Linux Server Configuration
This is the final project for Udacity's Full Stack Web Developer Nanodegree
Objective
You will take a baseline installation of a Linux distribution on a virtual machine and prepare it to host your web applications, to include installing updates, securing it from a number of attack vectors and installing/configuring web and database servers.
Description
This page explains how to secure and set up a Linux distribution on a virtual machine, install and configure a web and database server to host a web application.
- The Linux distribution is Ubuntu 16.04 LTS.
- The virtual private server is Amazon Lighsail.
- The web application is my Item Catalog project created earlier in this Nanodegree program.
- The database server is PostgreSQL.
- My local machine is a MacBook Pro (macOS Mojave 10.14.1)
- Public IP Address: 13.209.11.93
- URL: http://ec2-13-209-11-93.ap-northeast-2.compute.amazonaws.com
- Accessible SSH port: 2200
※ Please visit http://ec2-13-209-11-93.ap-northeast-2.compute.amazonaws.com for testing.
You cannot login with Google account at http://13.125.200.246 because of Google's public-suffixes-and-private-domains policy
TL;DR;
ssh -i ~/.ssh/grader_key -p 2200 grader@13.209.11.93Visit http://ec2-13-209-11-93.ap-northeast-2.compute.amazonaws.com for testing.
Build a server 👨💻
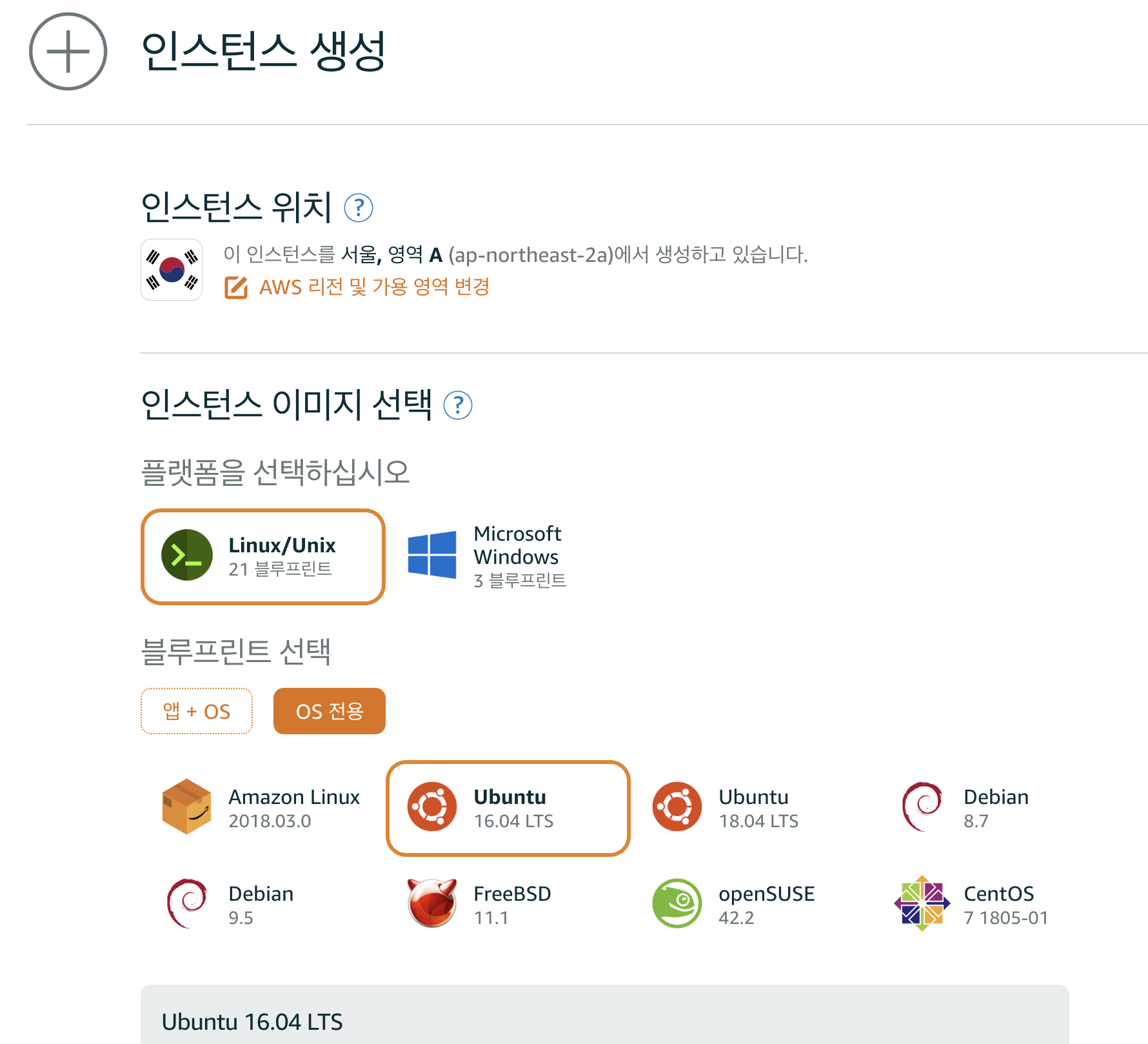
Step 1: Start a new Ubuntu Linux server instance on Amazon Lightsail
- Amazon Lightsail using an Amazon Web Services account.
