Overview
This is the basic Python library to read data from the PSI SwissFEL DataBuffer and Epics Archiver. The library accesses the data via the DataAPI REST service and (by default) loads it into a Pandas data frame.
What is a Pandas DataFrame? Think about it as a big table, where all values are indexed using either the
global timestampor thepulse_id. This allows you to execute statistical operations, correlations, filtering etc in a very easy and efficient way. More about Pandas you can find here:
- http://pandas.pydata.org
- http://pandas.pydata.org/index.html
- http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/10min.html
Usage
Import library:
import data_api as apiSearch for channels:
channels = api.search("SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE")The channels variable will hold something like this:
[{'backend': 'sf-databuffer',
'channels': ['SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE',
'SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE-AVG']},
{'backend': 'sf-archiverappliance',
'channels': ['SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE-AVG-P2P',
'SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE-JIT-P2P',
'SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE-STDEV']}]Get data by global timestamp:
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now()
end = now-datetime.timedelta(minutes=1)
start = end-datetime.timedelta(seconds=10)
data = api.get_data(channels=['SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE'], start=start, end=end)In the case to query a specific backend specify the base_url option in the get_data call. For example for hipa use api.get_data(... base_url='https://data-api.psi.ch/hipa')
Get data by pulseId:
import datetime
start_pulse_id = 123456
stop_pulse_id = 234567
data = api.get_data(channels=['SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE'], start=start_pulse_id, end=stop_pulse_id, range_type="pulseId")Get approximate pulseId by global timestamp:
Warning: This will not give you an exact pulse_id, just the closest pulse_id in the data buffer from the global timestamp you requested. The pulse id might be skewed by maximum 30 seconds.
from datetime import datetime
