The Alexa Voice Service (AVS) enables developers to integrate Alexa directly into their products, bringing the convenience of voice control to any connected device. AVS provides developers with access to a suite of resources to quickly and easily build Alexa-enabled products, including APIs, hardware development kits, software development kits, and documentation.
The AVS Device SDK provides C++-based (11 or later) libraries that leverage the AVS API to create device software for Alexa-enabled products. It is modular and abstracted, providing components for handling discrete functions such as speech capture, audio processing, and communications, with each component exposing the APIs that you can use and customize for your integration. It also includes a sample app, which demonstrates the interactions with AVS.
You can set up the SDK on the following platforms:
- Updated - Raspberry Pi (Raspbian Stretch)
- New - macOS
- Linux
You can also prototype with a third party development kit
Or if you prefer, you can start with our SDK API Documentation.
Watch this tutorial to learn about the how this SDK works and the set up process.
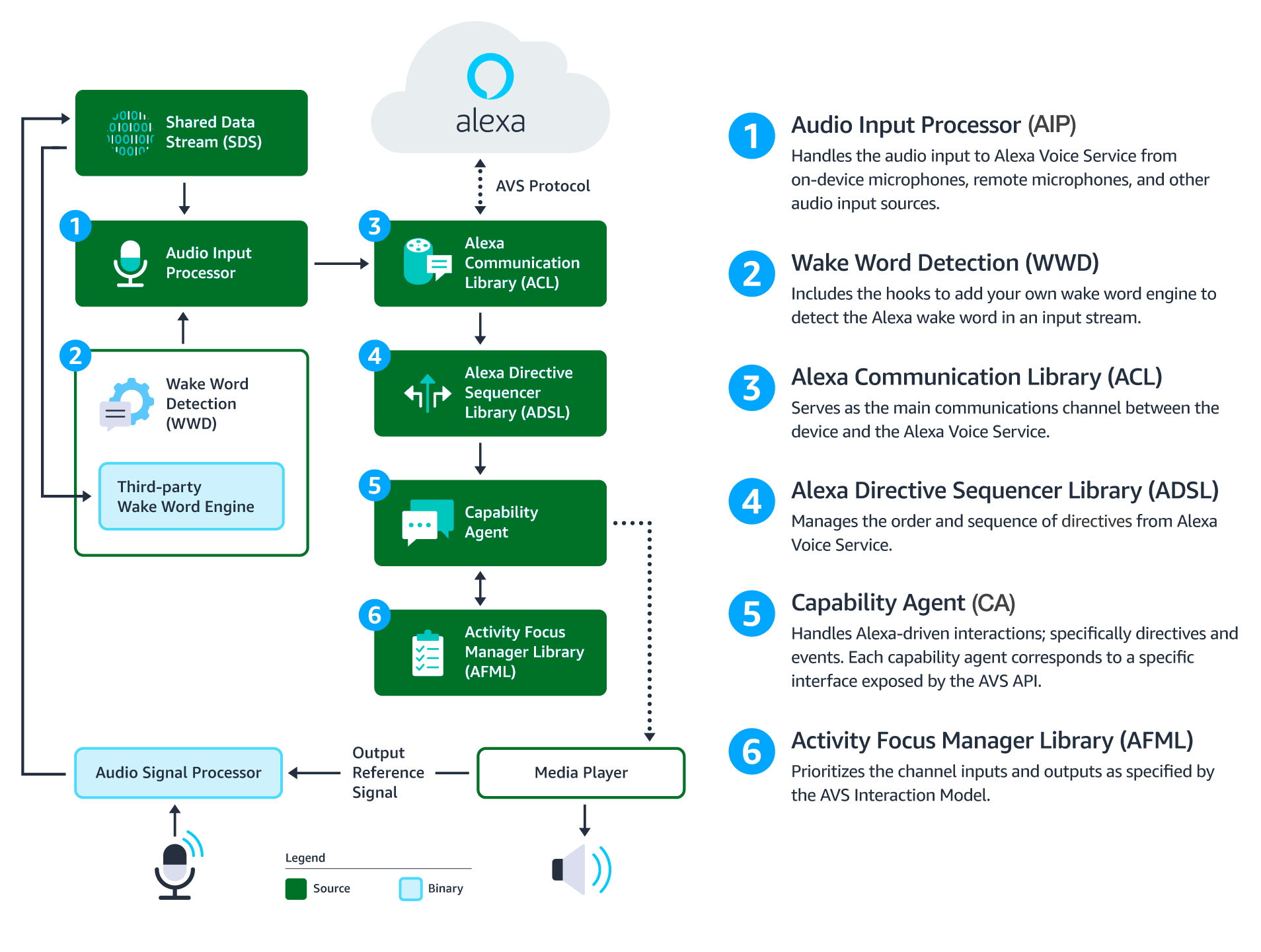
This diagram illustrates the data flows between components that comprise the AVS Device SDK for C++.