Create instance.- Choose
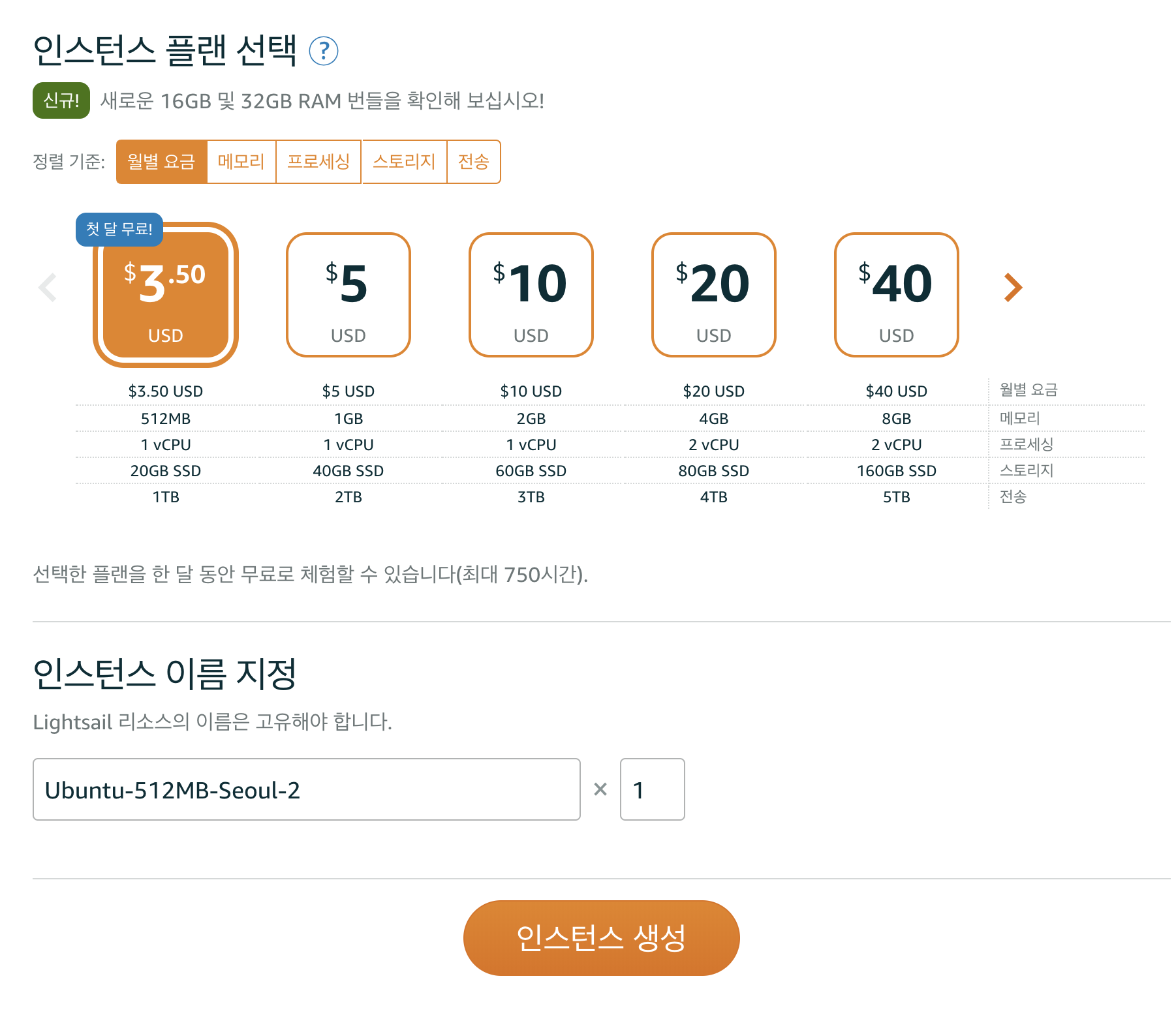
Linux/Unixplatform,OS OnlyandUbuntu 16.04 LTS. - Choose a
the cheapest plan. - Click the
Createbutton to create the instance.