global_timestamp = datetime.now()
# If you do not pass a global_timestamp, the current time will be used.
pulse_id = api.get_pulse_id_from_timestamp(global_timestamp)Show head of datatable:
data.head()Find all data corresponding to given index:
data.loc["1468476300.047550981"]Plot data:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
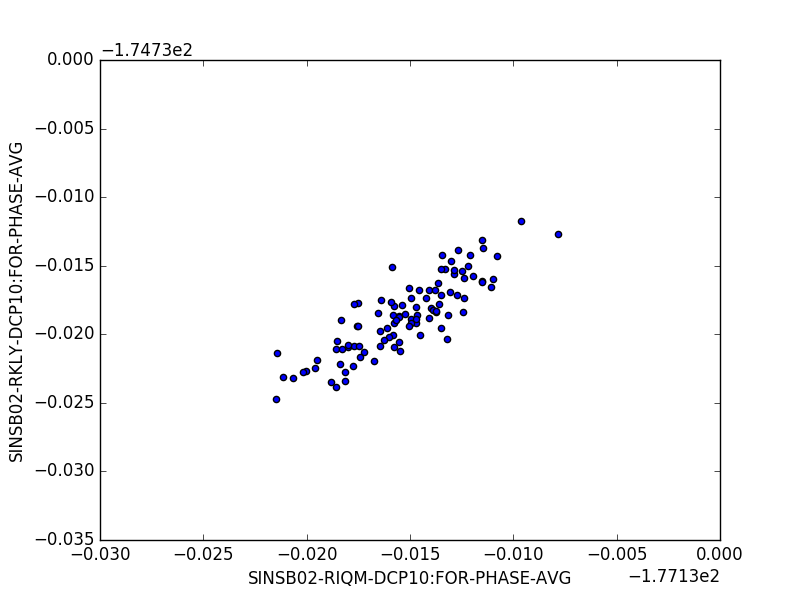
data.plot.scatter("SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE-AVG", "SINSB02-RKLY-DCP10:FOR-PHASE-AVG")
plt.show()import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
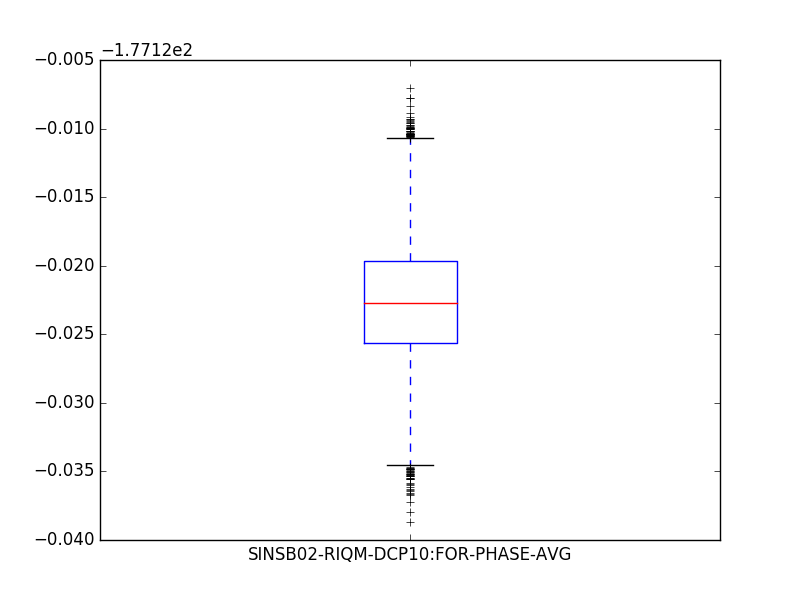
data[['SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE-AVG', ]].plot.box()
plt.show()Plot waveforms:
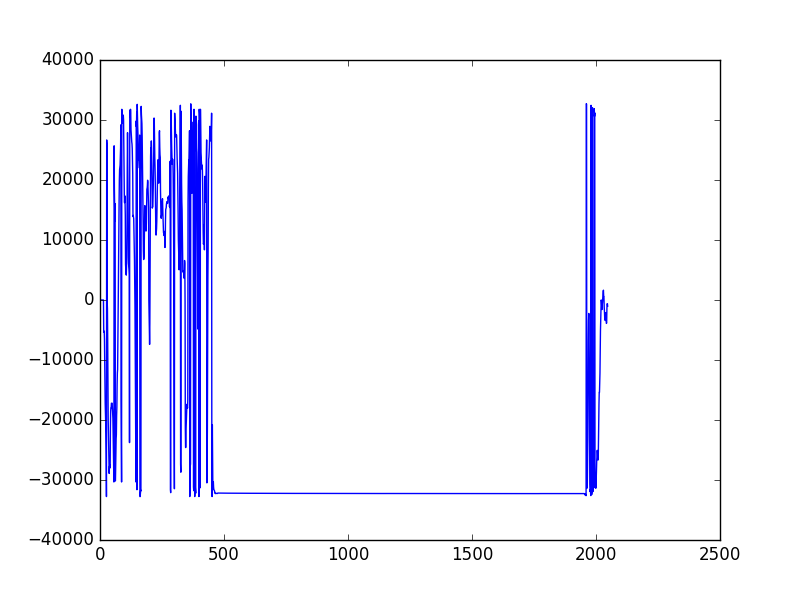
plt.plot(data['SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE']['1468476300.237551000'])
plt.show()Find where you have data:
data[data['SINSB02-RIQM-DCP10:FOR-PHASE'].notnull()]
Save data:
# to csv
data.to_csv("test.csv")
# to hdf5
data.to_hdf("test.h5", "/dataset")Use Server-Side Aggregation
To minimize data transfer requirements, data can be requested in an aggregated way from the API. The server than takes care of aggregating the values and only send the aggregated values to the client.
import data_api as api
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now()
end = now-datetime.timedelta(minutes=1)
start = end-datetime.timedelta(seconds=10)
aggregation = api.Aggregation(aggregation_type="value", aggregations=["min", "mean", "max"], extrema=None, nr_of_bins=None, duration_per_bin=None, pulses_per_bin=None) # Just set the parameters you explicitly want to set - this example is showing the defaults - for more details about the parameters and their effect see https://git.psi.ch/sf_daq/ch.psi.daq.queryrest#data-aggregation
data = data_api.get_data(channel_list, start=start, end=end, aggregation=aggregation)For more details on the aggregation values and their effects see: https://git.psi.ch/sf_daq/ch.psi.daq.queryrest#data-aggregation
Query Specific Backend
By default the data API first queries the DataBuffer for the channel, if the channel is not found there, it then does a query to the Epics Archiver.
