The main function is the entry point of the program. It first checks whether the program was called with the name of an input file as an argument. If not, it prints an error message and exits. Otherwise, it reads the contents of the input file into the data variable. Next, it counts the frequencies of each character in the data string and stores them in a map object called freqmap. It then creates a node object for each character and pushes them into a priority queue called minHeap. The queue is sorted using the comparison operator defined in the comp class.
-------------------DECODE-------------------
Eplanation of DECODER bool dothuf(string s)
This function takes a string as input and returns true if the string ends with the substring ".huf", and false otherwise. This function is used to check whether the input file is in the correct format.
node buildTree(string& huffmanTree, ll hlen, ll& p)*
This function takes a string representing a Huffman tree, the length of the tree, and a reference to an integer p as input. It returns a pointer to the root node of the Huffman tree, which is constructed by recursively parsing the input string.
string toBinary(ll x)
This function takes an integer x as input and returns a string of 8 characters representing the binary representation of x.
Main Function
This is the main function of the program, which is responsible for reading in the input file, extracting the Huffman tree and encoded data from the file, constructing the Huffman tree, and using the tree to decode the encoded data.
The program begins by checking that the correct number of command line arguments have been provided and that the input file is in the correct format. If either of these checks fail, the program prints an error message and exits. Next, the program reads in the entire contents of the input file as a string, and extracts the padding and Huffman tree length from the first two lines of the file. The program then extracts the Huffman tree from the input file, and uses the buildTree function to construct the tree.
After the Huffman tree has been constructed, the program processes the encoded data by iterating through each character in the data string, and traversing the Huffman tree accordingly. When a leaf node is reached, the program adds the character stored at that node to the result string. Once all of the encoded data has been processed, the program removes the padding from the result string, and writes the result to the specified output file.