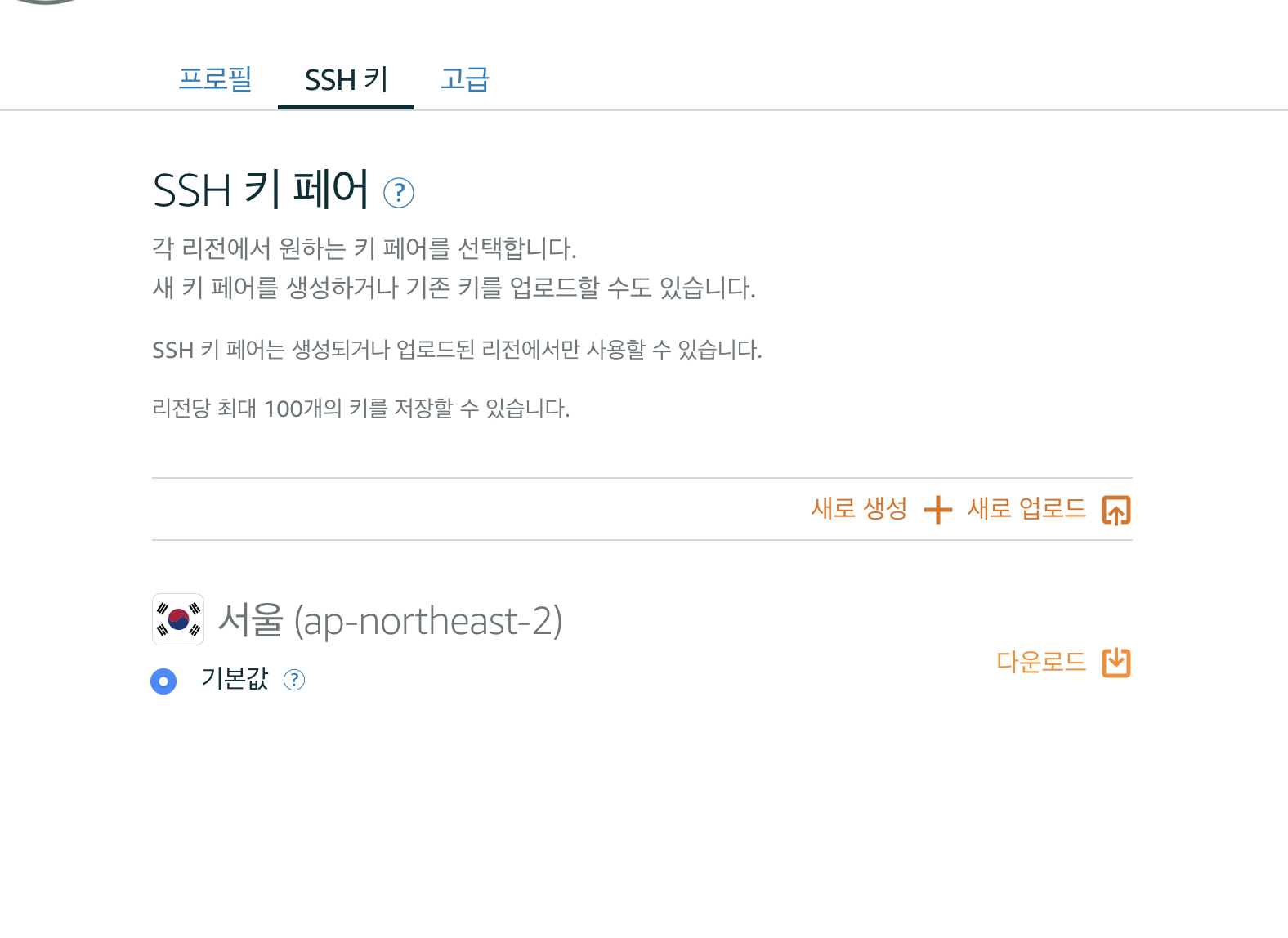
Step 2: SSH into the server
- From the
Accountmenu on Amazon Lightsail, click onSSH keystab and download the Default Private Key. - Move this private key file named
LightsailDefaultPrivateKey-*.peminto the local folder~/.sshand rename itlightsail_key.rsa.
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/lightsail_key.rsa
ssh -i ~/.ssh/lightsail_key.rsa ubuntu@13.209.11.93Secure the server 🔒
Step 3: Keep the package up to date.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 4: Change the SSH port from 22 to 2200
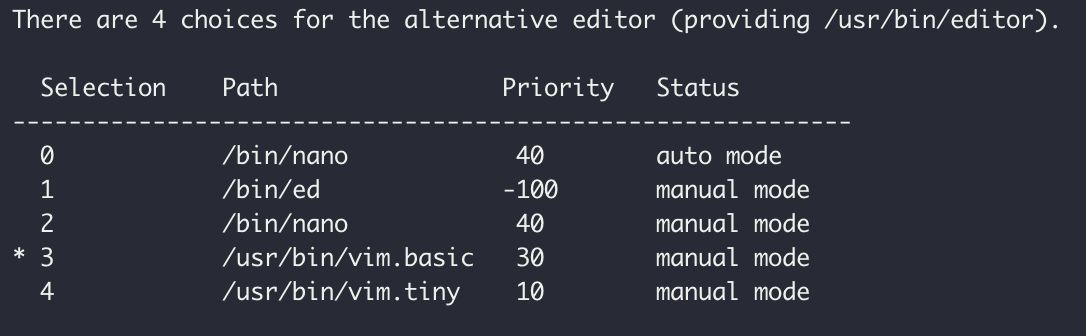
By the way, I don't wanna use nano editor.
sudo update-alternatives --config editor
If you are new to using vim, you may not be able to turn off the editor!!
vimtutor- Edit the
/etc/ssh/sshd_configfile:
sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config- Change the port number on line 5 from
22to2200 - Save and exit using
:wq - Restart SSH:
sudo service ssh restart.