If you want to explicitly specify which backend/system the channel should be queried from you can prepend the channel name with either sf-databuffer/ or sf-archiverappliance/
"sf-databuffer/CHAN1"
# or
"sf-archiverappliance/CHAN1"
Query For PulseId Global Timestamp Mapping
To find the correspondig global timestamp of a given pulseid this method can be used:
import data_api as api
api.get_global_date(pulseid)
# Query for multiple pulseids mappings
api.get_global_date([pulseid1, pulseid2])The method accepts a single or multiple pulseids and returns a list of global dates for the specified pulseids.
By default the method uses the beam ok channel (SIN-CVME-TIFGUN-EVR0:BEAMOK)
to do the mapping. If the mapping cannot be done the method raises an ValueException.
In that case a different mapping channel via the functions optional parameter mapping_channel can be specified
Command Line Interface
The packages functionality is also provided by a command line tool. On the command line data can be retrieved as follow:
$ data_api -h
usage: data_api [-h] [--regex REGEX] [--from_time FROM_TIME]
[--to_time TO_TIME] [--from_pulse FROM_PULSE]
[--to_pulse TO_PULSE] [--channels CHANNELS]
[--filename FILENAME] [--overwrite] [--split SPLIT] [--print]
[--binary]
action
Command line interface for the Data API
positional arguments:
action Action to be performed. Possibilities: search, save
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--regex REGEX String to be searched
--from_time FROM_TIME
Start time for the data query
--to_time TO_TIME End time for the data query
--from_pulse FROM_PULSE
Start pulseId for the data query
--to_pulse TO_PULSE End pulseId for the data query
--channels CHANNELS Channels to be queried, comma-separated list
--filename FILENAME Name of the output file
--overwrite Overwrite the output file
--split SPLIT Number of pulses or duration (ISO8601) per file
--print Prints out the downloaded data. Output can be cut.
--binary Download as binary
To export data to a hdf5 file the command line tool can be used as follows:
data_api --from_time "2017-10-30 10:59:45.788" --to_time "2017-10-30 11:00:45.788" --channels S10CB01-RLOD100-PUP10:SIG-AMPLT-AVG --filename testit.h5 saveTo improve download speeds use the --binary option for saving data into a hdf5 file.
As downloads might be pretty big and if you are not using the --binary option the current implementation need to keep all data in memory before writing you have to use the --split option to split up the data files.
When having this option specified the query will be split in several smaller queries.
In case of an pulse based query this argument takes an integer, in case of a time based query it takes an ISO8601 duration string. Please note that in the case of duration year and month durations are not supported!
Pulse based query:
data_api --from_pulse 5166875100 --to_pulse 5166876100 --channels sf-databuffer/SINEG01-RCIR-PUP10:SIG-AMPLT --split 500 --filename testit.h5 saveTime based query:
data_api --from_time "2018-04-05 09:00:00.000" --to_time "2018-04-05 10:00:00.000" --channels sf-databuffer/SINEG01-RCIR-PUP10:SIG-AMPLT --split PT30M --filename testit.h5 saveExample durations:
- PT2M - 2 minutes
- PT1H2M - 1 hour and 2 minutes
- PT10S - 10 seconds
- P1W - 1 week
- P1DT6H - one day and 6 hours
Examples
Jupyter Notebook
If you want to run our Jupyter Notebook examples, please clone this repository locally, then:
cd examples
ipython notebook
Installation
You can install through our Anaconda repository:
conda install -c paulscherrerinstitute data_api