一些R包提供了很好用的管道操作符,但是这些管道操作符通常至少有三个字母,输入起来有些麻烦,所以我就行自定义一些快捷键实现直接使用快捷键输入这些管道操作符。RStudio自定义快捷键很简单,只需要写一个简单的R包创建一些加载项,然后对加载项设置快捷键绑定即可。官方教程参考这个:Customizing Keyboard Shortcuts。
本文参考了:R语言中管道操作 %>%, %T>%, %$% 和 %%。
作为尝试,我写了一个小小的R包,里面包括整合了十多个R语言中的复合操作符的快捷输入。hotkeys
这个包里包含了十多个加载项,通过自定义快捷键可以插入以下十多个复合操作符,首先介绍一些符号操作符。
来源于R包:magrittr。
用法:
-
x %>% f 等价于 f(x)
-
x %>% f(y) 等价于 f(x, y)
-
x %>% f %>% g %>% h 等价于 h(g(f(x)))
-
x %>% f(y, .) 等价于 f(y, x)
-
x %>% f(y, z = .) 等价于 f(y, z = x)
-
x %>% f(y = nrow(.), z = ncol(.)) 等价于 f(x, y = nrow(x), z = ncol(x))
-
f <- . %>% cos %>% sin 等价于 f <- function(.) sin(cos(.))
来源于R包:base。
用法:x %in% y 等价于 match(x, y, nomatch = 0) > 0
也就是在y中逐个查找x中的元素,如果找到就返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE。
(1:10) %in% c(3,7,12)
# [1] FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
c(3,7,12) %in% (1:10)
# [1] TRUE TRUE FALSE
match((1:10), c(3, 7, 12), nomatch = 0) > 0
# [1] FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE
match(c(3, 7, 12), (1:10), nomatch = 0) > 0
# [1] TRUE TRUE FALSE启发至base包%in%的帮助文档里面的示例,是hotkeys包里的函数,代码为:
`%w/o%` <- function(x, y) x[!x %in% y]作用是从x中剔去y中的元素。
(1:10) %w/o% c(3, 7, 12)
# [1] 1 2 4 5 6 8 9 10来源于R包:magrittr。
不同于%>%,%T>%会不仅仅把左侧程序的值传递给右侧返回运行结果,还会保留返回左侧程序运行的值。例如比较下面两段命令:
set.seed(1)
rnorm(10000) %>%
abs %>% `*` (50) %>%
matrix(ncol=100) %>%
rowMeans %>% round %>%
`%%`(7) %>% hist这段程序仅仅返回一张直方图。
set.seed(1)
rnorm(10000) %>%
abs %>% `*` (50) %>%
matrix(ncol=100) %>%
rowMeans %>% round %>%
`%%`(7) %T>% hist
# [1] 0 5 1 1 2 2 1 3 4 6 5 5 2 2 0 4 4 1 3 5 5 3 5 0 4 1 3 6 5 6 3 6 3 0 2
# [36] 3 0 4 5 2 6 4 6 3 0 1 3 1 1 5 5 6 4 0 1 3 4 4 3 5 3 6 6 6 5 3 3 5 4 5
# [71] 2 1 2 1 2 1 5 5 6 0 0 6 6 6 0 4 4 1 1 1 1 6 5 6 3 0 6 0 2 4这段程序不仅返回了直方图还返回了hist前面程序的值。所以第二段程序后面可以继续接函数:
set.seed(1)
rnorm(10000) %>%
abs %>% `*` (50) %>%
matrix(ncol=100) %>%
rowMeans %>% round %>%
`%%`(7) %T>% hist %>%
sum
# [1] 303 来源于R包:magrittr。
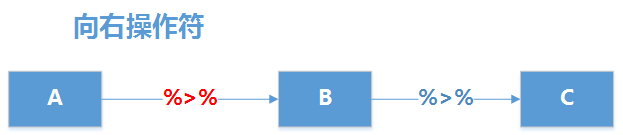
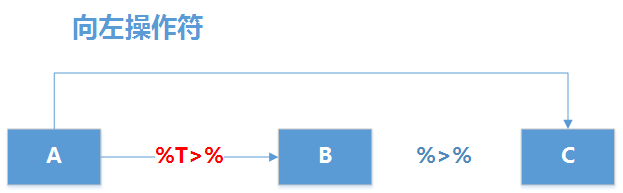
%$% 的作用是把左侧数据的属性名传给右侧,让右侧的调用函数直接通过名字,就可以获取左侧的数据。比如,我们获得一个data.frame类型的数据集,通过使用 %$%,在右侧的函数中可以直接使用列名操作数据。
现实原理如下图所示,使用%$%把左侧的程序的数据集A传递右侧程序的B函数,同时传递数据集A的属性名,作为B函数的内部变量方便对A数据集进行处理,最后完成数据计算。
例如比较下面两段代码:
set.seed(1)
data.frame(x = 1:10, y = rnorm(10), z = letters[1:10]) %$%
.[which(x > 5), ]
# x y z
# 6 6 -0.8204684 f
# 7 7 0.4874291 g
# 8 8 0.7383247 h
# 9 9 0.5757814 i
# 10 10 -0.3053884 jdata.frame(x = 1:10, y = rnorm(10), z = letters[1:10]) %>%
.[which(x > 5), ]
# Error in which(x > 5) : 找不到对象'x'来源于R包:magrittr。
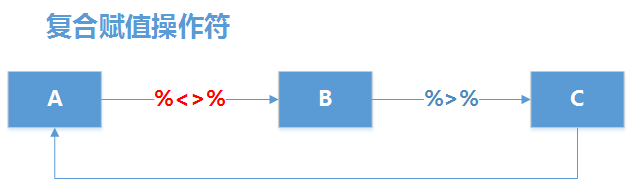
%<>%复合赋值操作符, 功能与 %>% 基本是一样的,对了一项额外的操作,就是把结果写到左侧对象。比如,我们需要对一个数据集进行排序,那么需要获得排序的结果,用%<>%就是非常方便的。
现实原理如下图所示,使用%<>%把左侧的程序的数据集A传递右侧程序的B函数,B函数的结果数据集再向右侧传递给C函数,C函数结果的数据集再重新赋值给A,完成整个过程。