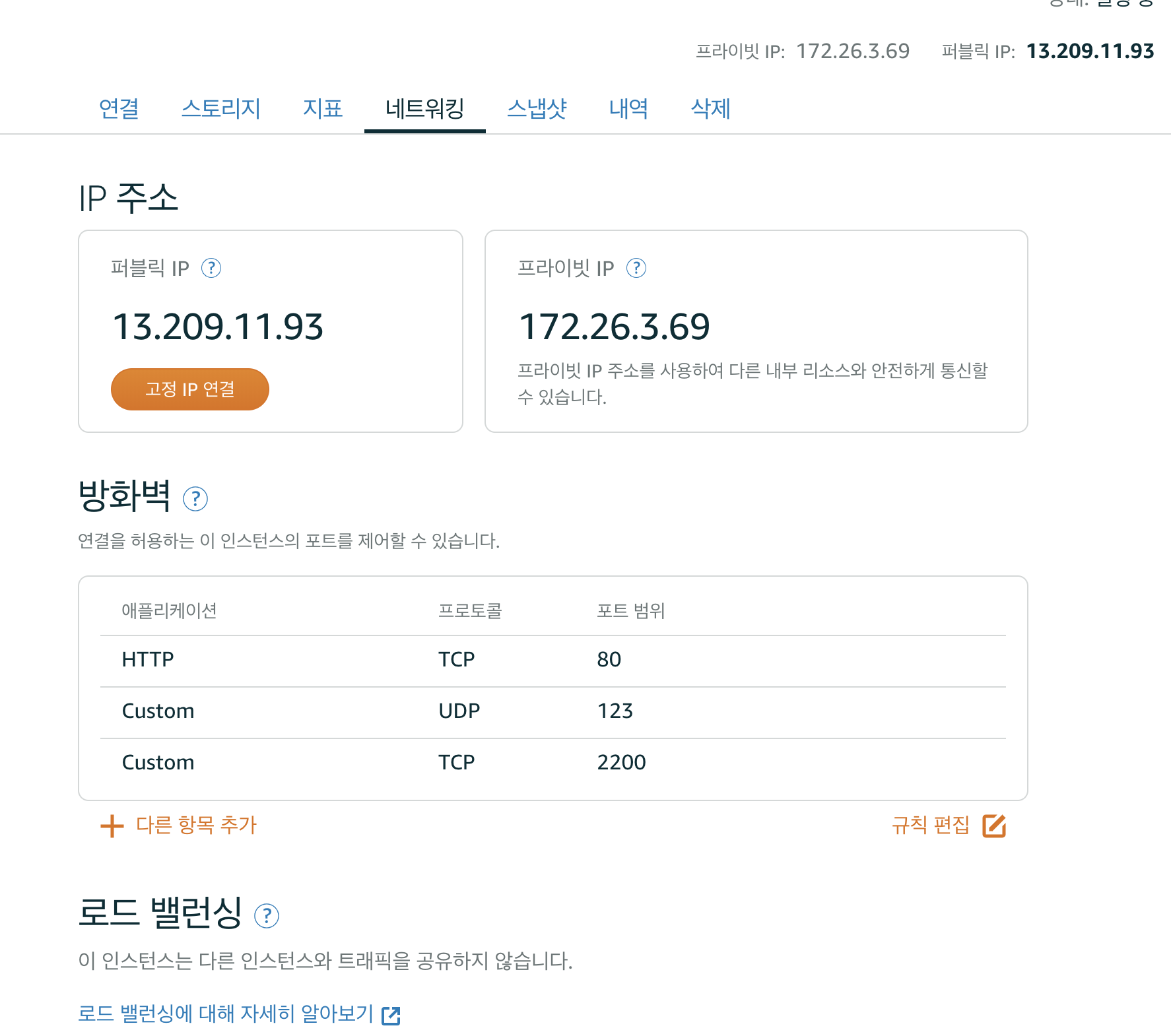
Step 5: Configure the Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) 🔥 🧱
- Configure the default firewall for Ubuntu to only allow incoming connections for SSH (port 2200), HTTP (port 80), and NTP (port 123).
sudo ufw status # The UFW should be inactive.
sudo ufw default deny incoming # Deny any incoming traffic.
sudo ufw default allow outgoing # Enable outgoing traffic.
sudo ufw allow 2200/tcp # Allow incoming tcp packets on port 2200.
sudo ufw allow www # Allow HTTP traffic in.
sudo ufw allow 123/udp # Allow incoming udp packets on port 123.
sudo ufw deny 22 # Deny tcp and udp packets on port 53.- Turn UFW on:
sudo ufw enable- Check the status of UFW to list current roles:
sudo ufw status
- Exit the SSH connection:
exit
- Click on the
Manageoption of the Amazon Lightsail Instance, then theNetworkingtab, and then change the firewall configuration to match the internal firewall settings above. Allow ports 80(TCP), 123(UDP), and 2200(TCP), and deny the default port 22.
