##Overview Big Data Lab is an open-source project created originally in SoftServe Inc. to serve as an accelerator for big data projects and to be an easy to deploy and use environment for education, prototyping, PoC, performance testing and other purposes. The main idea which lies in the root of Big Data Lab is a Log and Metrics processing system which allows certain set of users to use both raw and aggregated log and performance metrics data in their daily tasks.
###Marketecture
Diagram below shows main sources of data (log and performance metrics data being collected from web servers), as well as 3 types of analytics produced based on this data and 3 types of users using this data.

##Architecture
###Architecture Drivers
Below is a set of main architecture drivers which influences architecture and implementation of the project. We've used Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Insitute's ADD (Attribute Driven Design) methodology in building solution architecture.

Overview
As part of the design process, one of the first tasks is to create an overall logical structure for the system. To achieve this, it is generally not necessary to re-invent the wheel, but rather to use one particular type of design concept: a reference architecture. A reference architecture is a blueprint for structuring an application. For Big Data Analytics systems we distinguish five reference architectures:
- Traditional Relational
- Extended Relational
- Non-Relational
- Lambda Architecture (Hybrid)
- Data Refinery (Hybrid)
Design Rational
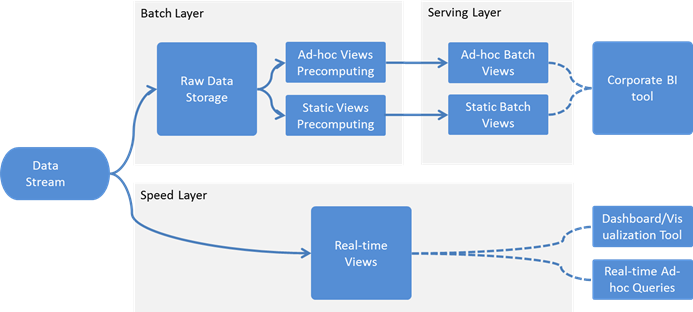
From the provided reference architectures Lambda Architecture promises the largest number of benefits, such as access to real-time and historical data at the same time. The parallel layers provide “complexity isolation”, meaning that design decisions and development of each layer can be done independently – which corresponds to “swim lanes” principle that increase fault-tolerance and scalability (which is true for a system and for parallelizing development tasks).
The below diagram represents proposed logical structure of the target system based on Lambda Architecture:
##Roadmap ###Components:
- LogGenerator
- Flume
- ElasticSearch 1.7
- Elastic Search Automatic Schema Creation
- Cloudera Director (Hadoop Cluster Deployment)
- Impala Schema Creation
- Kibana
- Kibana: Automatic Pre-defined Dashboards Import
###Client OS Support:
- Linux
- MacOS
###Guest OS Support:
- CentOS
- RedHat
###Platform Support:
- Amazon Web Services
- VMWare vShpere / ESX
- OpenStack
###Configuration Size:
- Small
- Medium
- Large
###Data Sources:
- Log Files (HTTP, Error)
- Performance metrics
- IoT
###Service Discovering:
- Buil-in DNS with hostname self-registering
- Consul
##Tested OS Below is a list of client OS which can be used to deploy solution from:
- CentOS 6/7 (64 bit)
- Ubuntu 14 (64 bit)
- OSX
##Deployment Guide ###Deploying Cluster Use below steps in order to create Big Data Lab cluster:
-
Run:
sudo ./core-install.sh ./ruby-install.sh ./terraform-install.sh source $HOME/.bashrc -
Copy puppet/hiera/hieradata/common.yaml-[small|medium|large] to common.yaml. Update it, if needed.
-
To turn on cluster deployment, change 'profiles::cloudera_director_client::deploy_cluster' property in common.yaml to true To get additional information about cluster configuration see 'cluster management' section.
-
Copy main.tf-[small|medium|large] to main.tf.
-
Prepare .pem file to be used for SSH connections.
-
Copy terraform.tfvars.stub to terraform.tfvars. Update it with actual values. You may also override other values from variables.tf.
-
To run unit tests, go to puppet folder and run:
bundle exec rake prep bundle exec rake rspec:classes bundle exec rake cleanUnit tests are being run during each terraform apply too.