Audio Signal Processor (ASP) - Third-party software that applies signal processing algorithms to both input and output audio channels. The applied algorithms are designed to produce clean audio data and include, but are not limited to acoustic echo cancellation (AEC), beam forming (fixed or adaptive), voice activity detection (VAD), and dynamic range compression (DRC). If a multi-microphone array is present, the ASP constructs and outputs a single audio stream for the array.
Shared Data Stream (SDS) - A single producer, multi-consumer buffer that allows for the transport of any type of data between a single writer and one or more readers. SDS performs two key tasks:
- It passes audio data between the audio front end (or Audio Signal Processor), the wake word engine, and the Alexa Communications Library (ACL) before sending to AVS
- It passes data attachments sent by AVS to specific capability agents via the ACL
SDS is implemented atop a ring buffer on a product-specific memory segment (or user-specified), which allows it to be used for in-process or interprocess communication. Keep in mind, the writer and reader(s) may be in different threads or processes.
Wake Word Engine (WWE) - Software that spots wake words in an input stream. It is comprised of two binary interfaces. The first handles wake word spotting (or detection), and the second handles specific wake word models (in this case "Alexa"). Depending on your implementation, the WWE may run on the system on a chip (SOC) or dedicated chip, like a digital signal processor (DSP).
Audio Input Processor (AIP) - Handles audio input that is sent to AVS via the ACL. These include on-device microphones, remote microphones, an other audio input sources.
The AIP also includes the logic to switch between different audio input sources. Only one audio input source can be sent to AVS at a given time.
Alexa Communications Library (ACL) - Serves as the main communications channel between a client and AVS. The ACL performs two key functions:
- Establishes and maintains long-lived persistent connections with AVS. ACL adheres to the messaging specification detailed in Managing an HTTP/2 Connection with AVS.
- Provides message sending and receiving capabilities, which includes support JSON-formatted text, and binary audio content. For additional information, see Structuring an HTTP/2 Request to AVS.
Alexa Directive Sequencer Library (ADSL): Manages the order and sequence of directives from AVS, as detailed in the AVS Interaction Model. This component manages the lifecycle of each directive, and informs the Directive Handler (which may or may not be a Capability Agent) to handle the message.
Activity Focus Manager Library (AFML): Provides centralized management of audiovisual focus for the device. Focus is based on channels, as detailed in the AVS Interaction Model, which are used to govern the prioritization of audiovisual inputs and outputs.
Channels can either be in the foreground or background. At any given time, only one channel can be in the foreground and have focus. If multiple channels are active, you need to respect the following priority order: Dialog > Alerts > Content. When a channel that is in the foreground becomes inactive, the next active channel in the priority order moves into the foreground.
Focus management is not specific to Capability Agents or Directive Handlers, and can be used by non-Alexa related agents as well. This allows all agents using the AFML to have a consistent focus across a device.
Capability Agents: Handle Alexa-driven interactions; specifically directives and events. Each capability agent corresponds to a specific interface exposed by the AVS API. These interfaces include:
- SpeechRecognizer - The interface for speech capture.
- SpeechSynthesizer - The interface for Alexa speech output.
- Alerts - The interface for setting, stopping, and deleting timers and alarms.
- AudioPlayer - The interface for managing and controlling audio playback.
- Notifications - The interface for displaying notifications indicators.
- PlaybackController - The interface for navigating a playback queue via GUI or buttons.
- Speaker - The interface for volume control, including mute and unmute.
- System - The interface for communicating product status/state to AVS.
- TemplateRuntime - The interface for rendering visual metadata.
- Review the AVS Terms & Agreements.
- The earcons associated with the sample project are for prototyping purposes only. For implementation and design guidance for commercial products, please see Designing for AVS and AVS UX Guidelines.
- Please use the contact information below to-
- Contact Sensory for information on TrulyHandsFree licensing.
- Contact KITT.AI for information on SnowBoy licensing.