ssh -i ~/.ssh/lightsail_key.rsa -p 2200 ubuntu@13.59.39.163
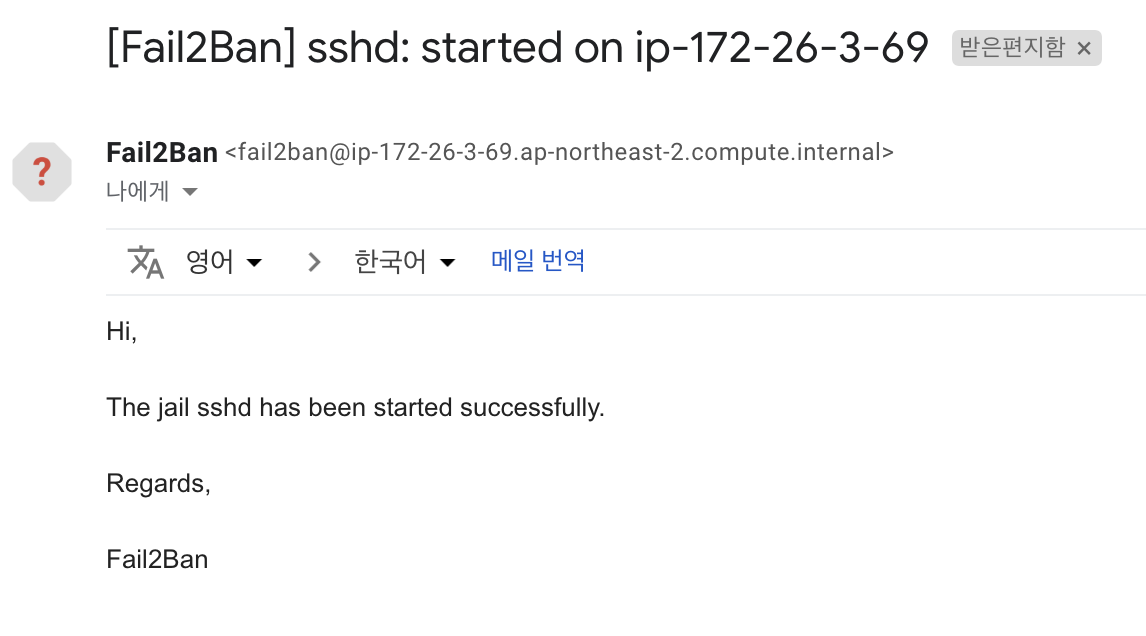
Step 5.1: Use Fail2Ban to ban attackers
Fail2Banis an intrusion prevention software framework that protects computer servers from brute-force attacks.
- Install Fail2Ban:
sudo apt-get install fail2ban
- Install sendmail for email notice
sudo apt-get install sendmail iptables-persistent
- Create a copy of a file:
sudo cp /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
-
Change the settings in
/etc/fail2ban/jail.localfile like below:show line number
:set nu```sh set bantime = 600 # 59 line destemail = useremail@domain # 129 line action = %(action_mwl)s # 204 line port = 2200 # 217 line ``` -
Restart the service:
sudo service fail2ban restart
- You should receive an email like this:
Step 5.2: Automatically install updates
The
unattended-upgradespackage can be used to automatically install important system updates.
-
Enable automatic (security) updates:
sudo apt-get install unattended-upgrades. -
Edit
/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/50unattended-upgrades, uncomment the line${distro_id}:${distro_codename}-updatesand save it. -
Modify
/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgradesfile like below:APT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists "1"; APT::Periodic::Download-Upgradeable-Packages "1"; APT::Periodic::AutocleanInterval "7"; APT::Periodic::Unattended-Upgrade "1";
-
Enable it:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure --priority=low unattended-upgrades
- Restart Apache:
sudo service apache2 restart
Step 5.3: Updated packages to most recent versions
Some packages have not been updated because the server need to be rebooted.
-
run commands like below:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get dist-upgrade sudo shutdown -r now -
Logged back in, and I now see this message:
Alains-MBP:udacity-linux-server-configuration boisalai$ ssh -i ~/.ssh/lightsail_key.rsa -p 2200 ubuntu@13.59.39.163 Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.3 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.4.0-1039-aws x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com * Management: https://landscape.canonical.com * Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage Get cloud support with Ubuntu Advantage Cloud Guest: http://www.ubuntu.com/business/services/cloud 0 packages can be updated. 0 updates are security updates. Last login: Tue Oct 31 06:35:28 2017 from 24.201.154.77 ubuntu@ip-172-26-0-7:~$
Grant grader access 🚧
Step 6: Create a grader
- While logged in as
ubuntu, add user:
sudo adduser grader
- Enter a password (e.g.
fsnd2018) and continue to press enter to set the default value.
Step 7: Give a sudo permission to grader
- Edits the sudoers file:
sudo visudo
-
Search for the line that looks like this:
show line number
:set nuroot ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL # 20 line -
Below this line, add a new line to give sudo privileges to
graderuser.root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL # 20 line grader ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL # 21 line
-
Save and exit using
:wq -
Verify that
graderhas sudo permissions. Runsu - grader, enter the password, runsudo -land enter the password again. The output should be like this:Matching Defaults entries for grader on ip-172-26-13-170.us-east-2.compute.internal: env_reset, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin\:/snap/bin User grader may run the following commands on ip-172-26-13-170.us-east-2.compute.internal: (ALL : ALL) ALL
Step 8: Create an SSH key pair for grader using the ssh-keygen tool
Not a VM linux, But on your local machine
- Run
ssh-keygen - Enter file in which to save the key (e.g.