例如,这两段代码的功能是一样的:
a <- 1
a <- a %>% as.character()
rm(a)
a <- 1
a %<>% as.character()a <- matrix(c(1:4), nrow = 2) %>% print()
# [,1] [,2]
# [1,] 1 3
# [2,] 2 4
a %*% a
# [,1] [,2]
# [1,] 7 15
# [2,] 10 22
a * a
# [,1] [,2]
# [1,] 1 9
# [2,] 4 1610 %/% 4
# [1] 210 %% 3
# [1] 1x <- 2
# 等价于
2 <- x来源于testit
用于判断两个对象是否完全一致。
a <- 5 %/% 2
b <- 2
a %==% b
# [1] TRUE来源于ggplot2,用于修改已经激活的ggplot2绘图主题。
theme_grey()$text
# List of 11
# $ family : chr ""
# $ face : chr "plain"
# $ colour : chr "black"
# $ size : num 11
# $ hjust : num 0.5
# $ vjust : num 0.5
# $ angle : num 0
# $ lineheight : num 0.9
# $ margin : 'margin' num [1:4] 0pt 0pt 0pt 0pt
# ..- attr(*, "valid.unit")= int 8
# ..- attr(*, "unit")= chr "pt"
# $ debug : logi FALSE
# $ inherit.blank: logi TRUE
# - attr(*, "class")= chr [1:2] "element_text" "element"
add_el <- theme_grey() +
theme(text = element_text(family = "Times"))
add_el$text
# List of 11
# $ family : chr "Times"
# $ face : chr "plain"
# $ colour : chr "black"
# $ size : num 11
# $ hjust : num 0.5
# $ vjust : num 0.5
# $ angle : num 0
# $ lineheight : num 0.9
# $ margin : 'margin' num [1:4] 0pt 0pt 0pt 0pt
# ..- attr(*, "valid.unit")= int 8
# ..- attr(*, "unit")= chr "pt"
# $ debug : logi FALSE
# $ inherit.blank: logi FALSE
# - attr(*, "class")= chr [1:2] "element_text" "element"
rep_el <- theme_grey() %+replace%
theme(text = element_text(family = "Times"))
rep_el$text
# List of 11
# $ family : chr "Times"
# $ face : NULL
# $ colour : NULL
# $ size : NULL
# $ hjust : NULL
# $ vjust : NULL
# $ angle : NULL
# $ lineheight : NULL
# $ margin : NULL
# $ debug : NULL
# $ inherit.blank: logi FALSE
# - attr(*, "class")= chr [1:2] "element_text" "element"使用示例:
ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, wt)) +
geom_point()
# 修改一下字体。
theme_set(theme_grey() +
theme(text = element_text(family = "STSongti-SC-Bold")))
ggplot(mtcars, aes(mpg, wt)) +
geom_point()最后值得补充的是,为了让链条传递看起来更友好,magrittr对于常见的计算符号操作符进行的重新定义,让每个操作都对应用一个函数,这样所有的传递调用代码都是风格统一的。比如,add()函数和+是等价的。
下面列出对应的列表:
extract `[`
extract2 `[[`
inset `[<-`
inset2 `[[<-`
use_series `$`
add `+`
subtract `-`
multiply_by `*`
raise_to_power `^`
multiply_by_matrix `%*%`
divide_by `/`
divide_by_int `%/%`
mod `%%`
is_in `%in%`
and `&`
or `|`
equals `==`
is_greater_than `>`
is_weakly_greater_than `>=`
is_less_than `<`
is_weakly_less_than `<=`
not (`n'est pas`) `!`
set_colnames `colnames<-`
set_rownames `rownames<-`
set_names `names<-`安装好 hotkeys 包之后,在 RStudio 菜单栏里点击 Tools -> Modify Keyboard Shortcuts。
以后遇到了再继续补充,有好想法还能自己写,例如什么%rstata%啊,%dwl%啊的。
Please note that this project is released with a Contributor Code of
Conduct.
By participating in this project you
agree to abide by its terms.