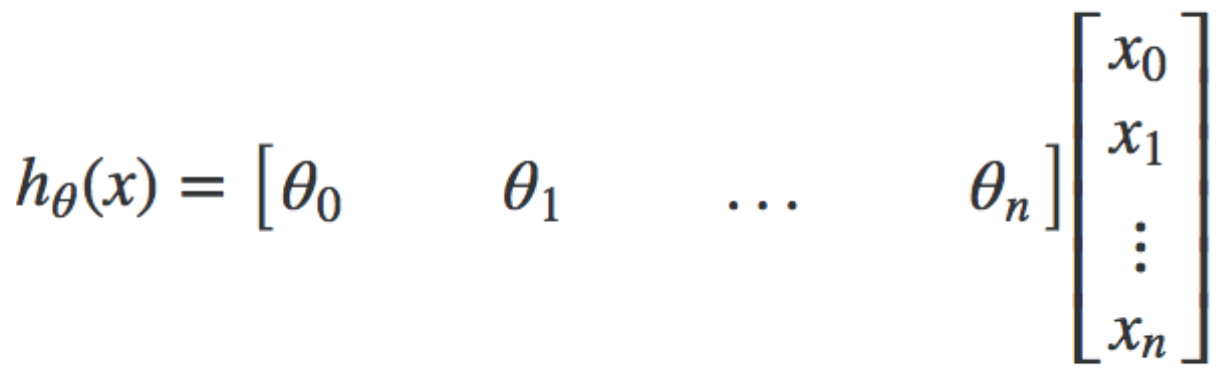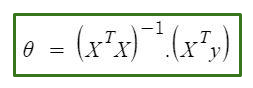Notes that I take while learning machine learning.
Firstly, machine learning is a subset of AI which includes several specific fields including neural network, natural language processing, and deep learning.
There are two common definitions until the moment. One is old, second one is recent.
- (Arthur Samuel, 1959): Machine Learning is the field of study that gives computer the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.
- (Tom M. Mitchell, 1997): Machine Learning is a computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.
Examples
- Database mining Large datasets from the growth of automation/web E.g: Web click data, medical records, biology, engineering
- Applications can be programmed by hands E.g: Autonomous helicopter, handwriting recognition, NLP, computer vision
- Self-customzing programs E.g: Amazon, Netflix product recommendations
- Understanding human learning (brain, real AI)
There are two main types of machine learning algorithms
- Supervised learning: "Right answers" given in the data set.
- Regression problem type: Predict continuous valued output
- Classification problem type: Discrete value output
- Unsupervised learning: "Right answers" not given in the data set.
Other algorithms: Reinforcement learning, recommender systems.
-
Model representation
- m : number of training examples
- x's : 'input' variable
- y's : 'output' variable
- (x,y) : single training example
- (x(i), y(i)) : i(th) training example
-
Hypothesis
The function to map x to y. The purpose of machine learning in regression problem is to find the best hypothesis. And if there is more data, it learn and update hypothesis (h) continuously. -
Cost function
It is a function that measures the performance of a Machine Learning model for given data, or the accuracy of our hypothesis function. Sometimes, this function is otherwise called "Squared Error Function", or "Mean Squared Error". Sympol: J(θ0, θ1) -
Contour plots
Contour plots (sometimes called Level Plots) are a way to show a three-dimensional surface on a two-dimensional plane. It is used to visualize the cost function.
-
Gradient Descent
An optimization algorithm used to minimize some functions by iteratively moving in the direction of steepest descent as defined by the negative of the gradient. In machine learning, we use gradient descent to update the parameters of our model. -
Multivariate Linear Regression
That is the linear regression issues with multiple inputs (or features). Notation: n: number of features x(i): input (features) of i(th) training example xj(i): value of feature j in i(th) training example
-
Mean normalization
-
Polynomial Regression
Our hypothesis function need not be linear (a straight line) if that does not fit the data well. We can change the behavior or curve of our hypothesis function by making it a quadratic, cubic or square root function (or any other form).
A method to calculate continous outcomes in the regression problem.
- Hypothesis (h-theta(x))
- Cost function (J(theta))
- Minimize the cost function to find theta
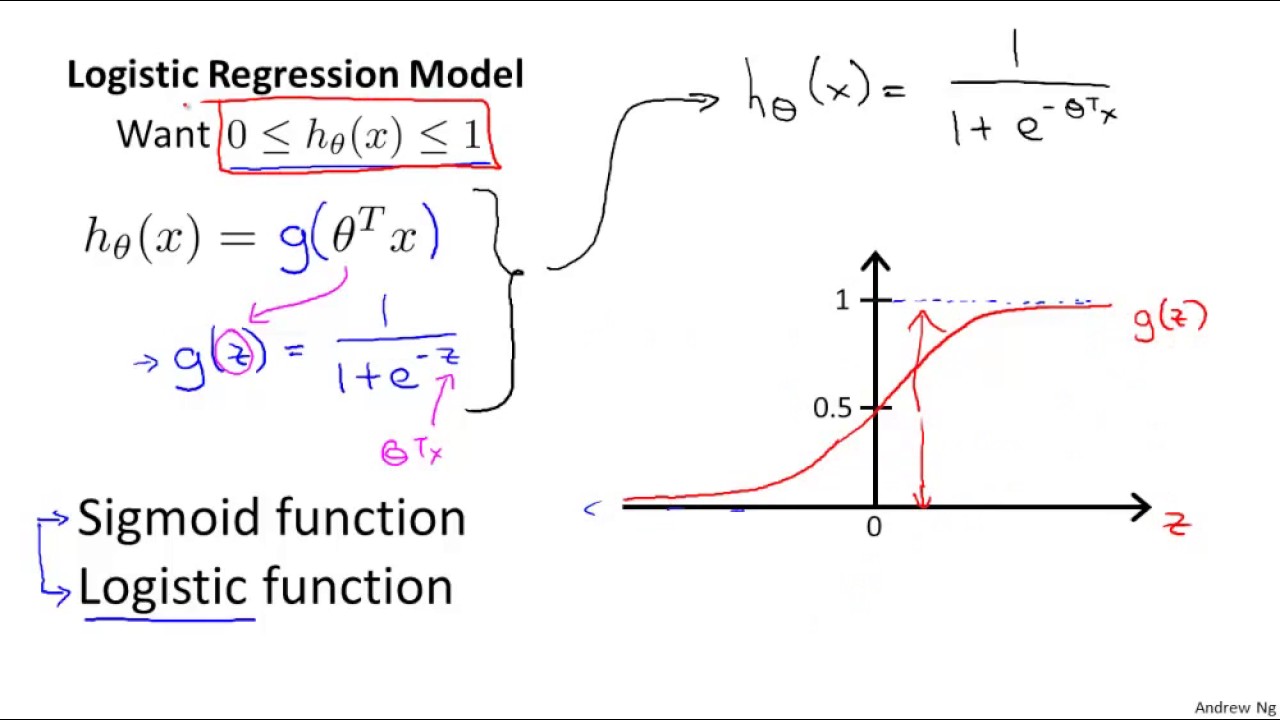
A method to classify data into discrete outcomes in the classification problem.
- Hypothesis function(h-theta(x))
- Cost function (J(theta))
- Minimize the cost function to find theta
- Conjugate gradient
- BFGS
- L-BFGS