grader_key) in the local directory~/.ssh - Enter in a passphrase twice (e.g. fsnd2018). Two files will be generated (
~/.ssh/grader_keyand~/.ssh/grader_key.pub) - Run
cat ~/.ssh/grader_key.puband copy the contents of the file - Log in to the grader's virtual machine
Not your local machine, But on VM linux
- Create a new directory called
~/.ssh(mkdir .ssh) - Run
sudo vim ~/.ssh/authorized_keysand paste the content into this file, save and exit - Give the permissions:
chmod 700 .sshandchmod 644 .ssh/authorized_keys - Check in
/etc/ssh/sshd_configfile ifPasswordAuthenticationis set tono - Restart SSH:
sudo service ssh restart
On your local machine again
ssh -i ~/.ssh/grader_key -p 2200 grader@13.209.11.93
Prerequisite for deployment 📋
Step 9: Configure the local timezone to UTC
- While logged in as
grader, configure the time zone:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
Step 10: Install and configure Apache to serve a Python mod_wsgi application
- While logged in as
grader, install Apache:
sudo apt-get install apache2
- Install the mod_wsgi package:
sudo apt-get install libapache2-mod-wsgi
- Enable
mod_wsgiusing:
sudo a2enmod wsgi
Step 11: Install and configure PostgreSQL
- While logged in as
grader, install PostgreSQL:
sudo apt-get install postgresql
- PostgreSQL should not allow remote connections. So, switch to the
postgresuser:
sudo su - postgres
-
Open PostgreSQL interactive terminal with
psql. -
Create the
cataloguser with a password (e.g.catalog) and give them the ability to create databases:postgres=# CREATE ROLE catalog WITH LOGIN PASSWORD 'catalog'; postgres=# ALTER ROLE catalog CREATEDB; -
List the existing roles:
\du. The output should be like this:List of roles Role name | Attributes | Member of -----------+------------------------------------------------------------+----------- catalog | Create DB | {} postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS | {} -
Exit psql:
\q. -
Switch back to the
graderuser:exit. -
Create a new Linux user called
catalog:sudo adduser catalog. Enter password and fill out information. -
Give to
cataloguser the permission to sudo. Run:sudo visudo. -
Search for the lines that looks like this:
root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL grader ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL -
Below this line, add a new line to give sudo privileges to