-
To run acceptance tests, go to puppet folder and run:
bundle exec rake prep bundle exec rake rspec:acceptance bundle exec rake cleanPlease note, that you need a physical machine to be able to run acceptance tests.
-
To create instances, run:
terraform applyIf "Error launching source instance: InvalidParameterValue: Value () for parameter groupId is invalid. The value cannot be empty" error appears, just restart the command.
-
To connect to any instance:
ssh -i <your .pem file> <SSH user>@<IP address>
You can find SSH users for all AMIs in variables.tf.
- Warning: If your turned on a cluster deployment (step #3), log to the machine where Cloudera Director Client is running and terminate the cluster with the console command:
cloudera-director terminate {path to cluster configuration file}
###Destroying Cluster To destroy Big Data Lab cluster, run following command:
-
To destroy instances, run:
terraform destroy
###Cloudera Cluster Deployment
Cluster is deployed to AWS by Cloudera director client tool. It is installed to AWS instance as a 'cloudera_director_client' terraform resource.
Before starting a deployment, cluster can be customized depending on specific needs. A default cluster presets were extracted to 'hiera/hieradata/common.yaml-[small|medium|large]' configuration files.
Mentioned properties described in the table below.
| Property | Description | Small | Medium | Large |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| profiles::cloudera_director_client ::deploy_cluster | When false, cluster won't be deployed to AWS. Otherwise it will. Set to false if you don't want to deploy cluster and to manage it outside the project | false | false | false |
| profiles::cloudera_director_client ::root_volume_size_GB | Size in GB that can be allocated for each instance in the cluster | 50 | 100 | 300 |
| profiles::cloudera_director_client ::data_node_quantity | Number of instances deployed on AWS and used in data nodes roles. Minimum recommended 3 | 1 | 3 | 10 |
| profiles::cloudera_director_client ::data_node_quantity_min_allowed | Minimal number of cluster data nodes allowed to be deployed to AWS. In case the number of instances can not be reached, cluster deployment will fail | 1 | 3 | 10 |
| profiles::cloudera_director_client ::data_node_instance_type | AWS instance type for data nodes to be deployed | t2.medium | t2.medium | m4.xlarge |
| profiles::cloudera_director_client ::cloudera_manager_instance_type | AWS instance type for Cloudera Manager to be deployed | t2.large | t2.large | m4.large |
| profiles::cloudera_director_client ::master_node_instance_type | AWS instance type for master cluster services to be run on | t2.large | m4.2xlarge | m4.4xlarge |
| profiles::cloudera_director_client ::aws_ami | AWS image to be used for each cluster instance | ami-3218595b | ami-3218595b | ami-3218595b |
| profiles::cloudera_director_client ::cluster_deployment_timeout_sec | Cluster deployment timeout in seconds. In order of increasing number of nodes, timeout has to be also increased | 7200 | 7200 | 7200 |
Follow below steps if you don't want Cloudera CDH to be automatically deployed during Big Data Lab cluster deployment:
Before project deployment set profiles::cloudera_director_client::deploy_cluster property to false (false by default)
To manually create (or change) cluster:
- Connect by ssh to the resource 'cloudera_director_client' created by terraform.
- Locate 'cloudera-director-cluster.conf' configuration file. (Default path is '/home/ec2-user')
- Go to the configuration file's directory and modify the configuration.
- To validate cluster configuration run:
cloudera-director validate cloudera-director-cluster.conf
- To create cluster run:
cloudera-director bootstrap cloudera-director-cluster.conf
- To modify cluster edit the configuration file and run:
cloudera-director update cloudera-director-cluster.conf
- To check cluster status run:
cloudera-director status cloudera-director-cluster.conf
-
Edge node: Cloudera Manager runs on a separate edge-node instance.
-
Master node:
- HDFS
- YARN
- ZOOKEEPER
- HIVE
- HUE
- OOZIE
- IMPALA
- Slave node(s):
- HDFS
- YARN
- IMPALA
After completion a Terraform environment applying stage, cluster can be accessed with Cloudera Manager (CM) UI. To open CM UI locate CM IP address in Terraform output and open the following URL in a browser:
To login into CM UI use:
- username: 'admin'
- password: 'admin'