- IMPORTANT: The Sensory wake word engine referenced in this document is time-limited: code linked against it will stop working when the library expires. The library included in this repository will, at all times, have an expiration date that is at least 120 days in the future. See Sensory's GitHub page for more information.
Note: Features, updates, and resolved issues from previous releases are available to view in CHANGELOG.md.
v1.3.0 released 12/08/2017:
Enhancements
- ContextManager now passes the namespace/name of the desired state to StateProviderInterface::provideState(). This is helpful when a single StateProvider object provides multiple states, and needs to know which one ContextManager is asking for.
- The mime parser was hardened against duplicate boundaries.
- Added functionality to add and remove AudioPlayer observers to the DefaultClient.
- Unit tests for Alerts were added.
- Added en-IN, en-CA and ja-JP to the SampleApp locale selection menu.
- Added default alert and timer audio data to the SDK SampleApp. There is no longer a requirement to download these audio files and configure them in the json configuration file.
- Added support in SDS Reader and AttachmentReader for seeking into the future. This allows a reader to move to an index which has not yet arrived in the SDS and poll/block until it arrives.
- Added support for blocking Writers in the SharedDataStream class.
- Changed the default status code sent by MessageRequestObserverInterface::onSendCompleted() to SERVER_OTHER_ERROR, and mapped HTTP code 500 to SERVER_INTERNAL_ERROR_V2.
- Added support for parsing stream duration out of playlists.
- Added a configuration option ("sampleApp":"displayCardsSupported") that allows the displaying of display cards to be enabled or disabled.
- Named Timers and Reminders have been updated to fall back to the on-device background audio sound when cloud urls cannot be accessed or rendered.
Bug Fixes
- Removed floating point dependencies from core SDK libraries.
- Fixed bug in SpeechSynthesizer where it's erroneously calling stop more than once.
- Fixed an issue in ContentFetcher where it could hang during destruction until an active GET request completed.
- Fixed a couple of parsing bugs in LibCurlHttpContentFetcher related to case-sensitivity and mime-type handling.
- Fixed a bug where MediaPlayerObserverInterface::onPlaybackResumed() wasn't being called after resuming from a pause with a pending play/resume.
- Fixed a bug in LibCurlContentFetcher where it could error out if data is written to the SDS faster than it is consumed.
- The GStreamer-based MediaPlayer reference implementation now uses the ACL HTTP configured client.
- An API change has been made to MediaPlayerInterface::setSource(). This method now takes in an optional offset as well to allow for immediately streaming to the offset if possible.
- Next and Previous buttons now work with Audible.
- Pandora resume stuttering is addressed.
- Pausing and resuming Amazon music no longer seeks back to the beginning of the song.
- libcurl CURLOPT_NOSIGNAL option is set to 1 (https://curl.haxx.se/libcurl/c/CURLOPT_NOSIGNAL.html) to avoid crashes observed in SampleApp.
- Fixed the timing of the PlaybackReportIntervalEvent and PlaybackReportDelayEvent as specified in the directives.
- Fixed potential deadlocks in MediaPlayer during shutdown related to queued callbacks.
- Fixed a crash in MediaPlayer that could occur if the network is disconnected during playback.
- Fixed a bug where music could keep playing while Alexa is speaking.
- Fixed a bug which was causing problems with pause/resume and next/previous with Amazon Music.
- Fixed a bug where music could briefly start playing between speaks.
- Fixed a bug where HLS playlists would stop streaming after the initial playlist had been played to completion.
- Fixed a bug where Audible playback could not advance to the next chapter.
- Fixed some occurrences of SDK entering the IDLE state during the transition between Listening and Speaking states.
- Fixed a bug where PlaybackFinished events were not reporting the correct offset.
- An API change has been made to MediaPlayerInterface::getOffset(). This method is now required to return the final offset when called after playback has stopped.
- Fixed a problem where AIP was erroneously resetting its state upon getting a cancelDirective() callback.
Known Issues
- Capability agent for Notifications is not included in this release.
ACL's asynchronous receipt of audio attachments may manage resources poorly in scenarios where attachments are received but not consumed.- GUI cards don't show for Kindle.
- The new SpeechSynthesizerState state values GAINING_FOCUS and LOSING_FOCUS were added as part of a work-around. The will likely be removed in subsequent releases.
- With the gstreamer-based MediaPlayer, after muting and unmuting, the next item starts playing rather than continuing with the current item.