cataloguser.root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL grader ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL catalog ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL -
Save and exit using
:wq. -
Verify that
cataloghas sudo permissions. Runsu - catalog, enter the password, runsudo -land enter the password again. -
While logged in as
catalog, create a database:createdb catalog. -
Run
psqland then run\lto see that the new database has been created. The output should be like this:List of databases Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges -----------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+----------------------- catalog | catalog | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres + | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres + | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres (4 rows) -
Exit psql:
\q. -
Switch back to the
graderuser:exit.
Step 12: Install git
- While logged in as
grader, installgit:
sudo apt-get install git
Deploy my project to the world 🌐
Step 13.1: Clone and setup the Item Catalog project from the GitHub repository
-
While logged in as
grader, create/var/www/catalog/directory. -
Change to that directory and clone the catalog project:
sudo git clone https://github.com/reck1ess/item-catalog.git catalog
- From the
/var/wwwdirectory, change the ownership of thecatalogdirectory tograderusing:
sudo chown -R grader:grader catalog/
cd /var/www/catalog/catalog- Rename the
application.pyfile to__init__.pyusing:
mv application.py __init__.py-
In
__init__.py, replace line immediately below the import statement:# engine = create_engine("sqlite:///catalog.db") engine = create_engine('postgresql://catalog:catalog@localhost/catalog') -
In
__init__.py, replace last line:# app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=8000, debug=True) app.run() -
In
database_setup.py, replace last line:# engine = create_engine("sqlite:///catalog.db") engine = create_engine('postgresql://catalog:catalog@localhost/catalog')
Step 13.2: Authenticate login through Google
-
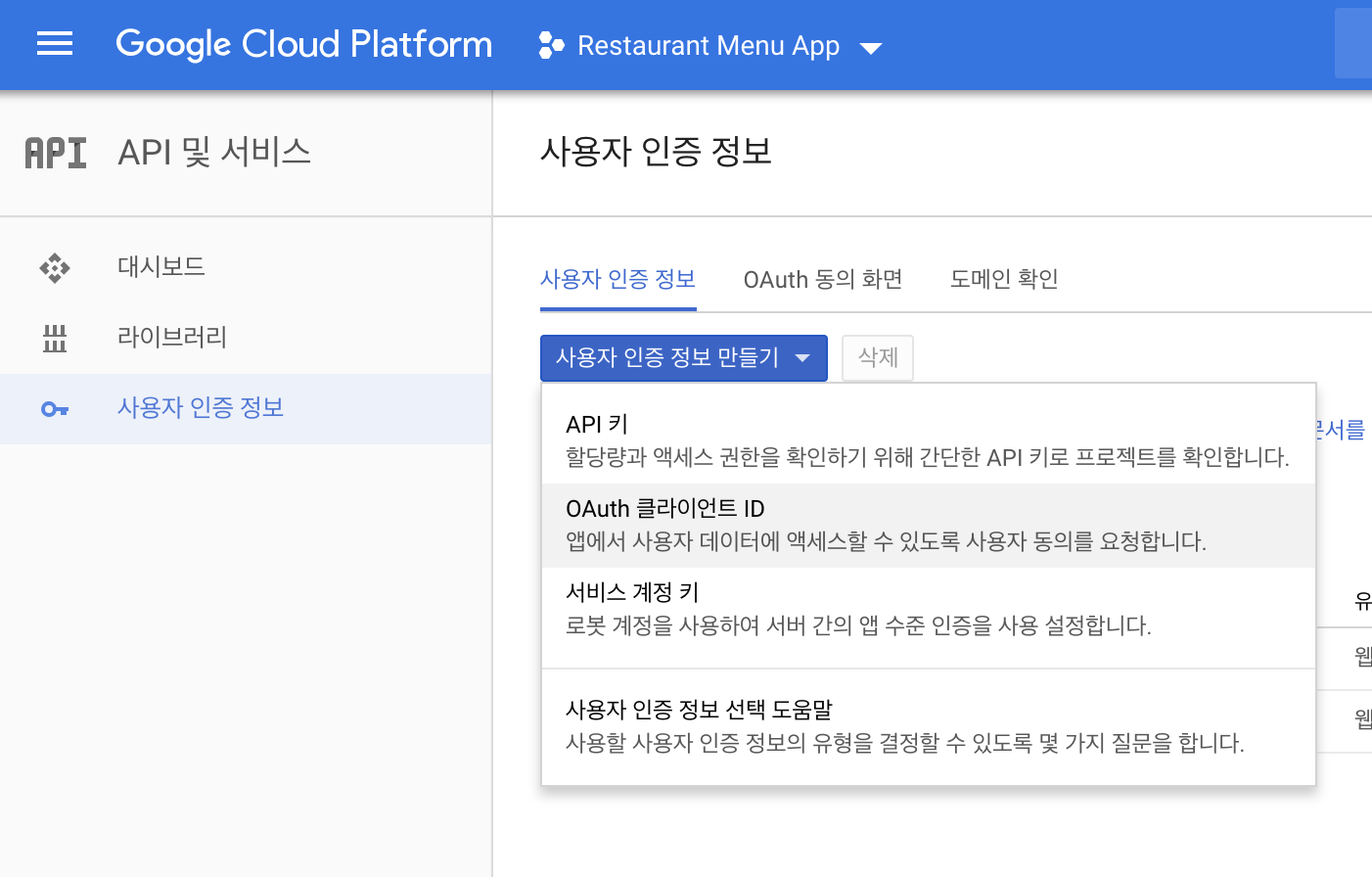
Go to Google Cloud Plateform
-
Click
APIs & serviceson left menu. -
Click
Credentials.
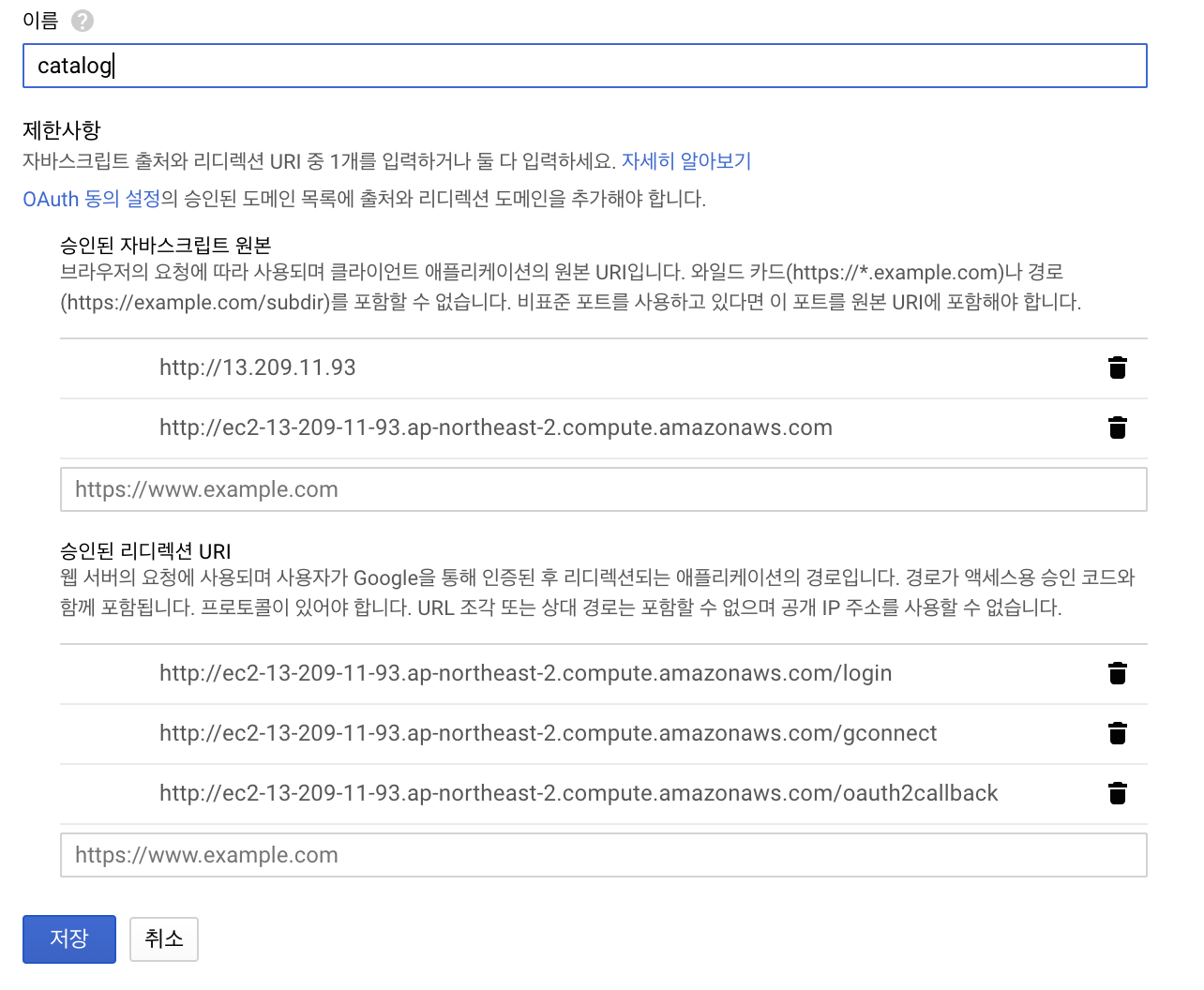
-
Create an OAuth Client ID (under the Credentials tab), and add
http://13.209.11.93andhttp://ec2-13-209-11-93.ap-northeast-2.compute.amazonaws.comas authorized JavaScript origins. -
Add
http://ec2-13-209-11-93.ap-northeast-2.compute.amazonaws.com/oauth2callbackas authorized redirect URI.
-
Download the corresponding JSON file, and copy&paste to
/var/www/catalog/catalog/client_secrets.jsonfile. -
Replace the client ID to line 67 of the
templates/login.htmlfile in the project directory.
Step 14.1: Install the virtual environment and dependencies
- While logged in as
grader, install pip:
sudo apt-get install pip
- Install the virtual environment:
sudo apt-get install python-virtualenv
cd /var/www/catalog/catalog/
- Create the virtual environment:
sudo virtualenv -p python venv
- Change the ownership to
graderwith:
sudo chown -R grader:grader venv/
- Activate the new environment:
. venv/bin/activate
-
Install the following dependencies:
pip install flask pip install httplib2 pip install psycopg2 pip install requests pip install sqlalchemy pip install sqlalchemy_utils pip install --upgrade oauth2client sudo apt-get install libpq-dev -
Run
python __init__.pyand you should see:* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit) -
Deactivate the virtual environment:
deactivate.
Step 14.2: Set up and enable a virtual host
- Create config file:
sudo vim /etc/apache2/sites-available/catalog.conf
-
Add following lines to above file:
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName 13.209.11.93 ServerAlias http://ec2-13-209-11-93.ap-northeast-2.compute.amazonaws.com WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/catalog/catalog.wsgi <Directory /var/www/catalog/catalog/> Order allow,deny Allow from all </Directory> Alias /static /var/www/catalog/catalog/static <Directory /var/www/catalog/catalog/static/> Order allow,deny Allow from all </Directory> ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log LogLevel warn CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined </VirtualHost>
-
Enable virtual host:
sudo a2ensite catalog
- Reload Apache:
sudo service apache2 reload
Step 14.3: Set up the Flask application
-
Create
/var/www/catalog/catalog.wsgifile add the following lines:activate_this = '/var/www/catalog/catalog/venv3/bin/activate_this.py' with open(activate_this) as file_: exec(file_.read(), dict(__file__=activate_this)) #!/usr/bin/python import sys import logging logging.basicConfig(stream=sys.stderr) sys.path.insert(0, "/var/www/catalog/catalog/") sys.path.insert(1, "/var/www/catalog/") from catalog import app as application application.secret_key = "super_secret_key" -
Restart Apache:
sudo service apache2 restart
Step 14.4: Set up the database schema and populate the database
- From the
/var/www/catalog/catalog/directory, activate the virtual environment:. venv/bin/activate. - Run:
python seed.py. - Deactivate the virtual environment:
deactivate.
Step 14.5: Disable the default Apache site
-
Disable the default Apache site:
sudo a2dissite 000-default.conf. The following prompt will be returned:Site 000-default disabled. To activate the new configuration, you need to run: service apache2 reload -
Reload Apache:
sudo service apache2 reload.
Step 14.6: Launch the Web Application
- Change the ownership of the project directories:
cd ..
# at grader@ip-172-26-3-69:/var/www/catalog
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data catalog/
-
Restart Apache again:
sudo service apache2 restart. -
Open your browser to
http://13.209.11.93orhttp://ec2-13-209-11-93.ap-northeast-2.compute.amazonaws.com -
Enjoy my project!
Fix issues 🔧
Step 15.1: Log in with Google OAuth
-
When I try to log in with Google OAuth 2.0, I get the following error:
No such file or directory: 'client_secrets.json' -
To correct that problem, edit
__init__.py -
Near line
27, replace relative path with absolute path.
# CLIENT_ID = json.loads(open('client_secrets.json', 'r').read())[
'web']['client_id']
CLIENT_ID = json.loads(open('/var/www/catalog/catalog/client_secrets.json', 'r').read())[
'web']['client_id']- Near line
219, replace relative path with absolute path.try: # oauth_flow = flow_from_clientsecrets('client_secrets.json', scope='') oauth_flow = flow_from_clientsecrets('/var/www/catalog/catalog/client_secrets.json', scope='') oauth_flow.redirect_uri = 'postmessage'
- Save and exit using
:wq. - Reload Apache:
sudo service apache2 reload.
Useful commands 🔮
- To get log messages from Apache server:
sudo tail /var/log/apache2/error.log. - To restart Apache:
sudo service apache2 restart.